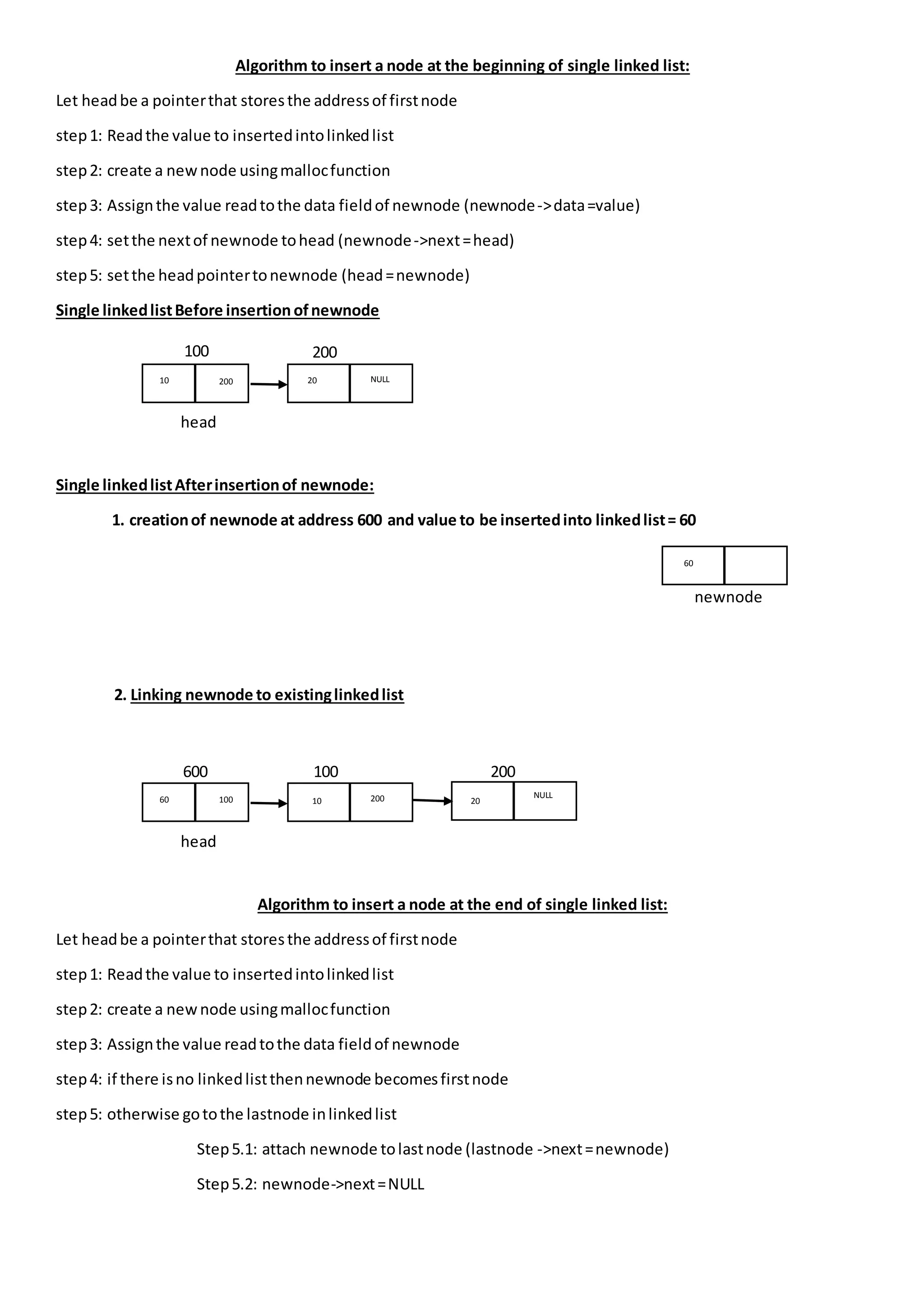
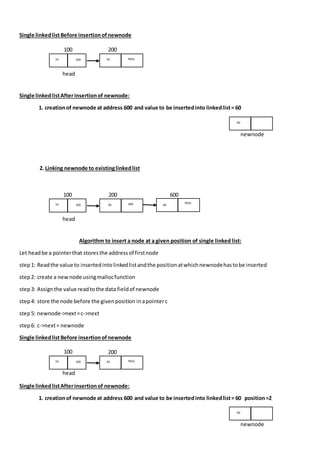
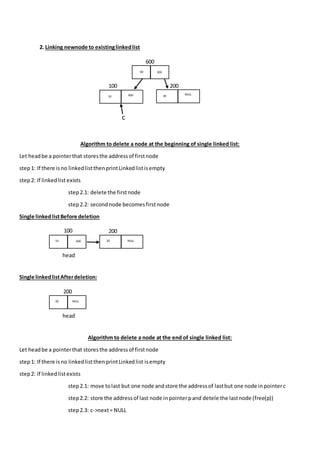
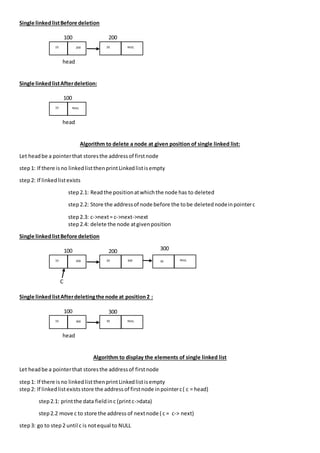
The document outlines algorithms for inserting and deleting nodes in a singly linked list, including methods to insert at the beginning, end, or a specific position, as well as methods to delete from the beginning, end, or a specific position. It provides step-by-step instructions for each operation, demonstrating how to manage pointers for linking and unlinking nodes during these processes. Additionally, it includes a procedure for displaying elements within the linked list.