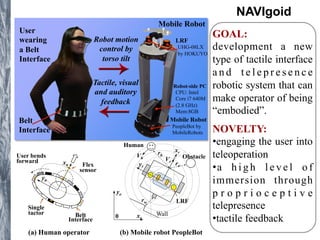
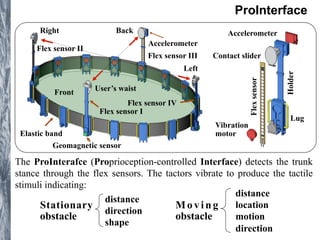
The document discusses various projects in teleoperation and wearable technology spearheaded by Dzmitry Tsetserukou, including systems for mobile robot navigation, haptic feedback, and emotional communication interfaces. Key systems mentioned are the navigoid for immersive robot navigation and the ifeel_im! communication system which utilizes haptic channels for enhanced interpersonal communication. The work emphasizes user engagement through proprioceptive telepresence and tactile feedback mechanisms.











![[█■ 퐹↓푡 @ 퐹↓푛 ]=[█■ 푆↓12 퐶↓2 &− 푆↓43 퐶↓3 @−
푆↓12 푆↓2 & 푆↓43 푆↓3 ] [█■ 휏↓1 ∕ 푙↓2 @ 휏↓2 ∕ 푙↓5 ]
F
Operation principle of PulseTouch
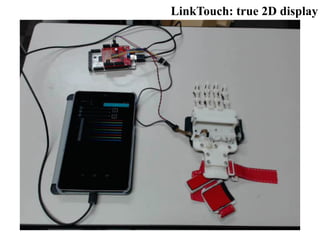
LinkTouch: true 2D display
Inverted five-bar linkage mechanism
C Fn
Fn
Ft
l1
l3 l4
l2
l5
Motor Faulhaber DC
Motor 0615 4,5 S
Gear Ratio GH Series 06/1
64:1
Encoder HXM3-64
D i m e n s i o n s
(W)×(H)×(D) [mm] 26.1×32×38.5
Link length l1, l2, l3,
l4, l5 [mm] 18, 25, 10, 10,25
Weight [g] 13.5
Normal force [N] 0.58](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-141202040537-conversion-gate02/85/Skoltech-2014-15-320.jpg)

![iFeel_IM!: communication system with
emotional and haptic channels
The philosophy behind iFeel_IM! (intelligent system for Feeling
enhancement powered by affect sensitive Instant Messenger) is
“I feel [therefore] I am!”
D. Tsetserukou, et al. Enhancing mediated interpersonal communication through affective haptics,
INTETAIN 2009, pp. 246-251.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-141202040537-conversion-gate02/85/Skoltech-2014-17-320.jpg)




