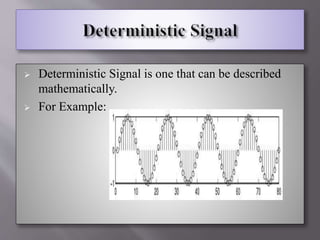
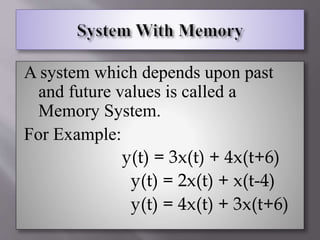
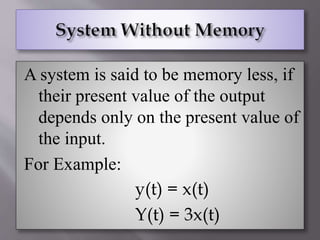
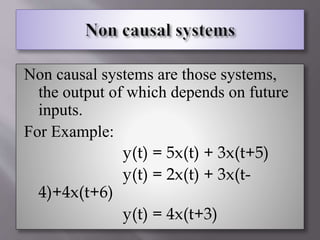
This document defines and provides examples of various types of signals and systems. It discusses continuous and discrete time signals, even and odd signals, deterministic and random signals, periodic and aperiodic signals. It also defines linear and nonlinear systems, time invariant systems, causal and non-causal systems, memory and memoryless systems, and stable and unstable systems. Examples are provided for each type of signal and system defined.