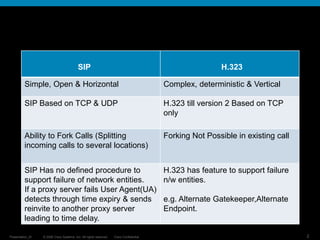
SIP is a simpler, more open and modular protocol than H.323. It uses TCP and UDP for transport whereas H.323 used only TCP until version 2. SIP allows for call forking by splitting incoming calls to several locations, while forking is not possible in existing H.323 calls. H.323 is better able to support failure of network entities through features like alternate gatekeepers and endpoints, while SIP has no defined procedure for proxy server failures. Overall, SIP is more lightweight and flexible than the more full-featured but complex H.323 protocol.