This document provides an overview of the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and its relevance in Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology, including its history, architecture, and various SIP messages. It discusses the advantages of SIP over other protocols like H.323 and highlights the role of VoIP in modern telecommunications. Additionally, it covers network elements, SIP addressing, supplementary services, and tools like Wireshark for analyzing SIP traffic.




![8
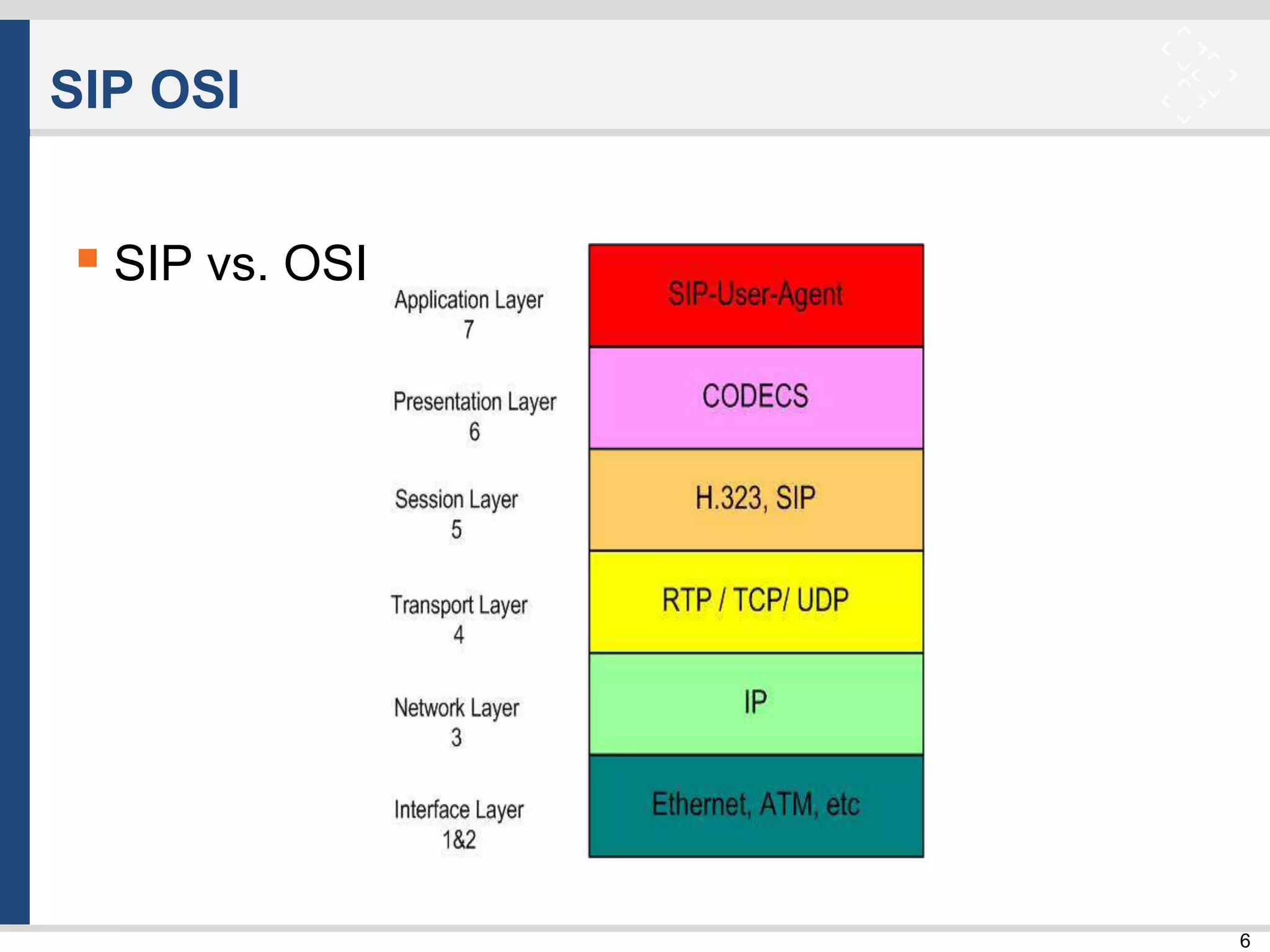
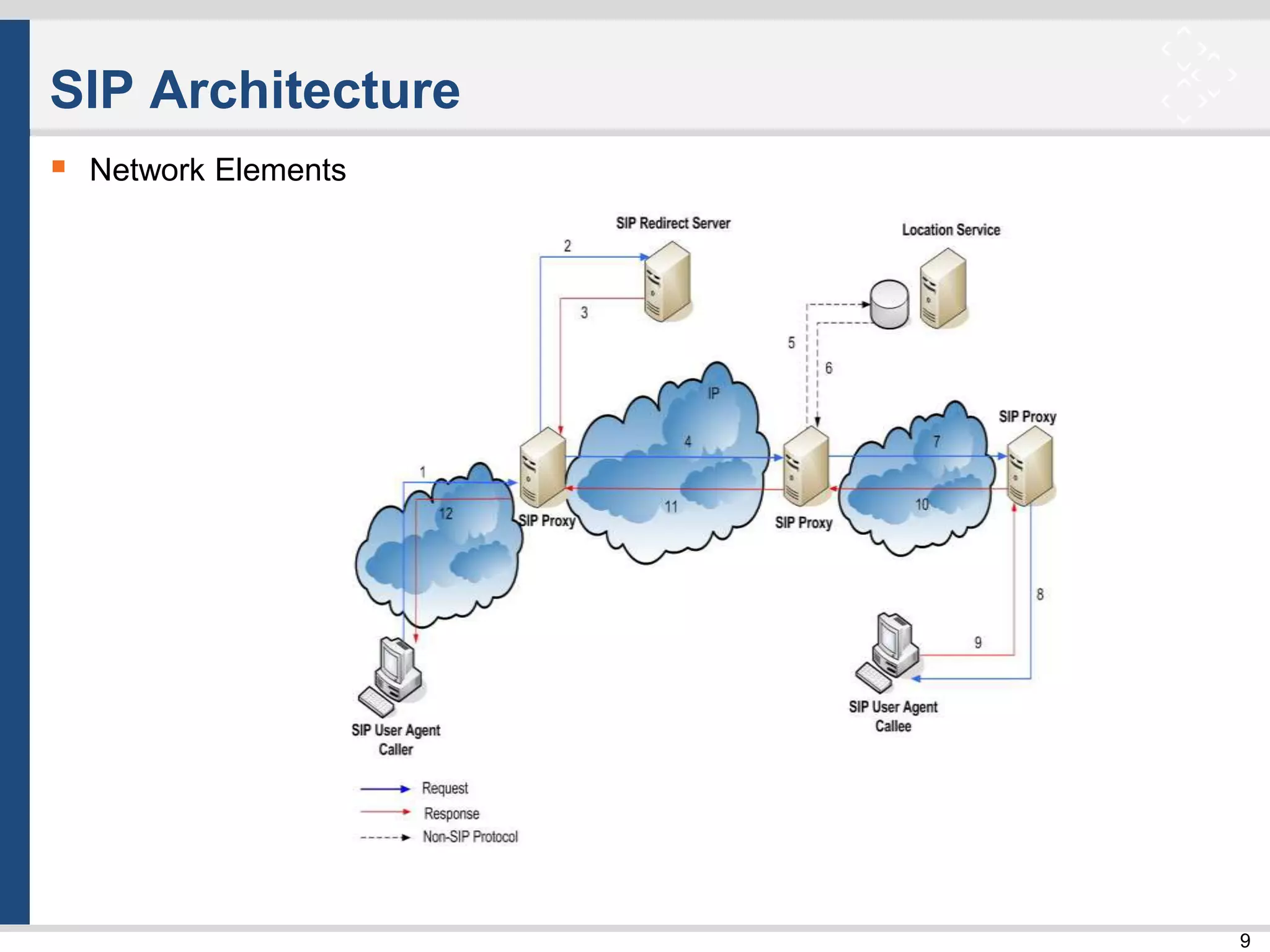
SIP Architecture
Network Elements:
– UA – User Agent
UAC – User Agent Client [request]
UAS – User Agent Server [response]
– Server Elements [RFC 3261]
Proxy Server [phone – proxy – proxy – phone]
Registrar [REGISTER]
Redirect Server [3XX]
– Other Network Elements
SBC – Session Border Controller
Gateway](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tlc-004-takeasipofsip-160418083320/75/Tlc-004-take-a-sip-of-sip-8-2048.jpg)


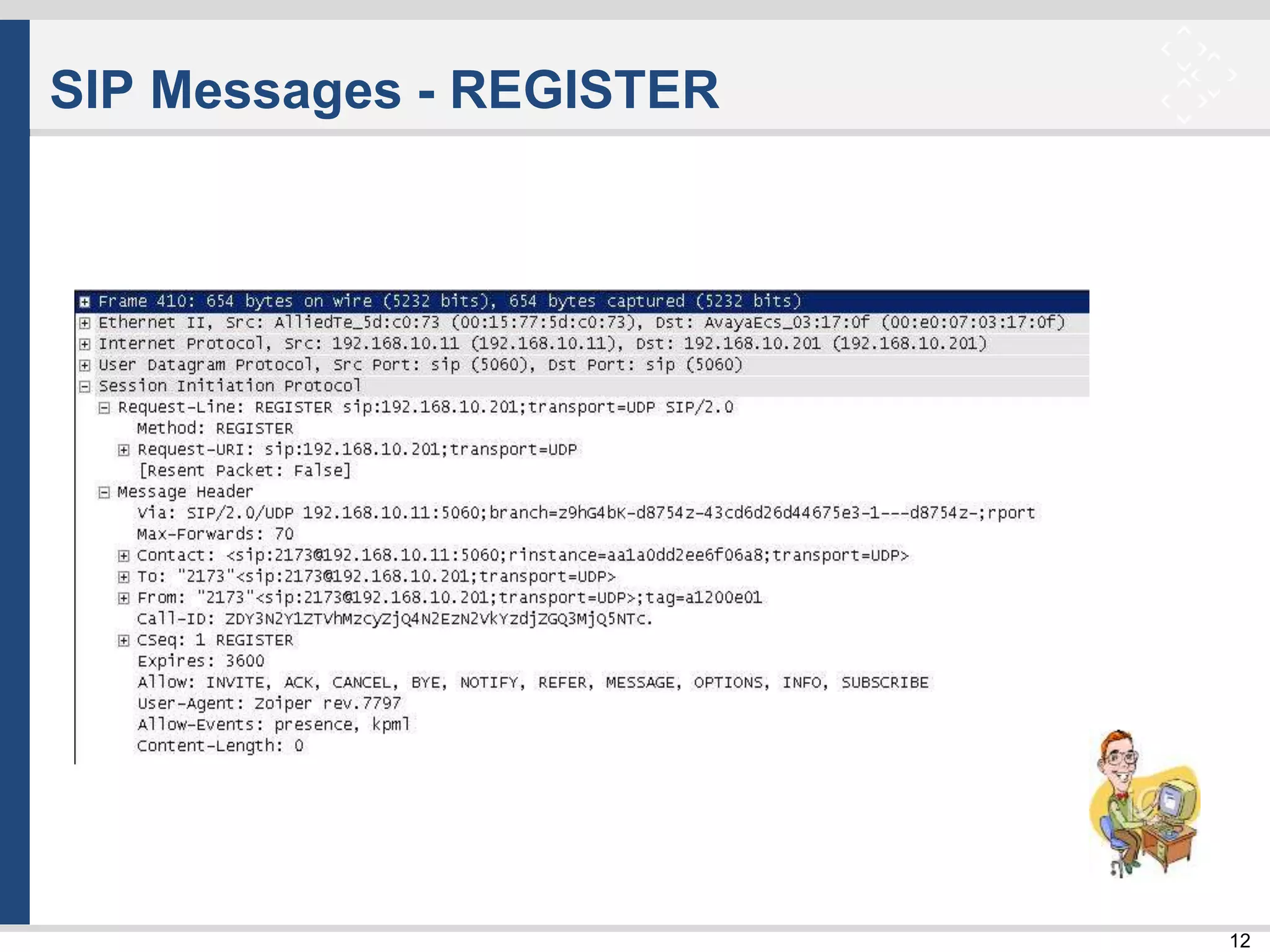
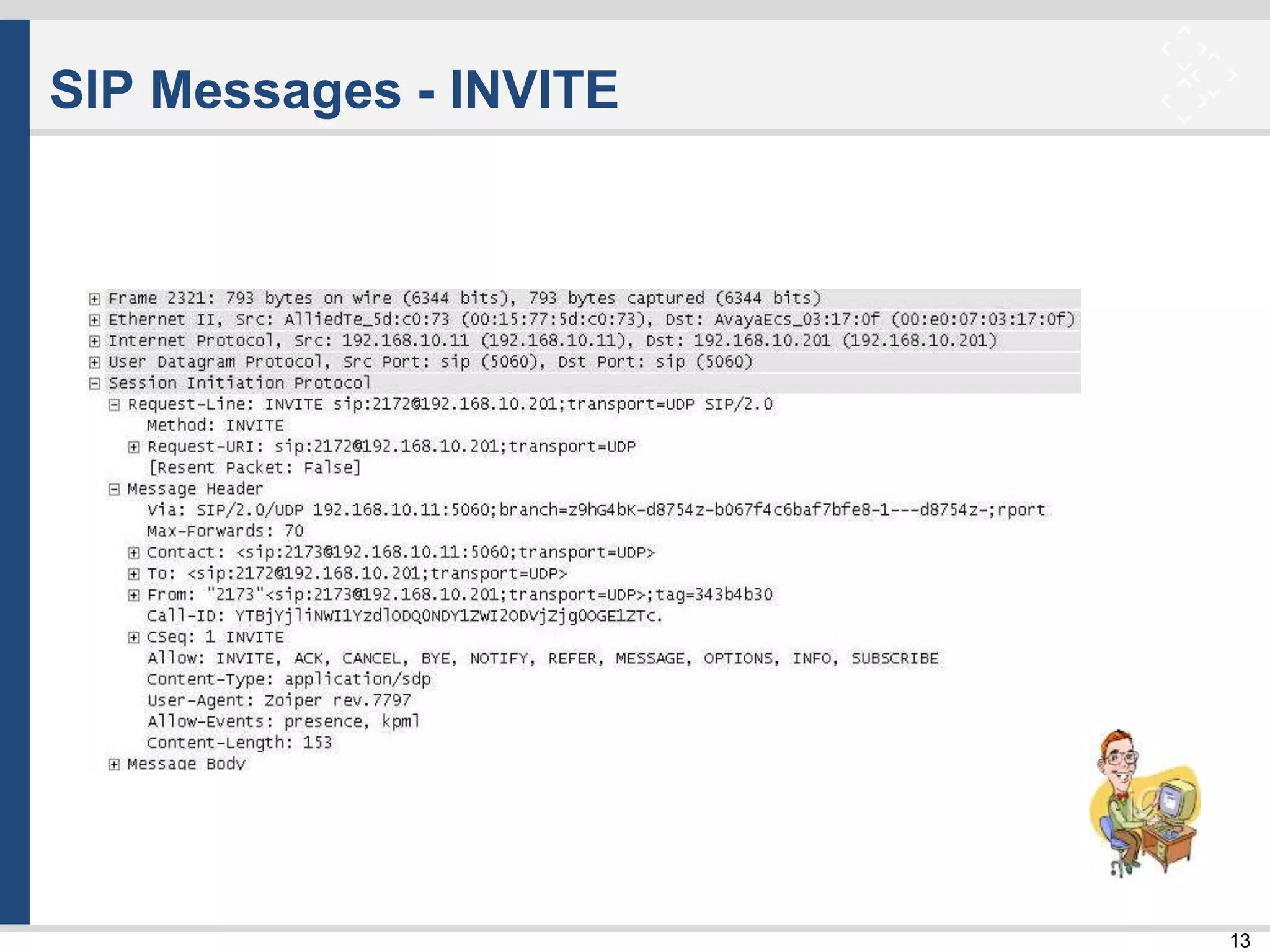
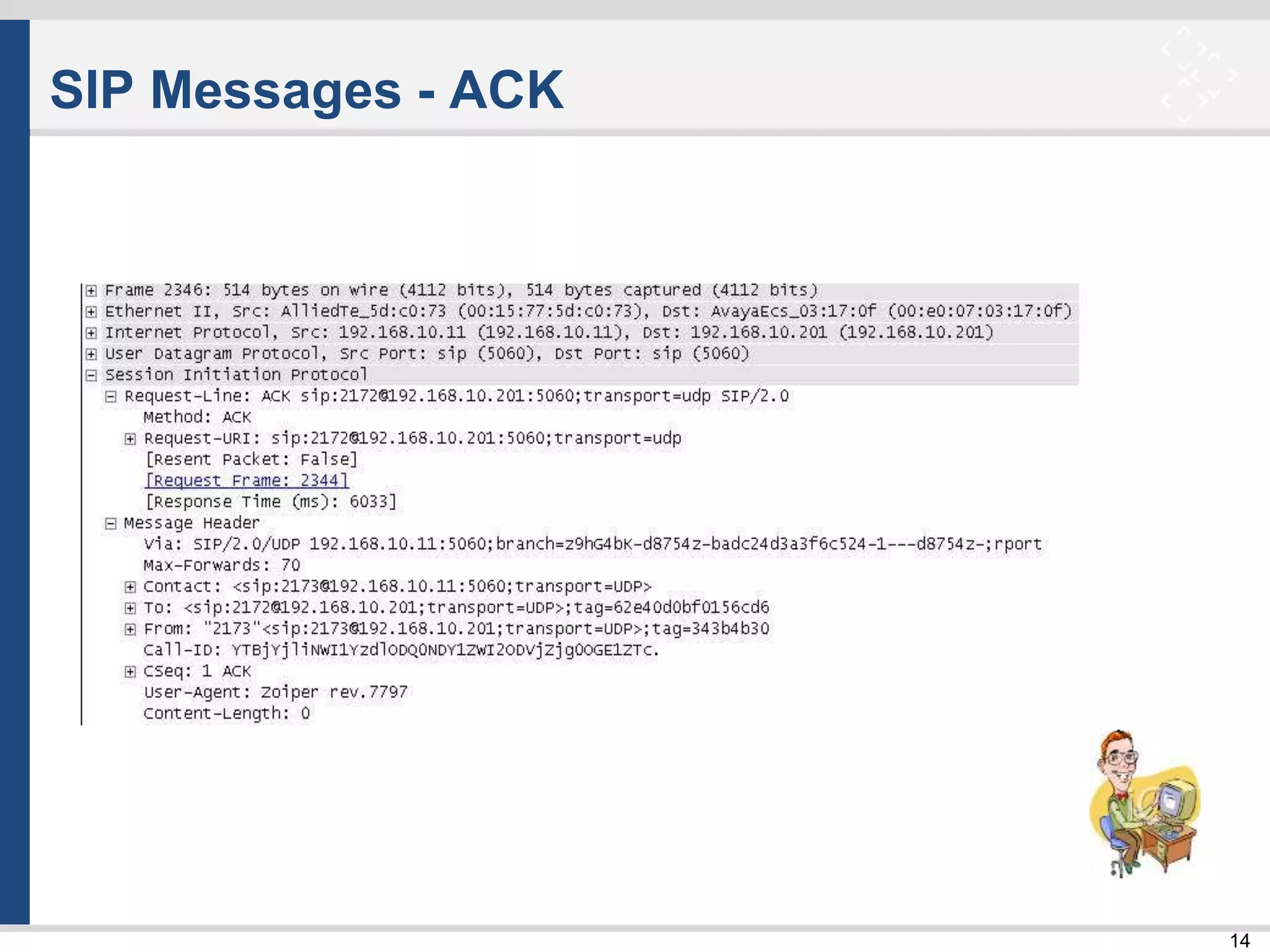


![33
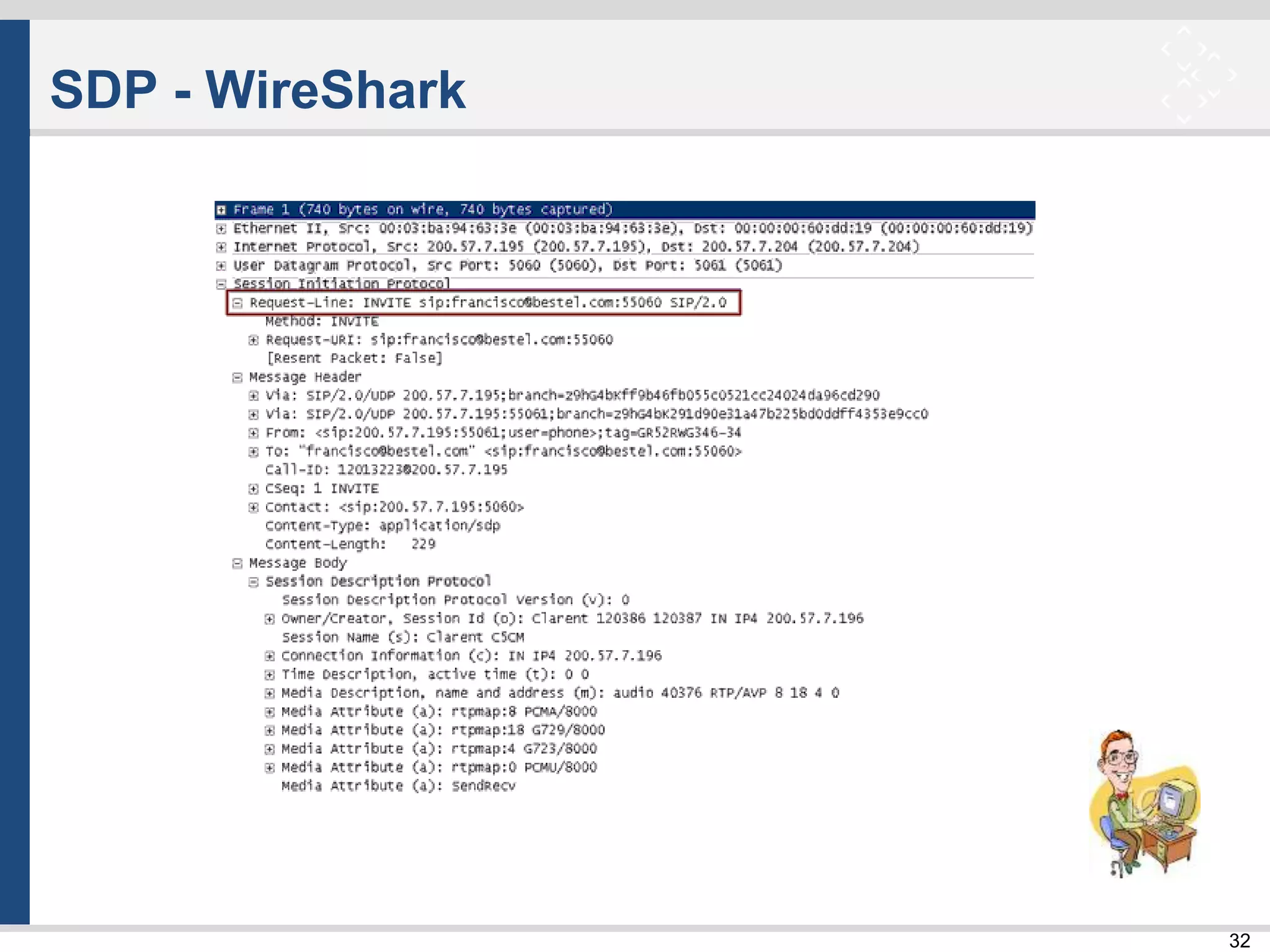
SDP - WireShark
Session Description Protocol Version - 0
Owner / Creator of the session or Owner / Creator. Identification is made by:
– Owner username. User.
– Session ID. ID of the session. Random number as a unique identifier of the session.
– Session Version. Version.
– Network Type. Tipe network. Always IN.
– Address Type. It can be IP4 (IPv4) or IP 6 (IPv6).
– Address (IP). IP Address. (200.57.7.197)
– Session Name. Name of the session.
Connection Information:
– C = Connection Type Network (IN)
– Connection Address Type: (IP4 or IPv6)
– Connection Address: (200.57.7.197)
Time Description, active time. (t): 0 0, start stop time = 0. [unrestricted and permanent session].
Media Description, name and address (m): audio 40376 RTP / AVP 4 0 8 18. Type of data being transported (audio or telephone session in this
case), UDP port used (40 376), protocol used (Real Time Transport Protocol RTP / AVP Audio Video Profiles). Codecs formats:
– 8 G.711 PCMA
– 18 G.729
– 4 G.723
– 0 G.711 PCMU
Media Attribute (a). This is a list of format codes outlined above with data from Sample rate or sampling frequency, fieldname, etc.
Media Attribute (a). SendRecv. So send / receive.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tlc-004-takeasipofsip-160418083320/75/Tlc-004-take-a-sip-of-sip-33-2048.jpg)