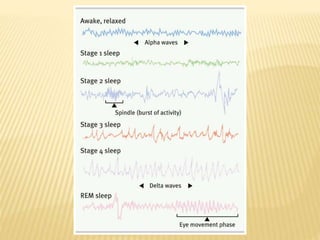
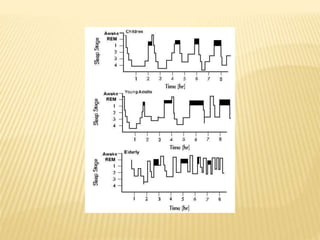
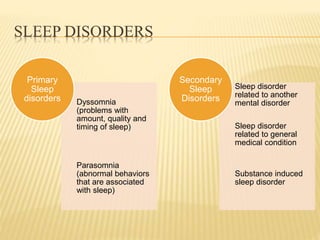
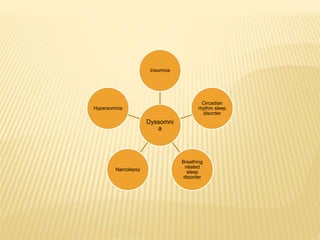
This document provides an overview of sleep disorders including insomnia, hypersomnia, narcolepsy, breathing-related sleep disorders, circadian rhythm disorders, parasomnias, and jet lag. It discusses the stages of normal sleep including light, intermediate, deep, and REM sleep. It covers causes, symptoms, and treatments for different sleep disorders. The functions of sleep are also reviewed including restoring the body, boosting immunity and mood, and facilitating memory processing.