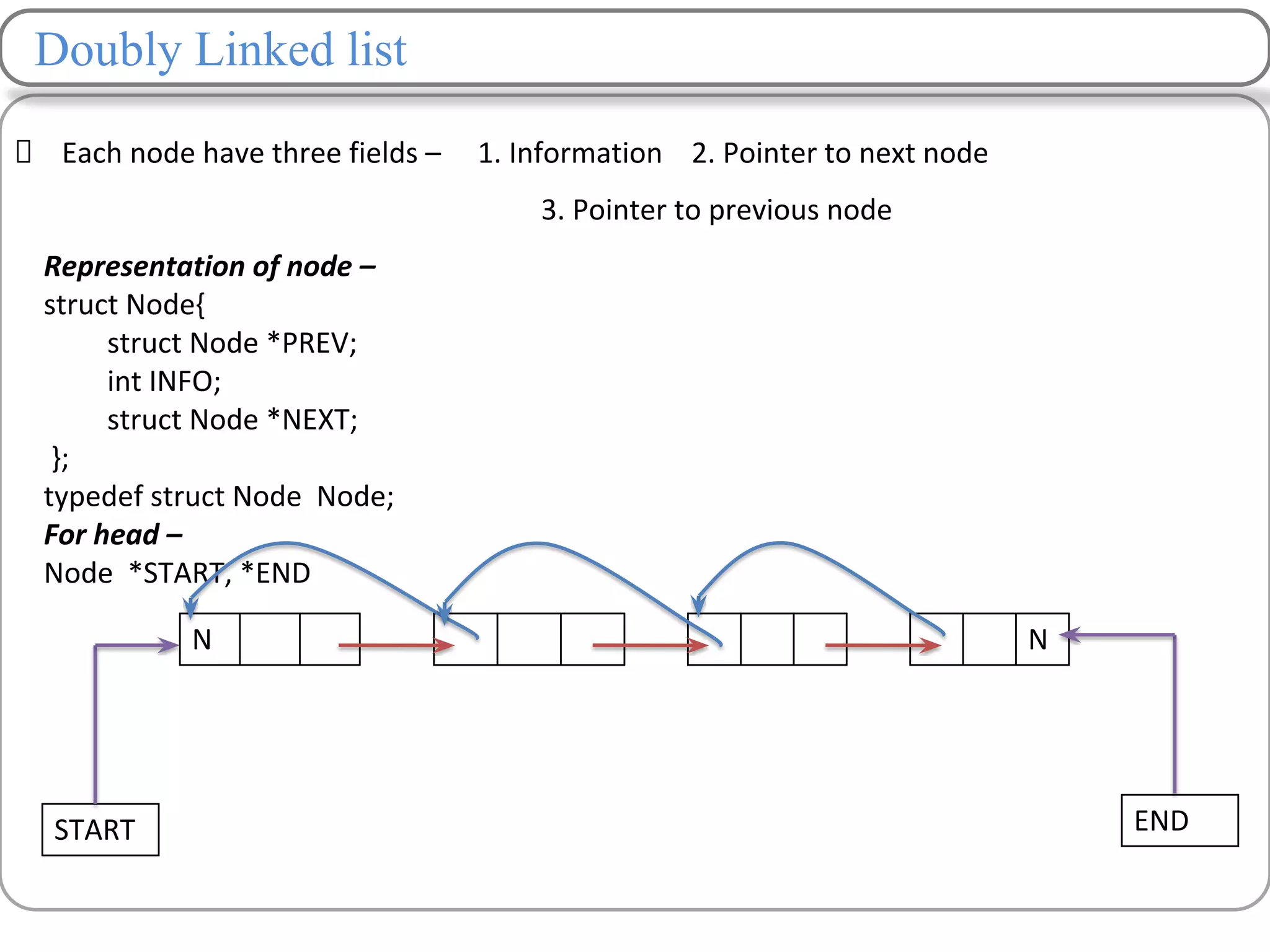
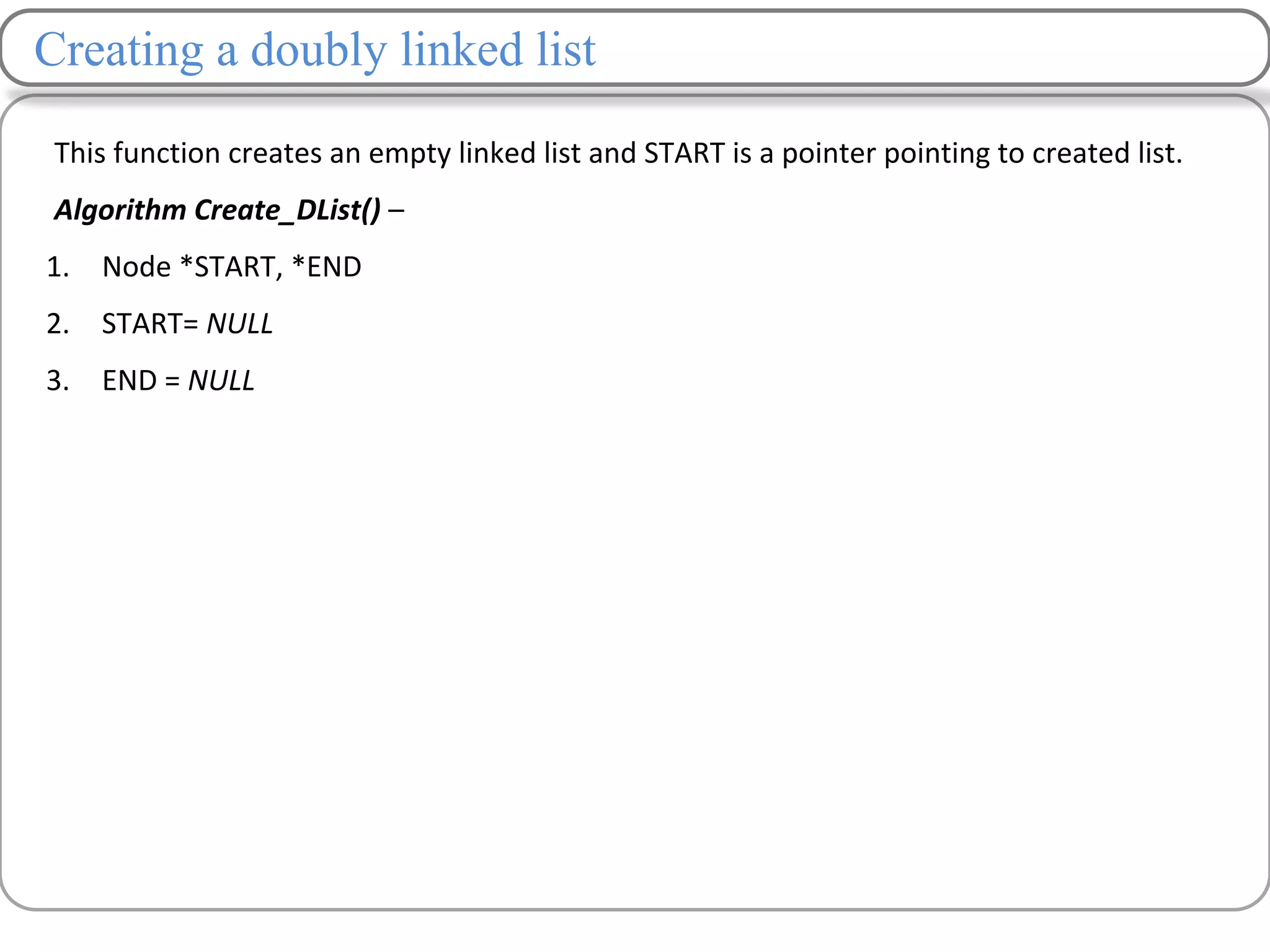
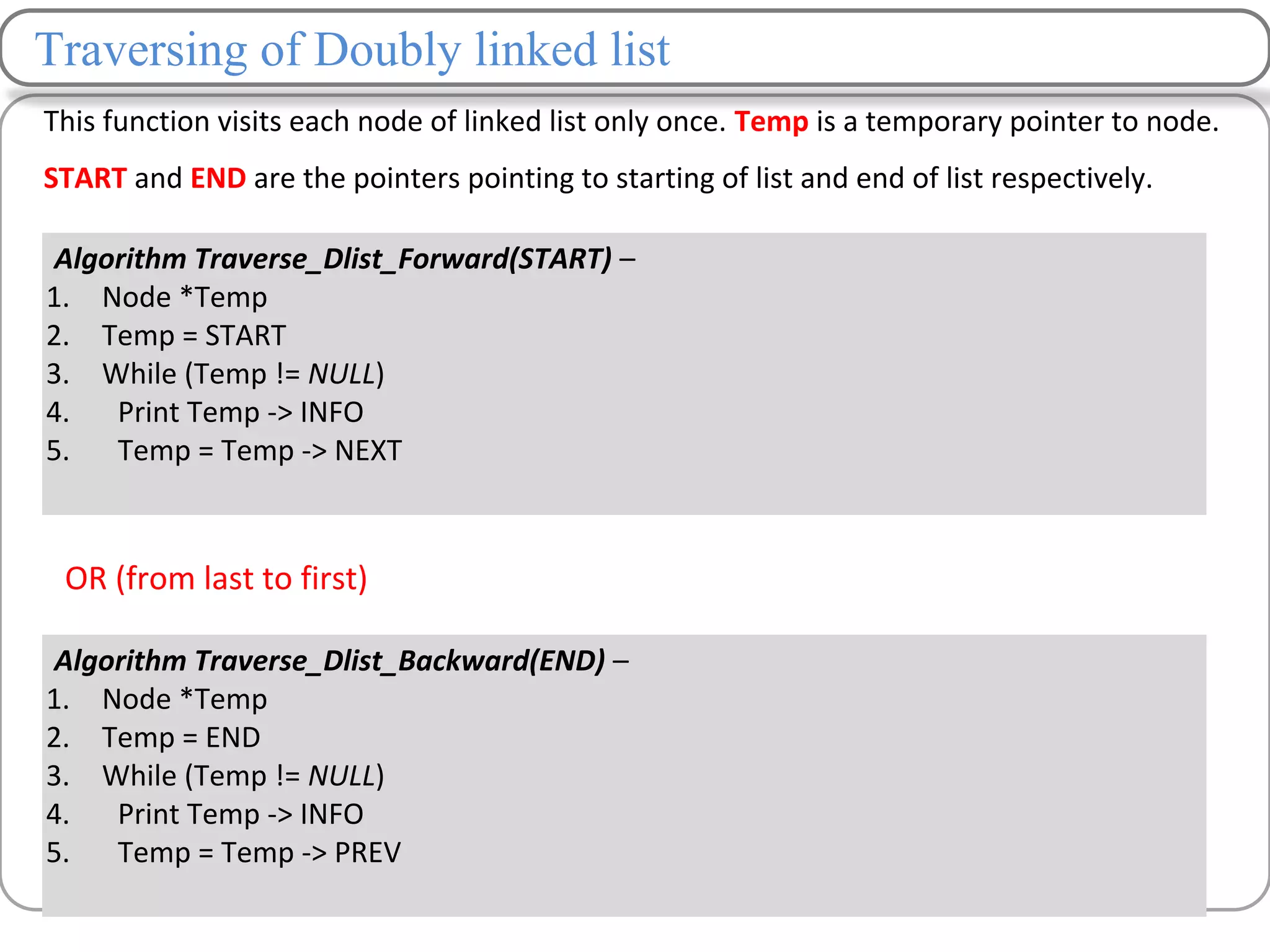
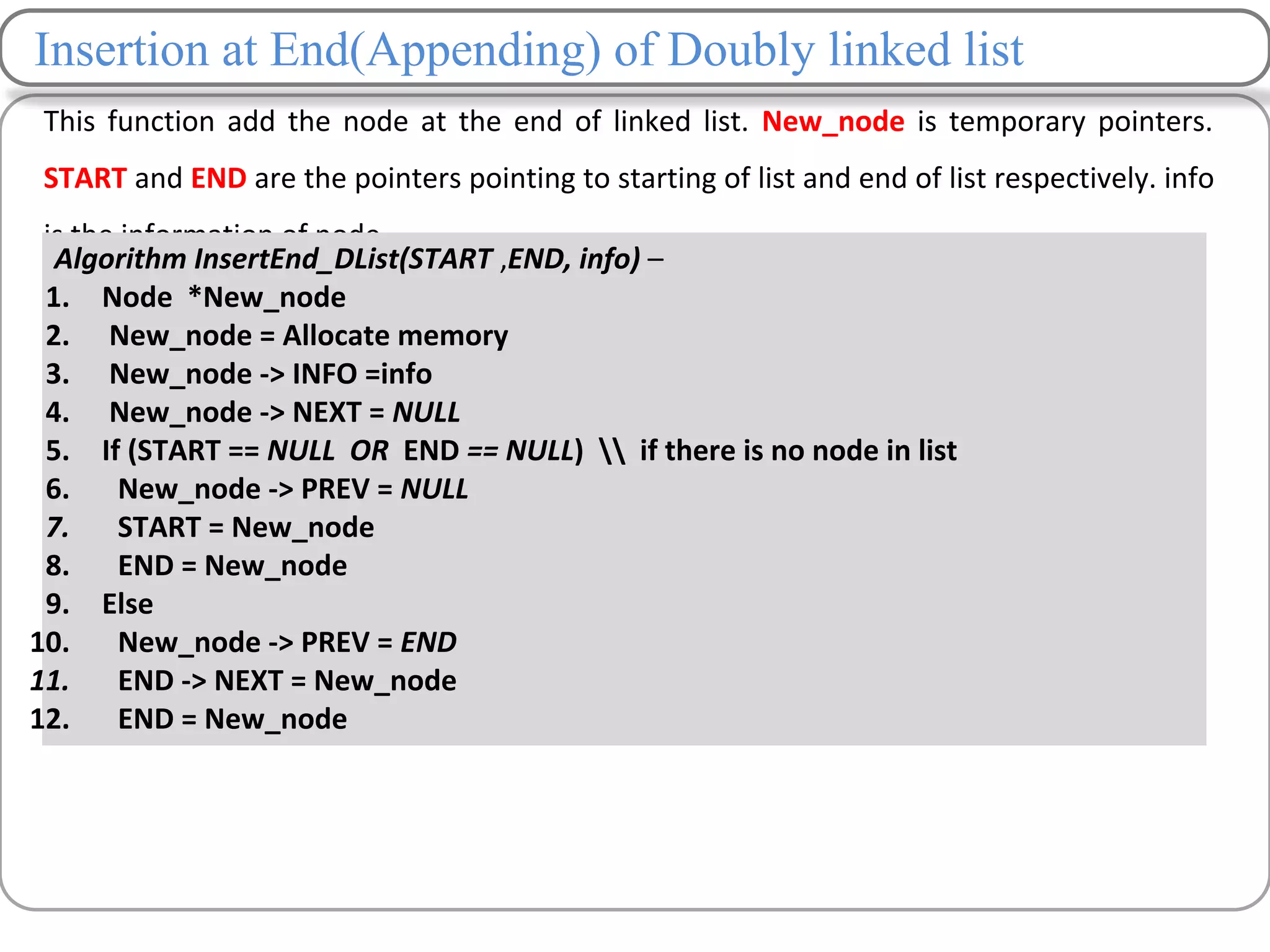
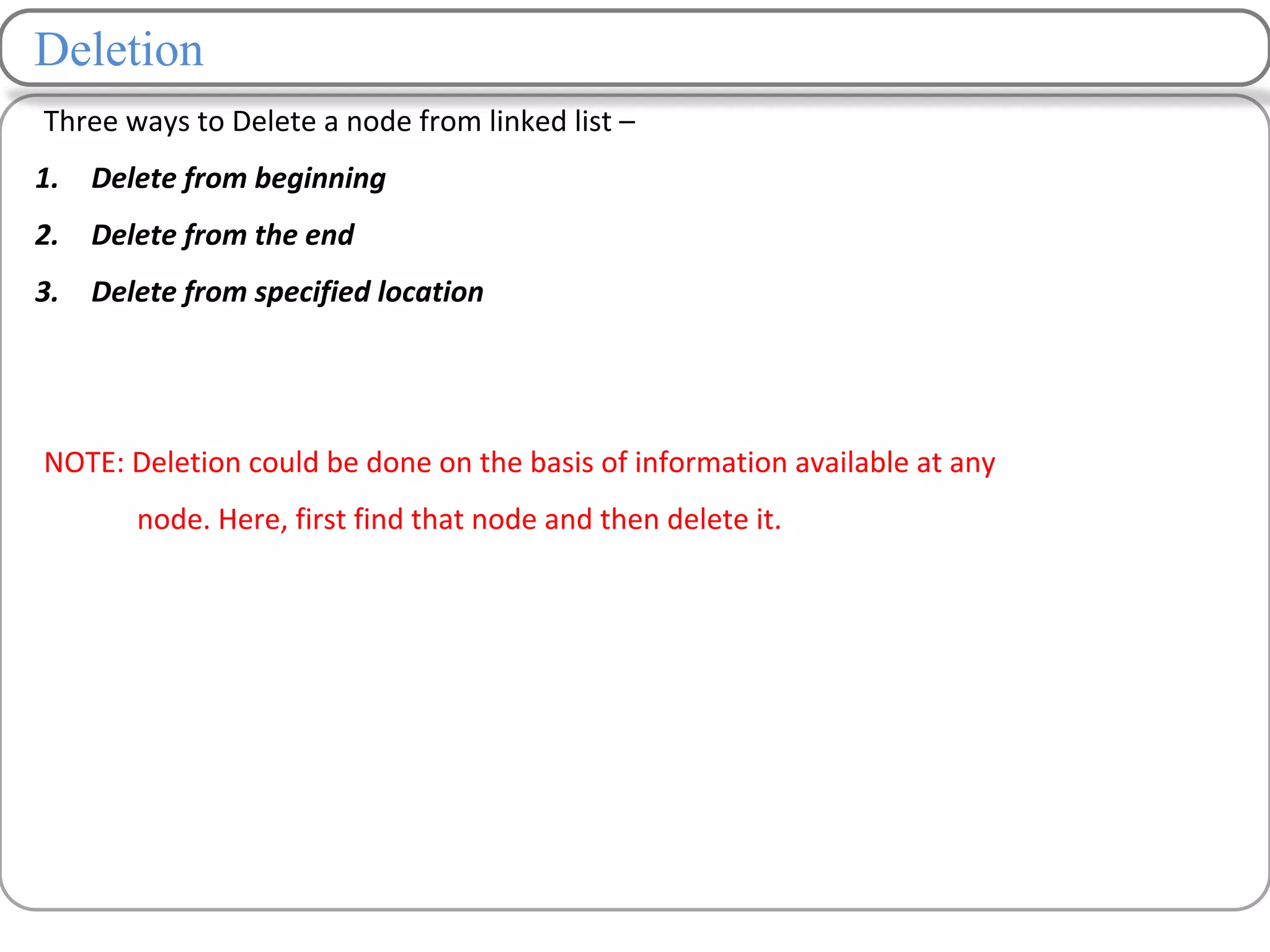
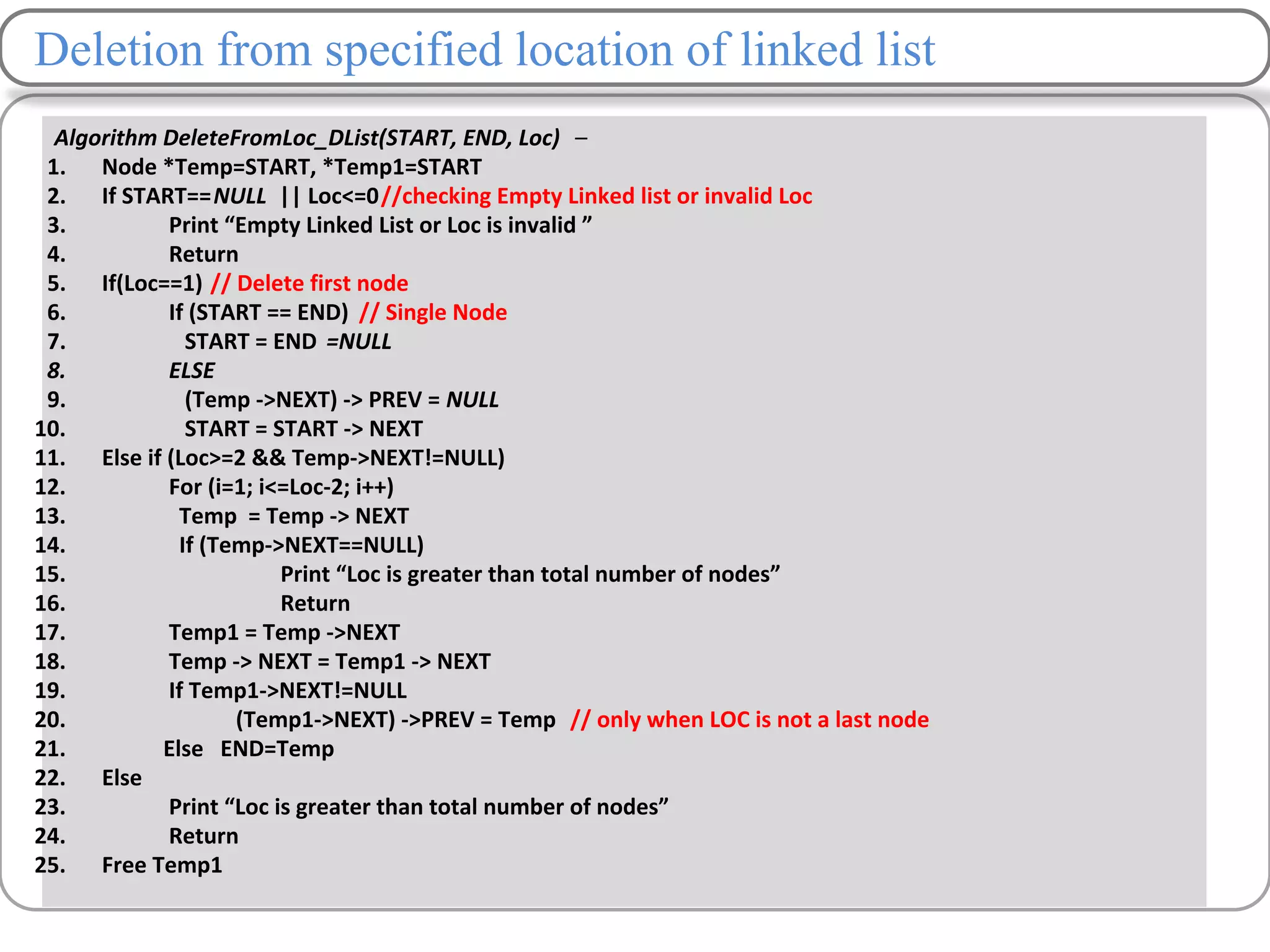
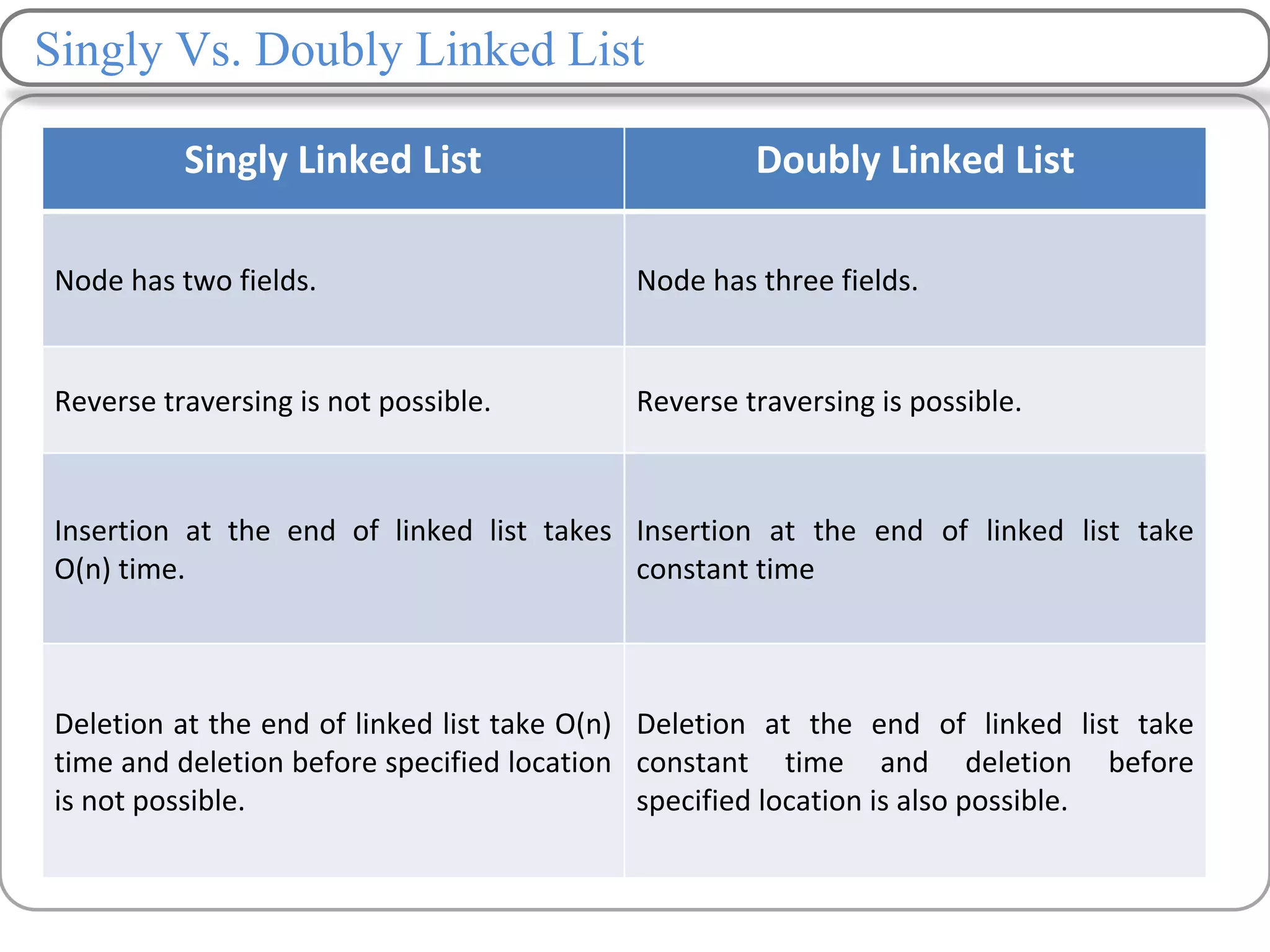
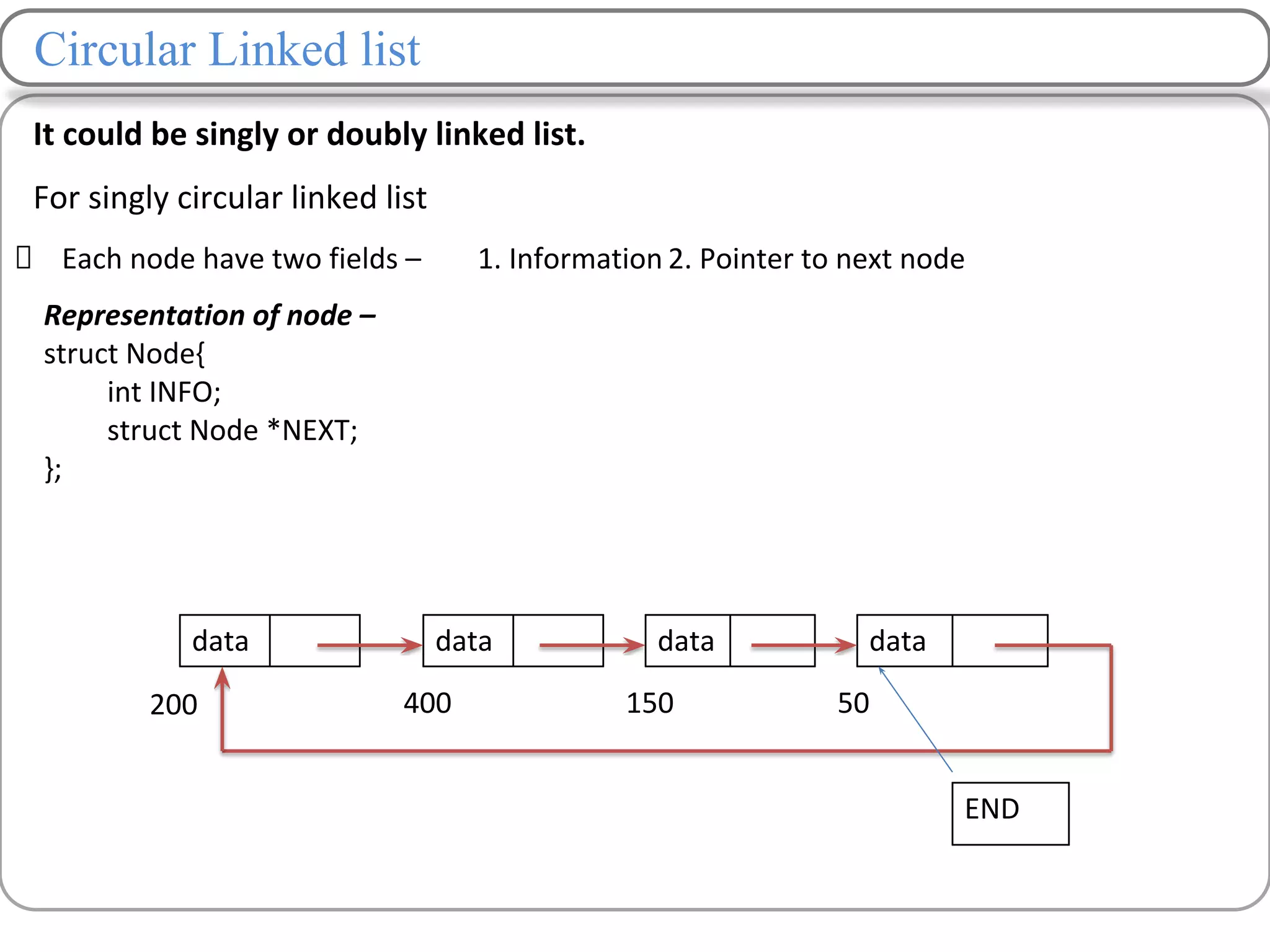
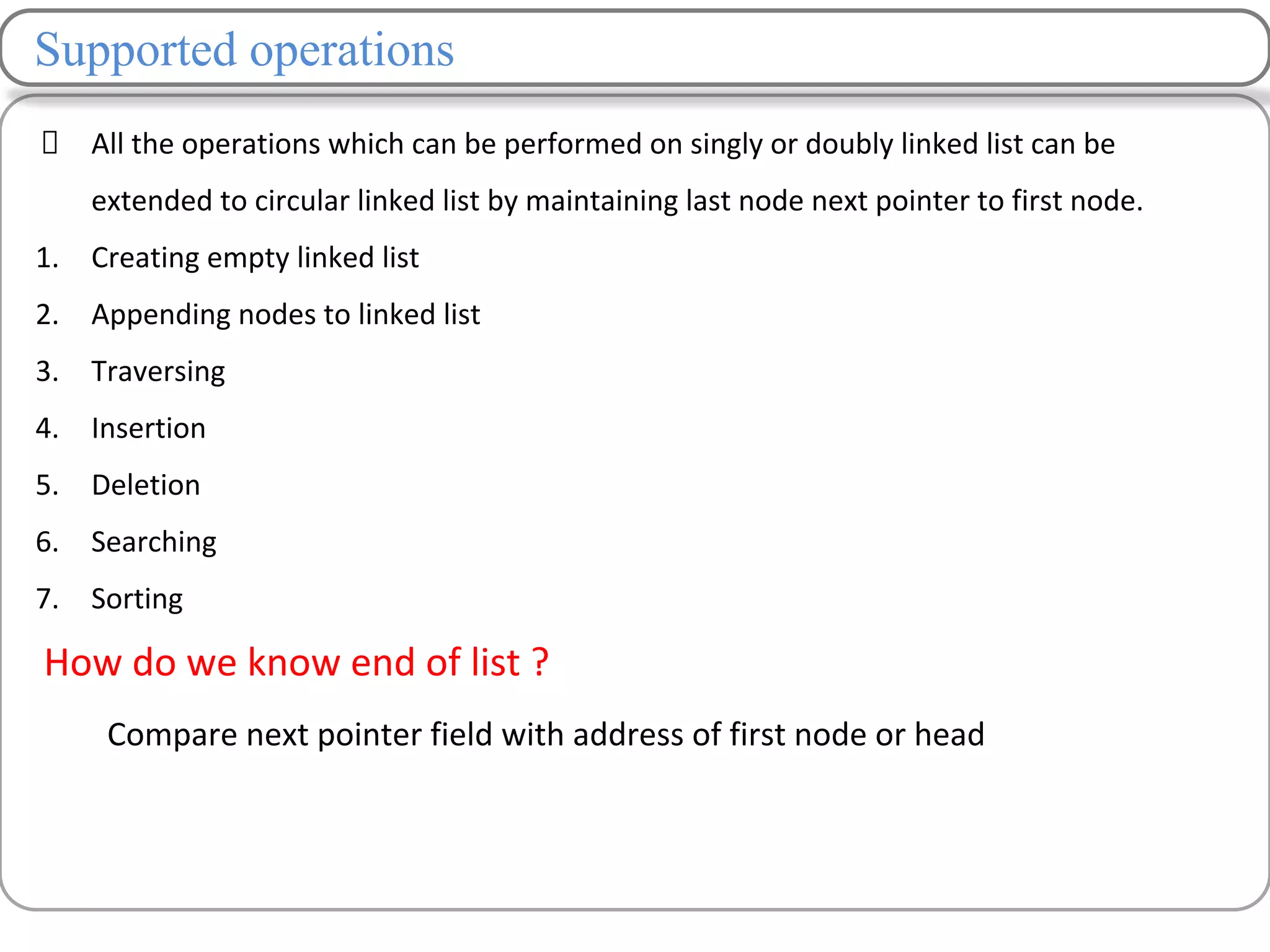
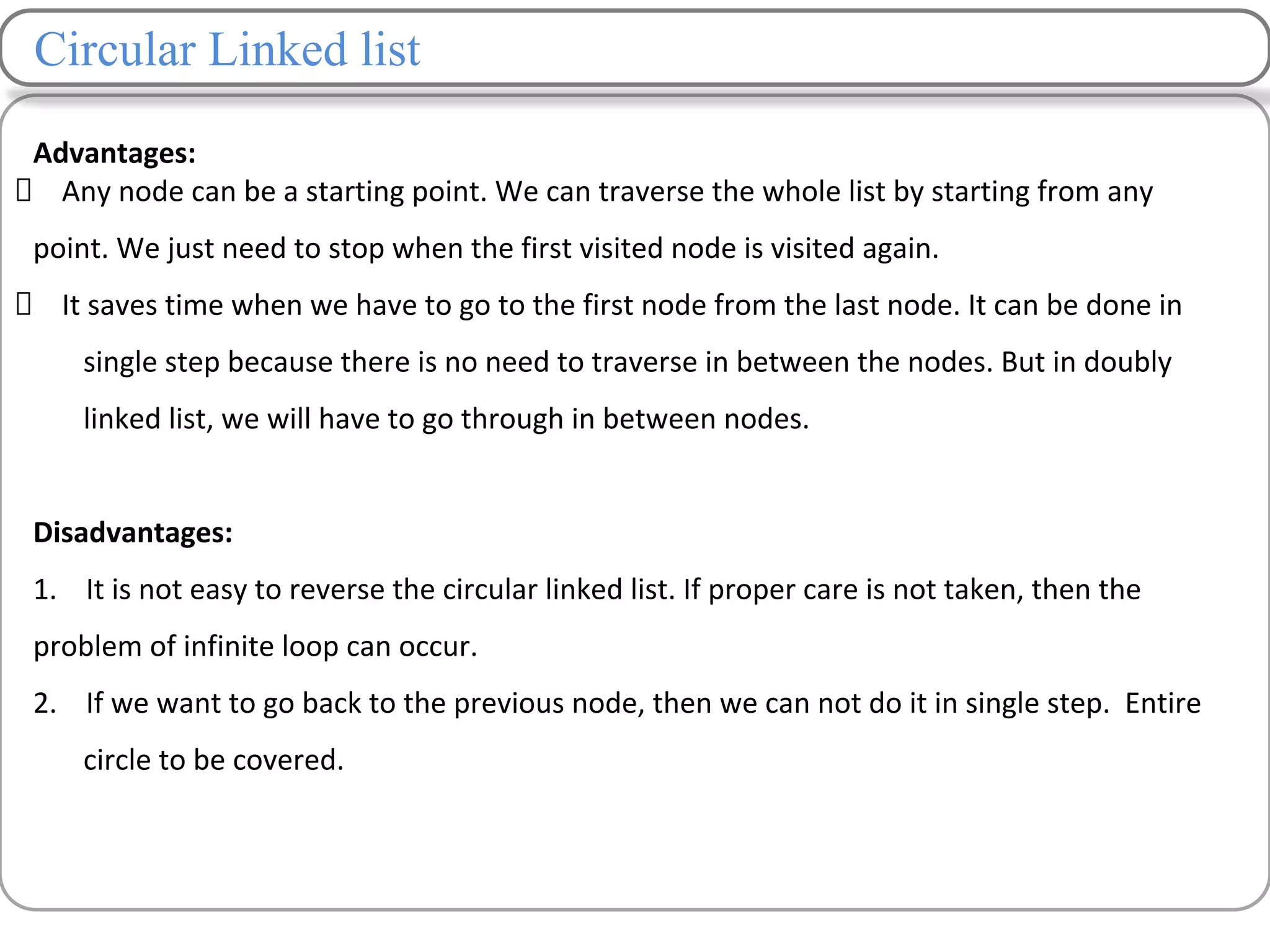
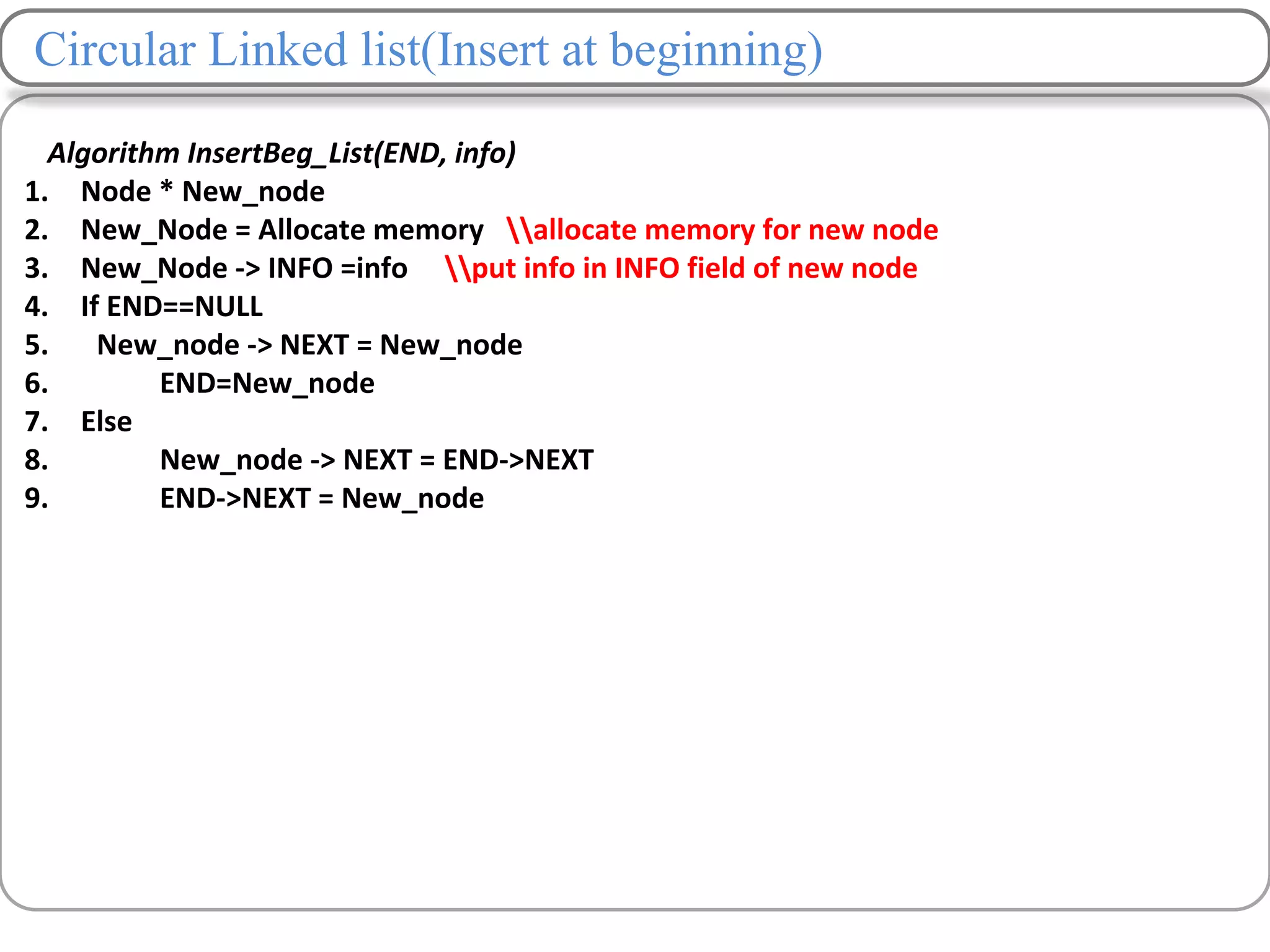
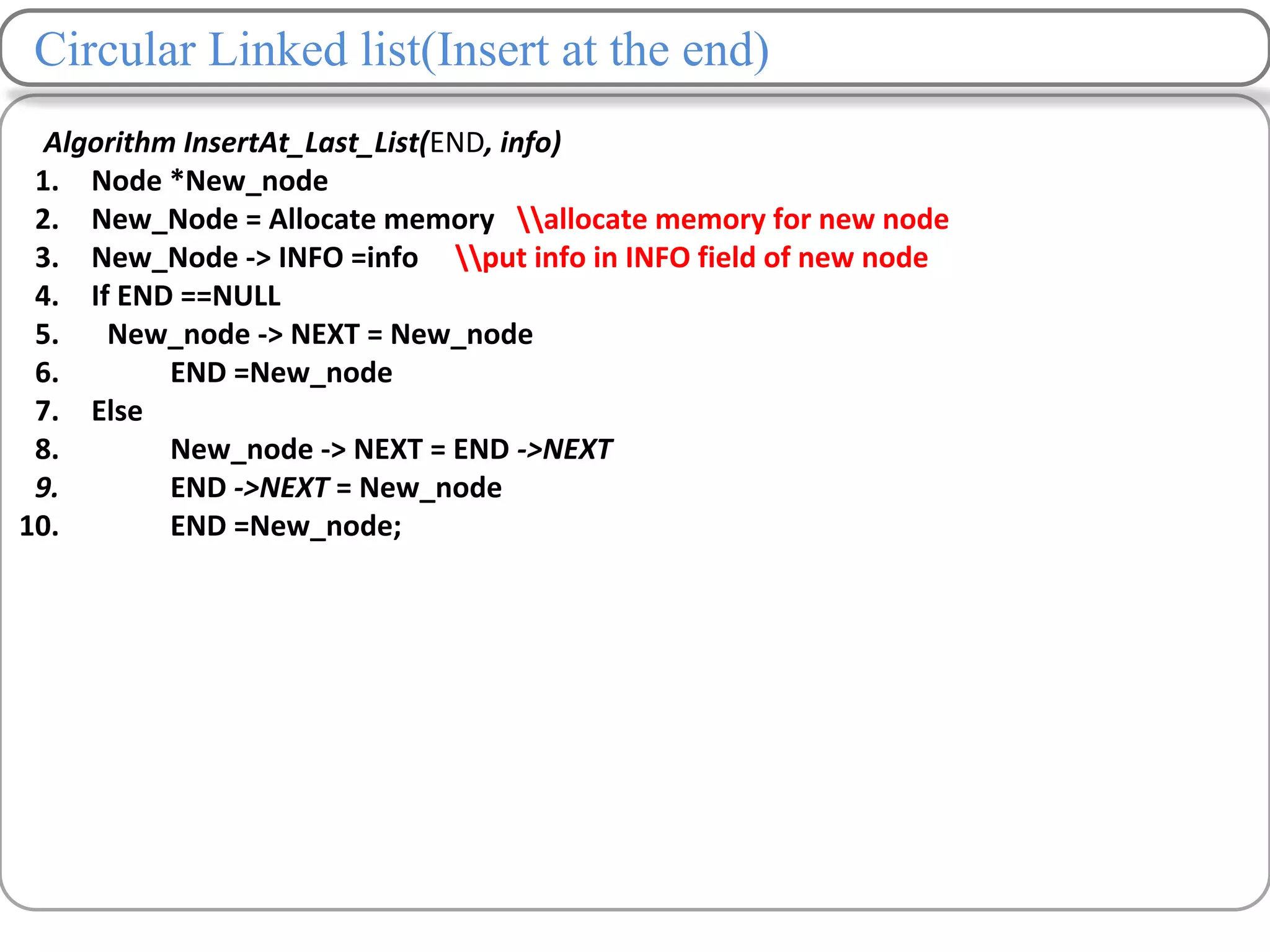
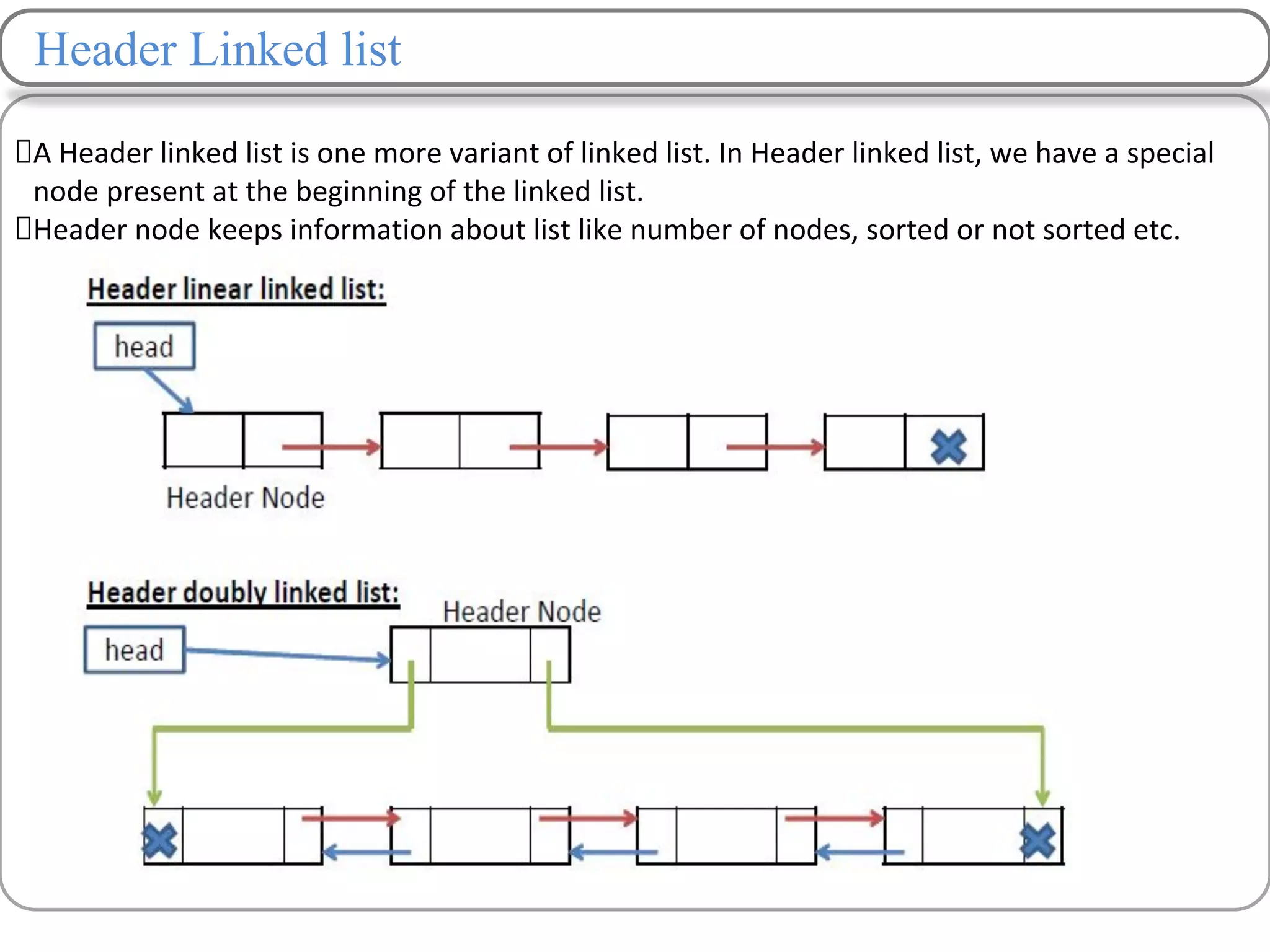
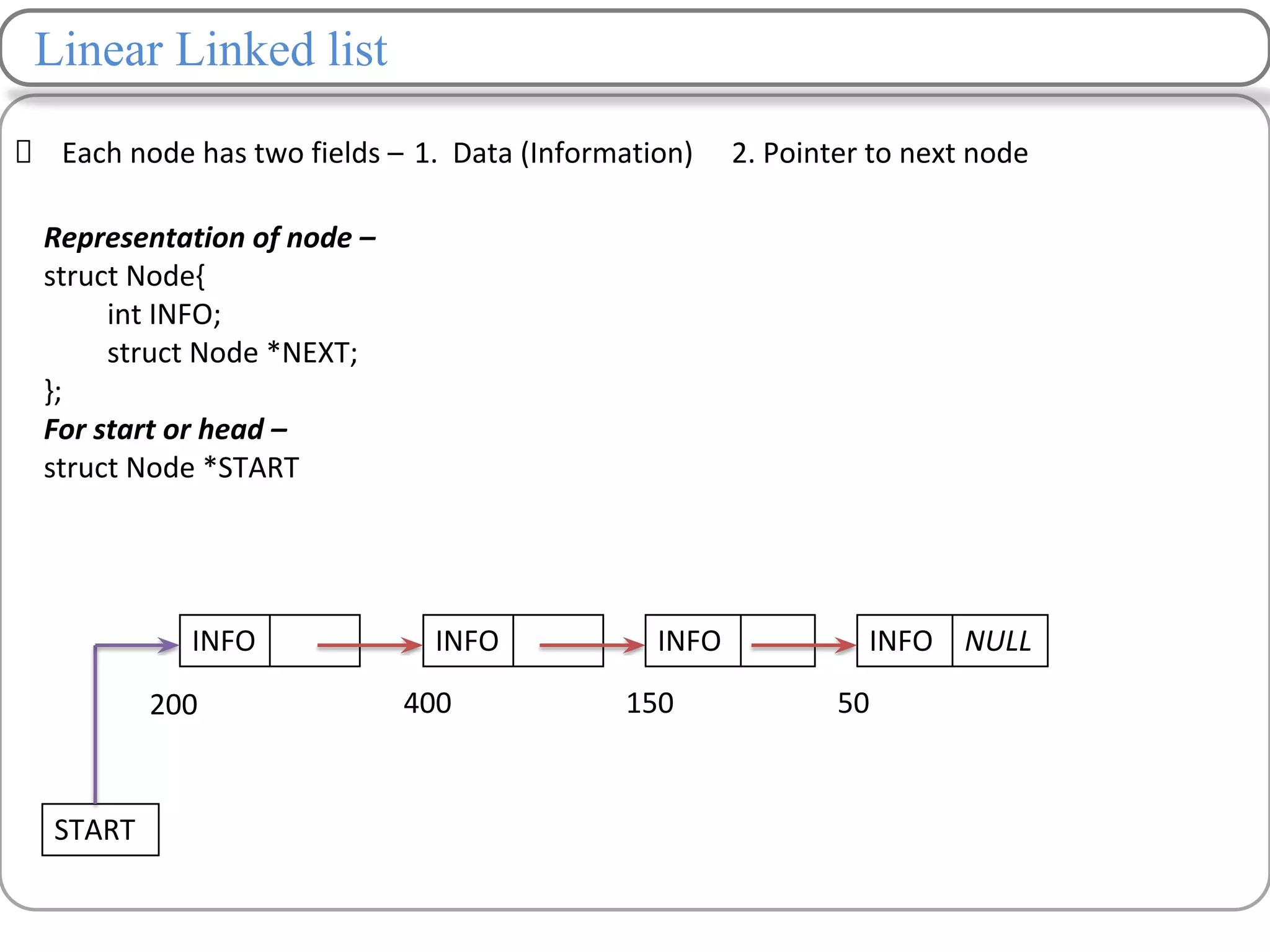
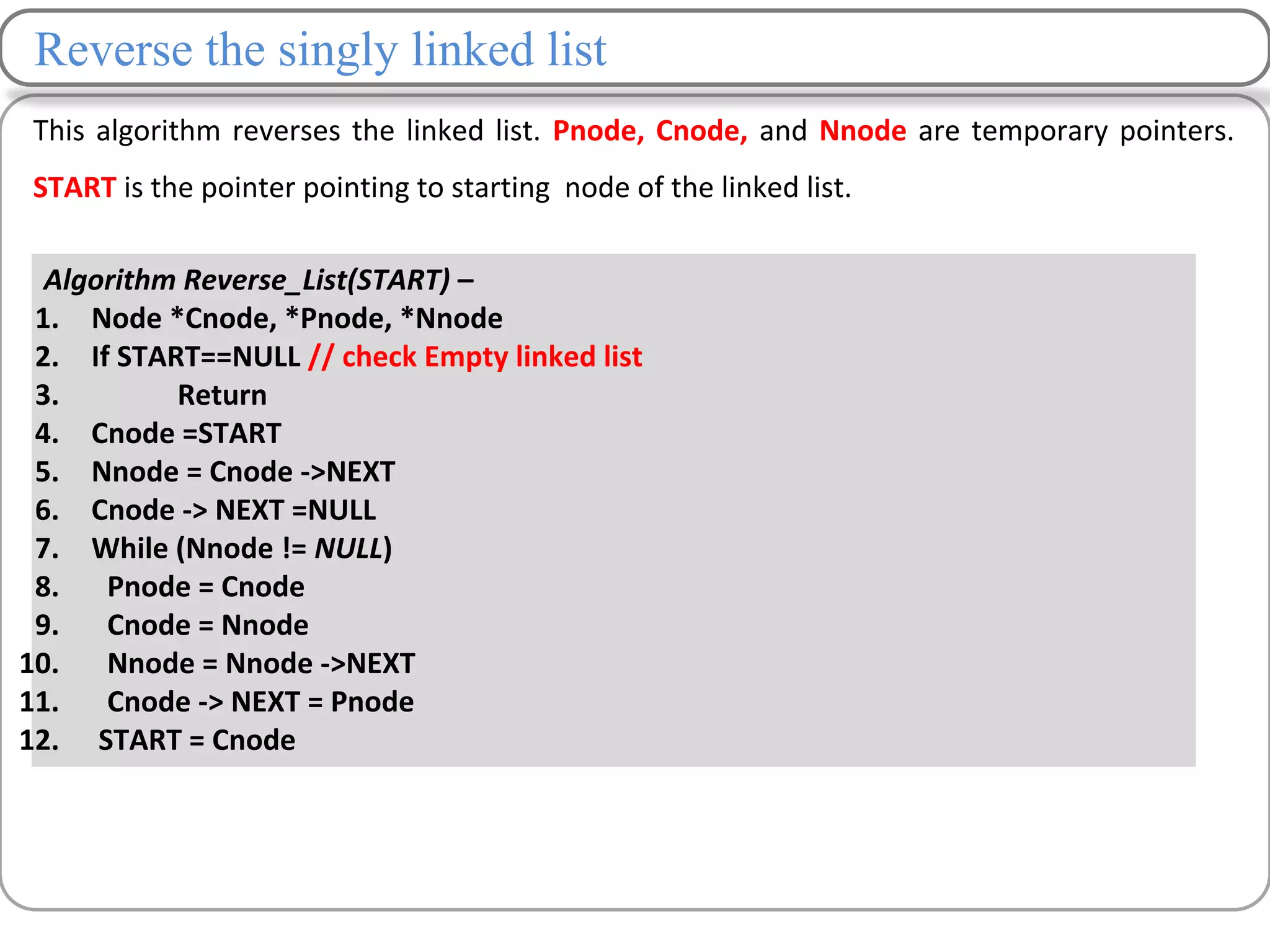
Linked lists are a data structure that store elements non-contiguously in memory. Each element, called a node, contains data and a pointer to the next node. There are several types of linked lists including singly linked lists where each node has a next pointer, doubly linked lists where each node has next and previous pointers, and circular linked lists where the last node points to the first. Common operations on linked lists include traversing, inserting nodes, deleting nodes, and searching for elements. Insertion and deletion have lower time complexity than arrays since they only require updating pointers rather than shifting elements.






![Arrays Vs. Linked List
Array Linked List
Elements stored at contiguous memory
locations.
Elements stored at discrete memory
locations.
Size of array is static and can not be
changed at later stage if need arise.
No fixed size, can grow and shrink very
efficiently
Array elements can be randomly accessed
using subscript variable.
e.g. a[0],a[1],a[3] etc.
Random access of any node is not possible
in linked list we have to traverse through
the linked list for accessing element. So O(n)
time is required for accessing particular
element .
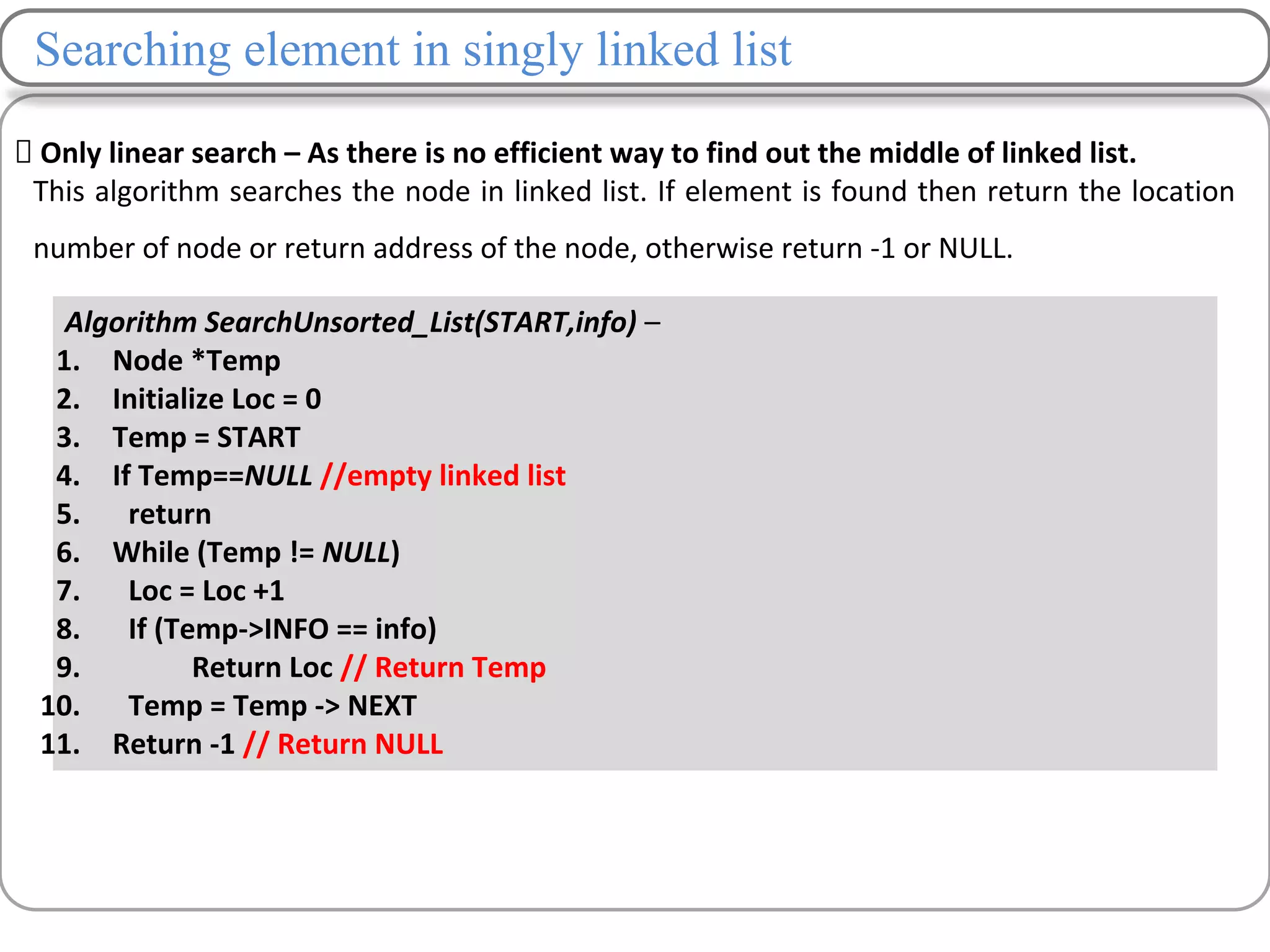
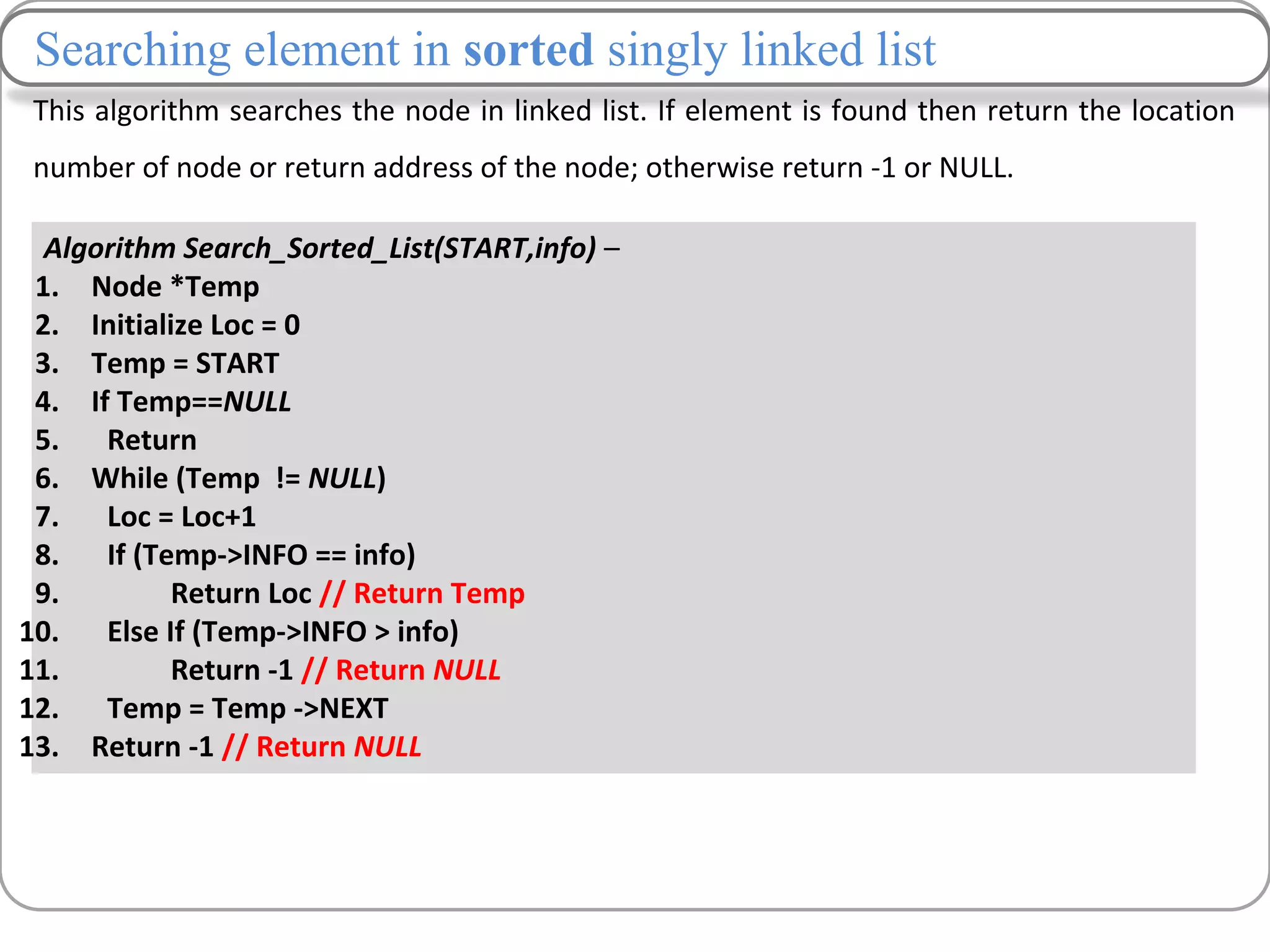
Searching –
Unsorted list – Linear O(n)
Sorted list – Binary O(log2
n)
Searching – Only Linear O(n)
Insertion –
Shift all element one position right,
Less efficient than in linked list
Insertion –
Only some pointers need to be managed,
more efficient than in array
Deletion – Shift all element one position
left, Less efficient than in linked list
Deletion – Only some pointers need to be
managed, more efficient than in array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linkrdlist-230505162054-8d08d632/75/linkrd_list-pdf-19-2048.jpg)