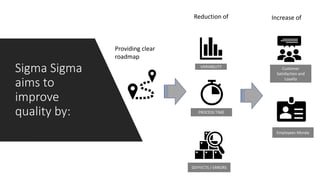
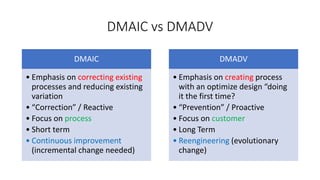
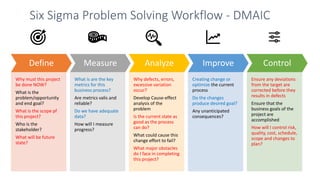
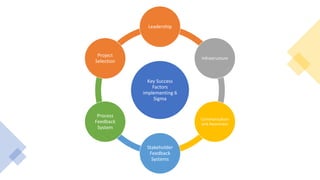
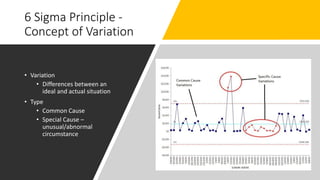
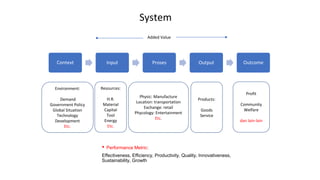
This document provides an overview of Six Sigma, including the key differences between the DMAIC and DMADV approaches. It discusses the main goals of Six Sigma as improving quality by reducing defects, variability, and improving customer satisfaction. DMAIC focuses on improving existing processes, while DMADV takes a proactive approach to designing new processes. The document also outlines the problem solving workflows for DMAIC and DMADV, and lists some of the key principles and success factors for Six Sigma implementation.