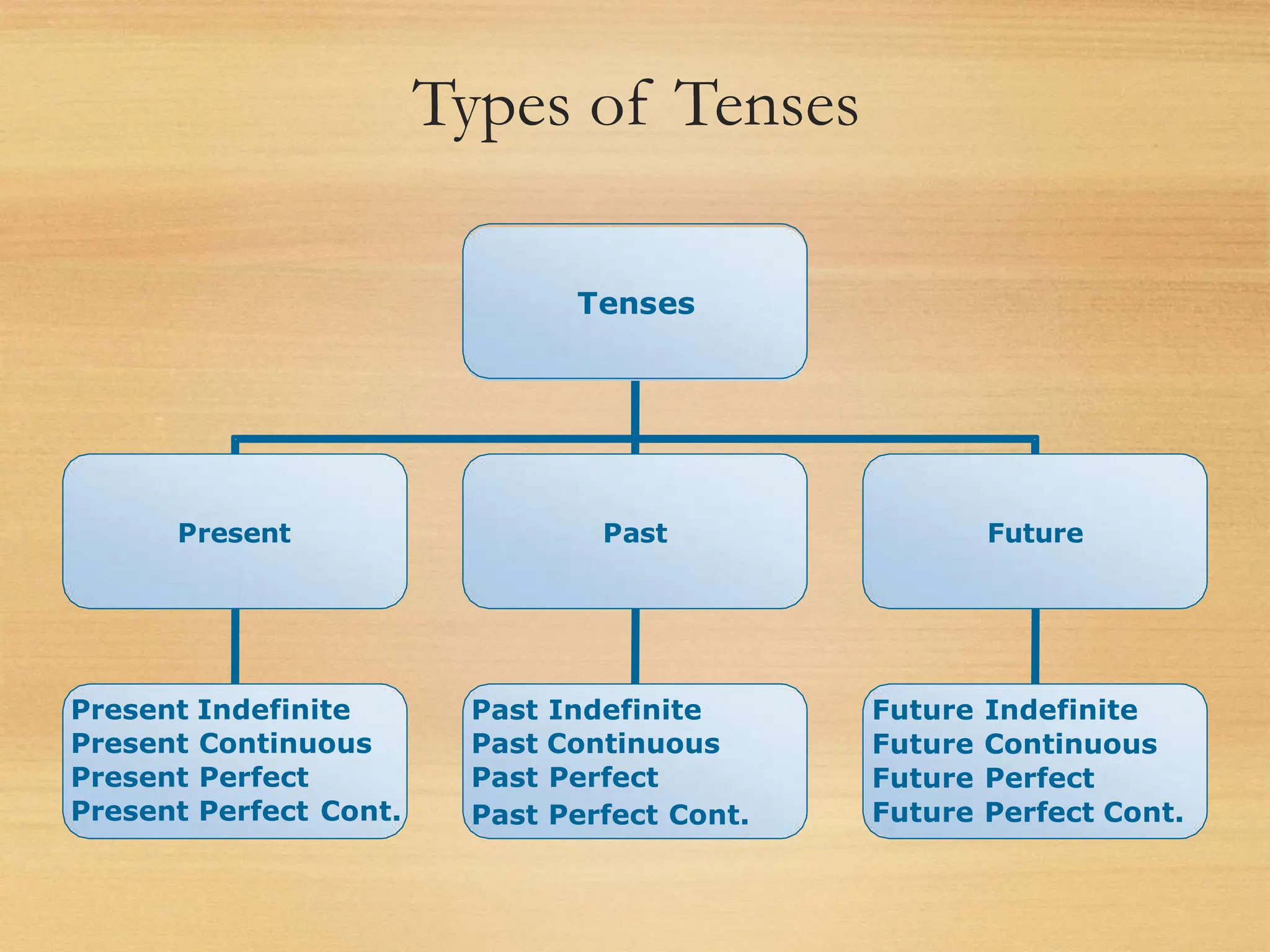
The document provides an overview of verb tenses, including classifications based on time frame (present, past, future) and aspect (simple, continuous, perfect, perfect continuous). It includes definitions and examples for each tense and aspect, explaining their usage in sentences. Additionally, it lists rules for forming various tenses and provides examples to illustrate these rules.