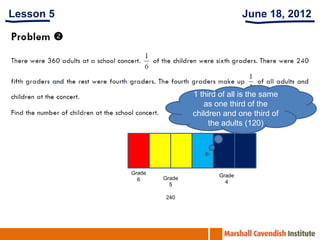
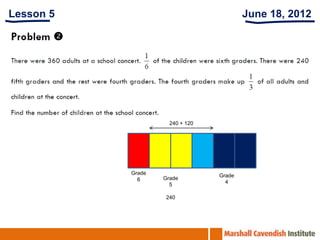
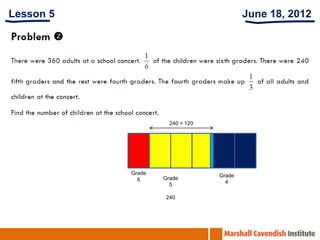
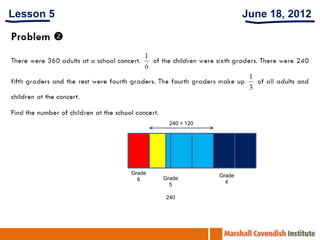
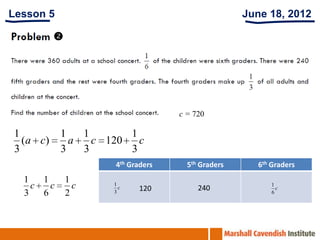
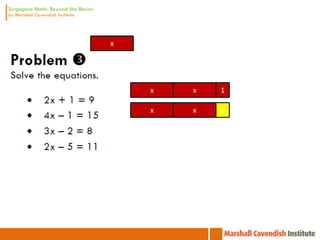
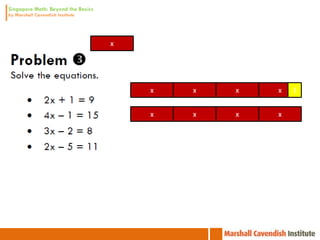
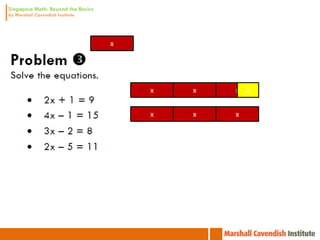
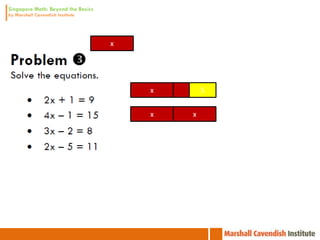
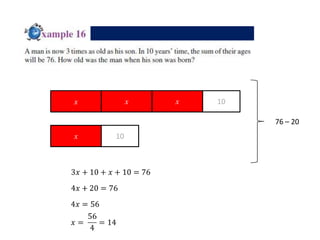
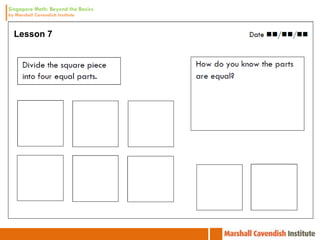
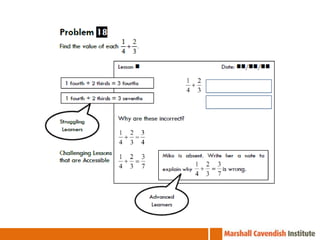
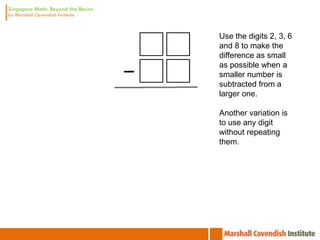
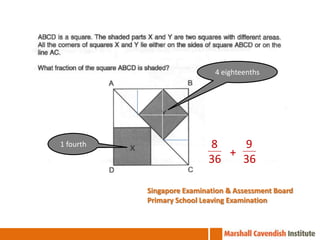
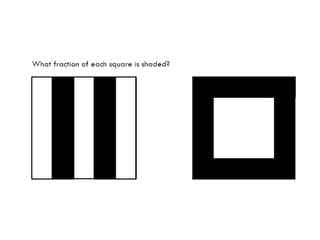
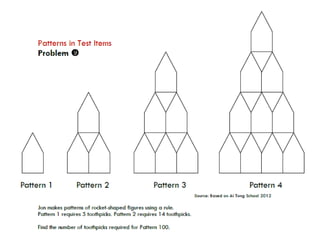
1. The document is a series of slides from Dr. Yeap Ban Har about teaching mathematics concepts like fractions, word problems, and patterns.
2. It provides examples of lessons, activities, and strategies to help students who struggle with math representation and word problems.
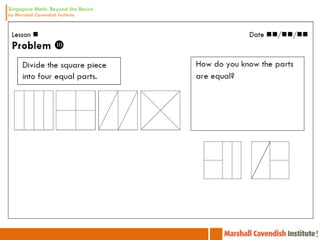
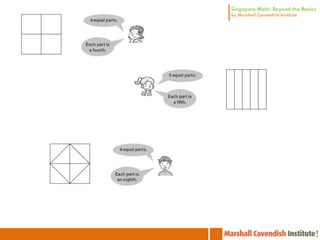
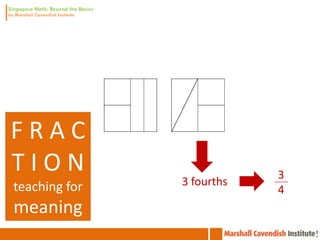
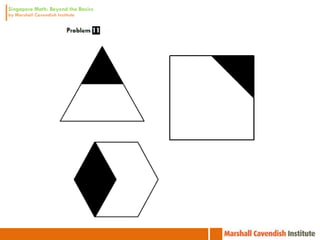
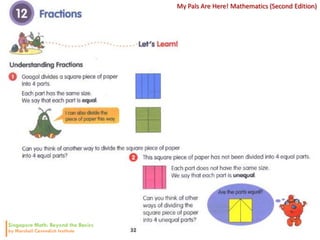
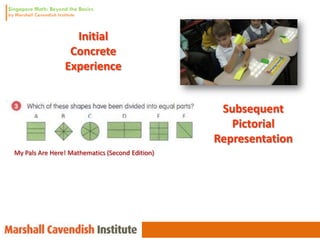
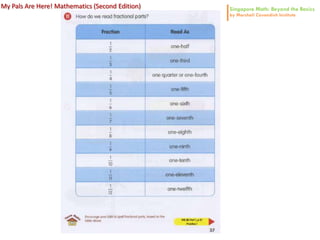
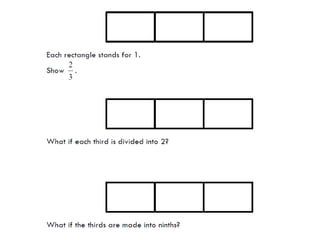
3. The lessons demonstrate concrete, pictorial, and abstract approaches to teach fractions as well as differentiation techniques.