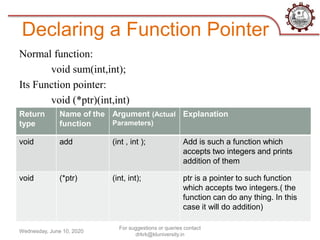
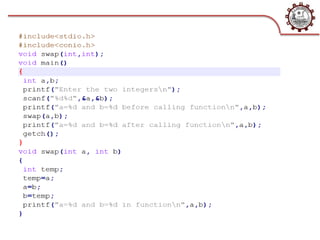
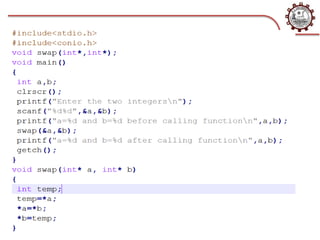
This document discusses function pointers, call by value, and call by reference. It defines a function pointer as storing the address of a function. It explains the steps to declare a function pointer and provides an example. It then describes call by value as copying the value of actual parameters into formal parameters, so changes within the function are not reflected in the original variables. Finally, it defines call by reference as passing the reference/address of the original variable, allowing the function to directly modify the original data.