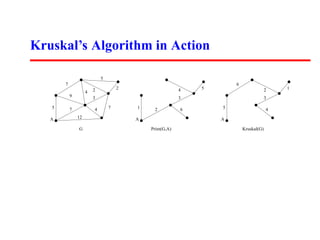
- Kruskal's algorithm finds a minimum spanning tree by greedily adding edges to a forest in order of increasing weight, as long as it does not form a cycle.
- It runs in O(m log m + n) time by sorting edges first and then using efficient data structures to test for cycles in constant time per edge.
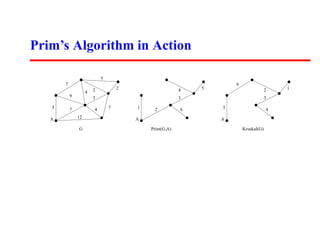
- Prim's algorithm grows a minimum spanning tree from a single vertex by always adding the lowest weight edge that connects a new vertex. It runs in O(n^2) time with basic implementations but can be optimized.














![Prim’s Implementation
To do it faster, we must identify fringe vertices and the
minimum cost edge associated with it fast.
prim(graph *g, int start)
{
int i; (* counter *)
edgenode *p; (* temporary pointer *)
bool intree[MAXV]; (* is the vertex in the tree yet? *)
int distance[MAXV]; (* distance vertex is from start *)
int v; (* current vertex to process *)
int w; (* candidate next vertex *)
int weight; (* edge weight *)
int dist; (* best current distance from start *)
for (i=1; i<=g− >nvertices; i++) {
intree[i] = FALSE;
distance[i] = MAXINT;
parent[i] = -1;
}
distance[start] = 0;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/skienaalgorithm2007lecture13minimumspanningtrees-111212074924-phpapp02/85/Skiena-algorithm-2007-lecture13-minimum-spanning-trees-18-320.jpg)
![v = start;
while (intree[v] == FALSE) {
intree[v] = TRUE;
p = g− >edges[v];
while (p ! = NULL) {
w = p− >y;
weight = p− >weight;
if ((distance[w] > weight) && (intree[w] == FALSE)) {
distance[w] = weight;
parent[w] = v;
}
p = p− >next;
}
v = 1;
dist = MAXINT;
for (i=1; i<= g− >nvertices; i++)
if ((intree[i] == FALSE) && (dist > distance[i])) {
dist = distance[i];
v = i;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/skienaalgorithm2007lecture13minimumspanningtrees-111212074924-phpapp02/85/Skiena-algorithm-2007-lecture13-minimum-spanning-trees-19-320.jpg)