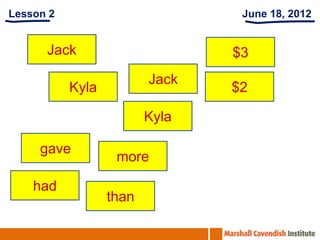
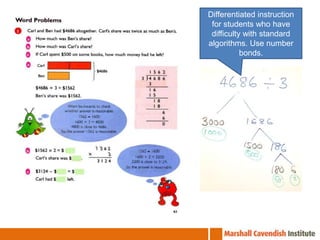
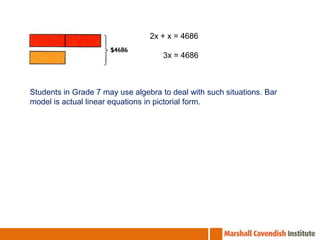
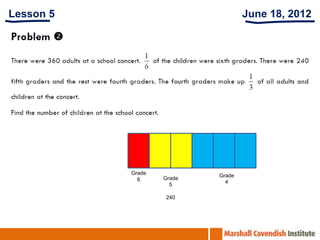
The document summarizes lessons from a workshop on the Singapore Math approach held at St Edward's School in Florida. It provides an overview of the Singapore education system and curriculum. It then summarizes 5 lessons that were observed which demonstrate the Singapore Math approach of using visual models and thinking strategies to teach basic math concepts and solve word problems. The lessons focused on multiplication facts, bar modeling techniques, and differentiated instruction strategies to help struggling students.