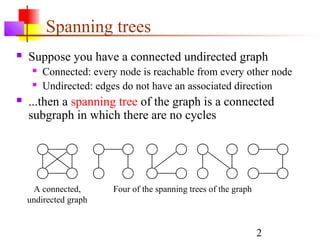
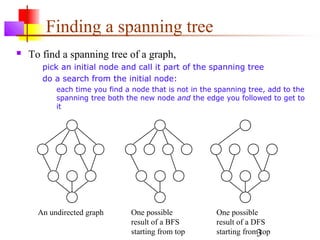
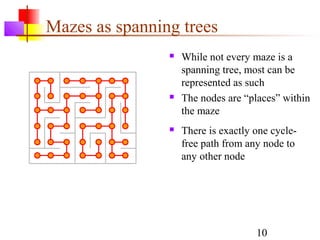
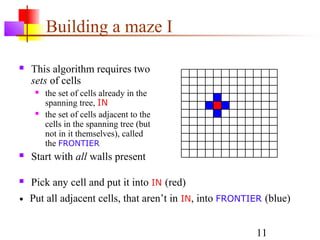
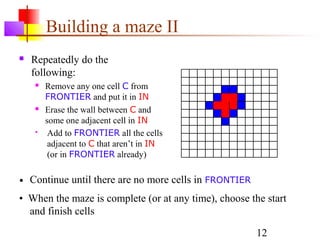
This document discusses spanning trees and their application to mazes. It defines a spanning tree as a connected subgraph of an undirected graph with no cycles. Two common algorithms for finding minimum-cost spanning trees are described: Kruskal's algorithm and Prim's algorithm. Mazes can be represented as spanning trees, with locations as nodes and open doors as edges, ensuring a single path between any two locations. An algorithm is provided for building a maze by iteratively adding locations to the spanning tree from a frontier of adjacent, unadded locations.