The document discusses service level agreements (SLAs) between companies and vendors. It provides the following key points:
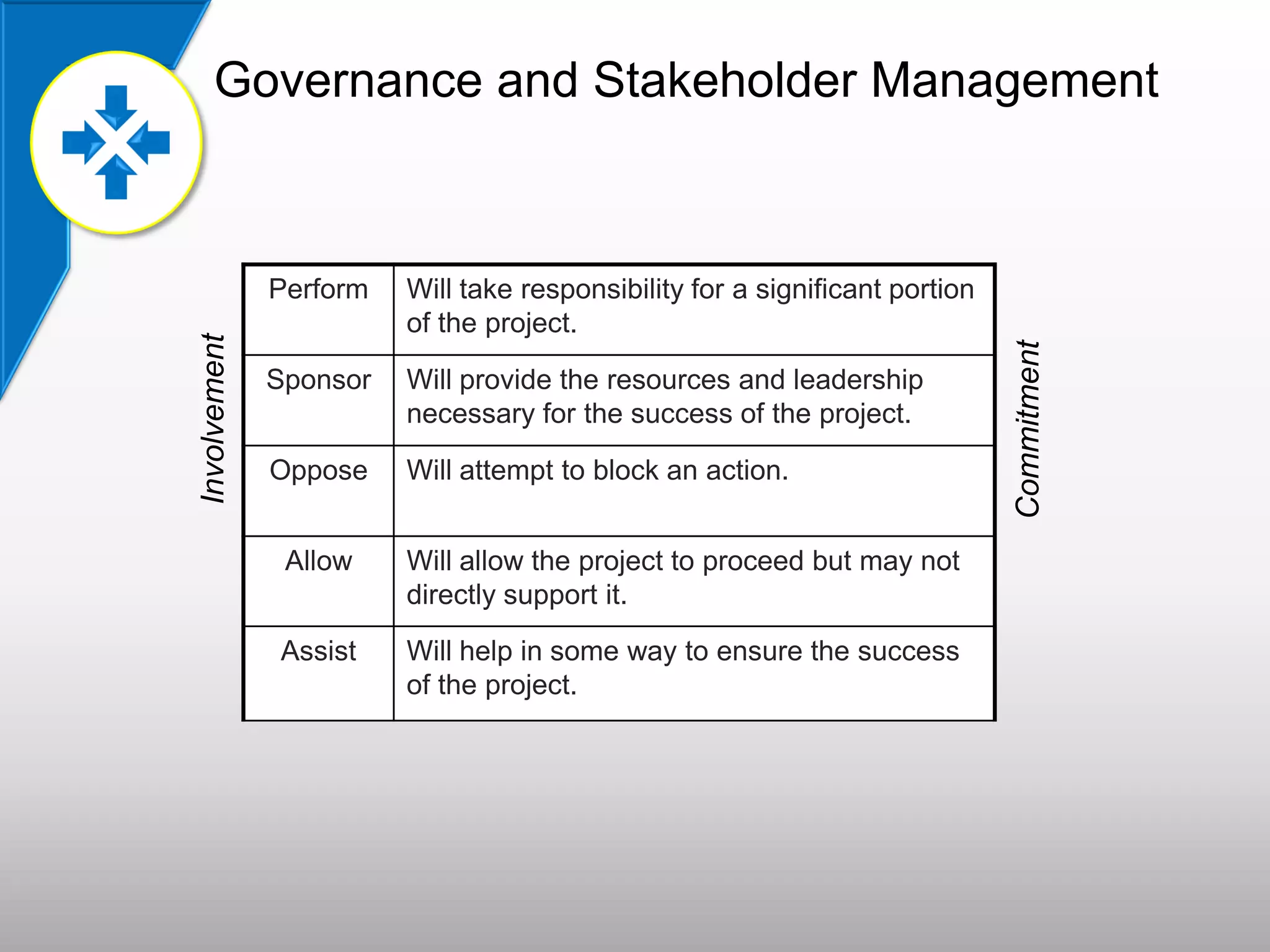
- SLAs define expectations for performance, responsibilities, and metrics to measure the success of the vendor. They are an important legal agreement between the parties.
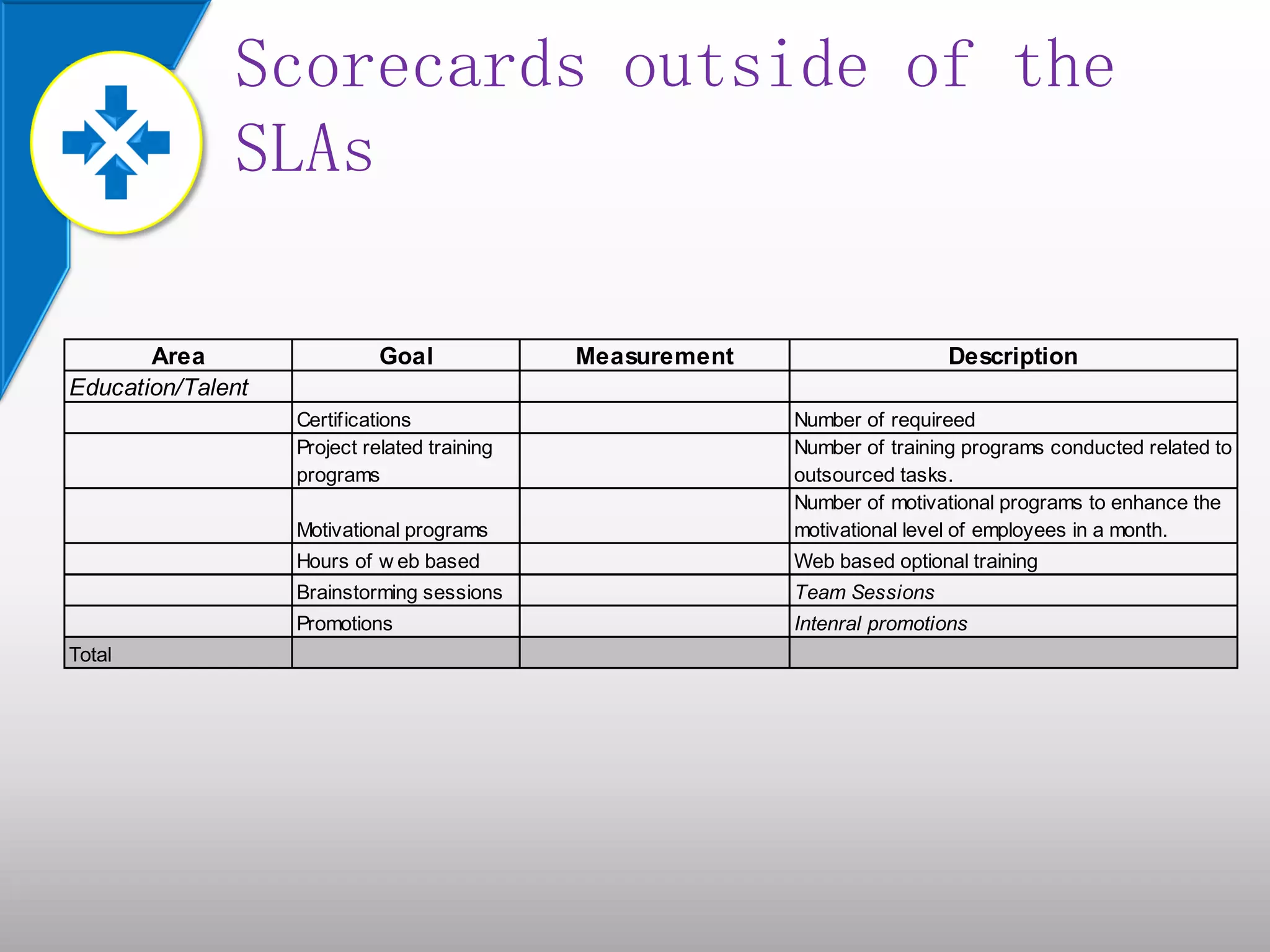
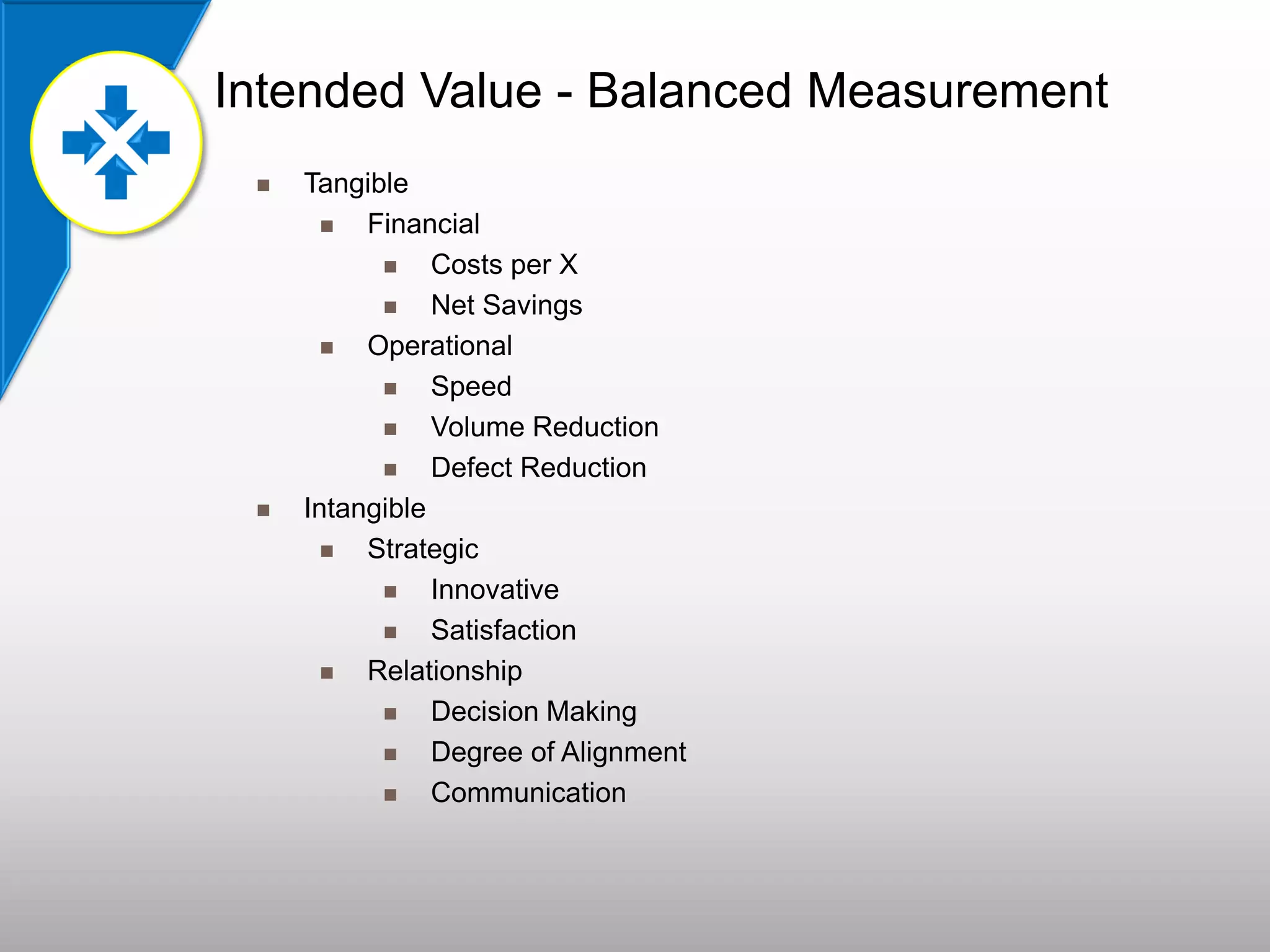
- SLAs should include metrics for assessing financial performance, responsiveness, technology utilization, processes, employee-related factors, customer satisfaction, and other deliverables.
- Properly utilized, SLAs help companies evaluate vendor performance, receive expected services, and manage changing expectations over time. However, SLAs are sometimes overlooked or underutilized.