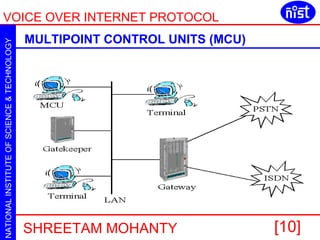
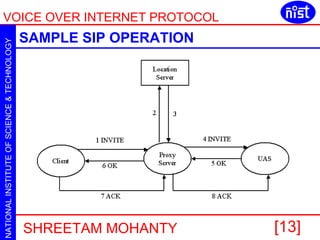
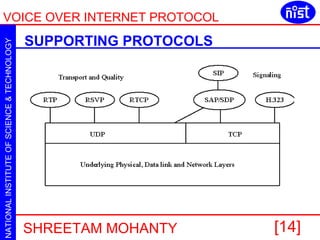
VOIP allows voice calls over the internet using IP packets. It uses protocols like H.323 and SIP to set up and manage calls. H.323 uses terminals, gateways and gatekeepers to make calls. SIP is a lighter alternative that uses messages like INVITE, ACK and BYE. Both protocols support RTP for carrying voice data and have grown significantly with telecom companies now offering VOIP services.