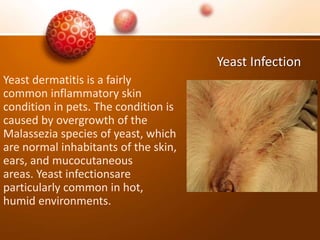
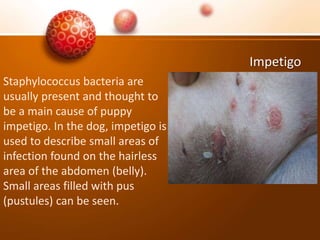
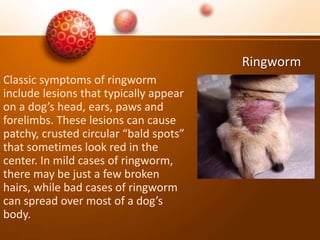
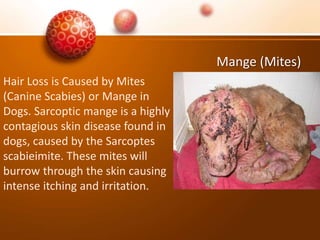
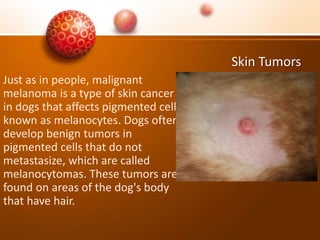
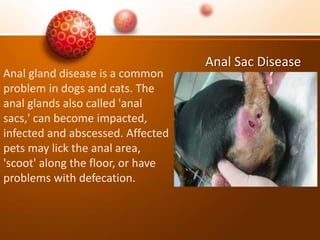
The document discusses various skin problems in dogs, highlighting conditions such as allergic dermatitis, yeast infections, folliculitis, and impetigo, which result from allergens, bacteria, or parasites. It also covers other issues like seborrhea, ringworm, mange, flea allergies, skin tumors, and immune disorders, outlining symptoms and potential causes of these conditions. Additionally, it addresses anal sac disease as a common concern in dogs and cats.