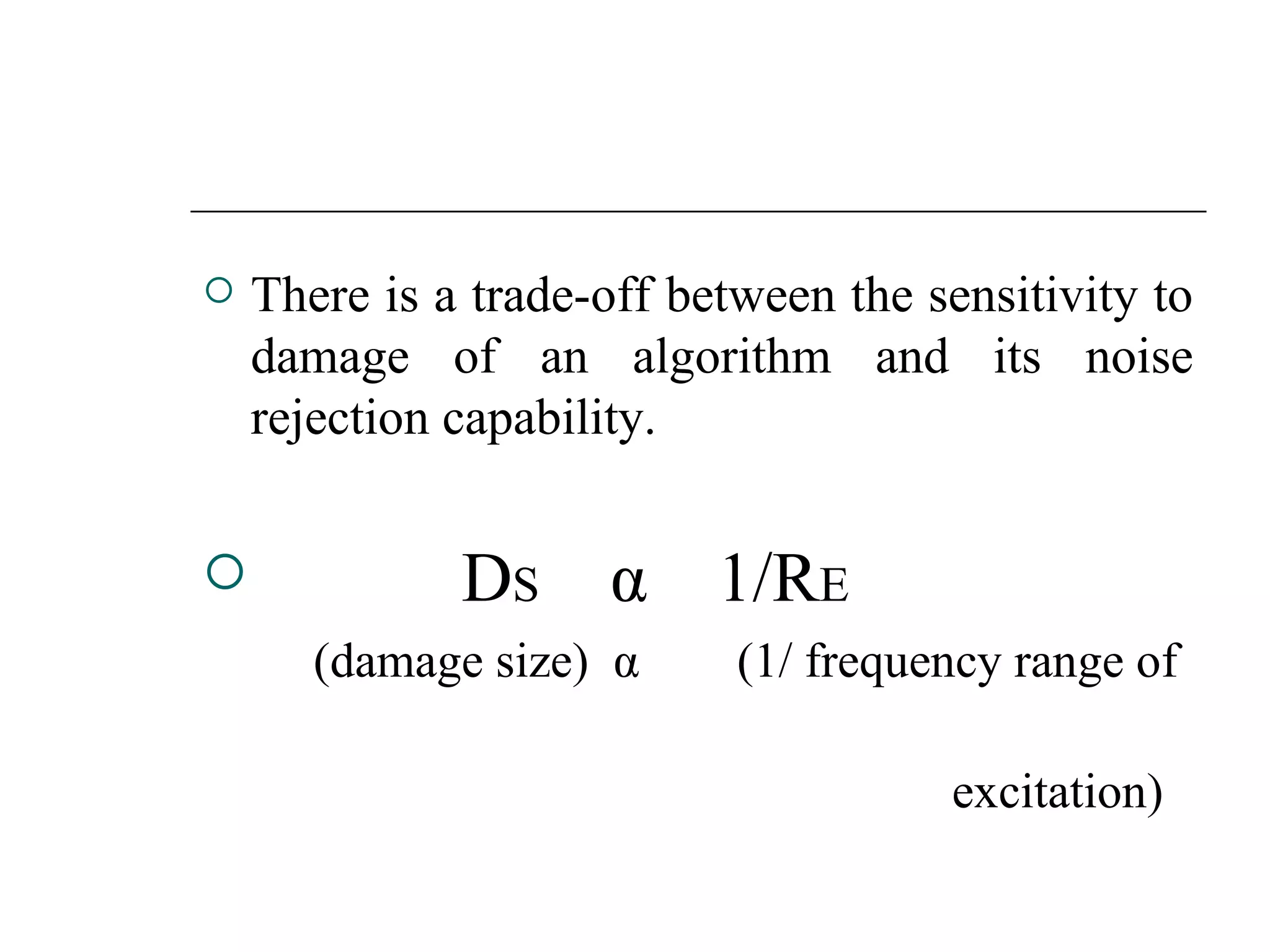
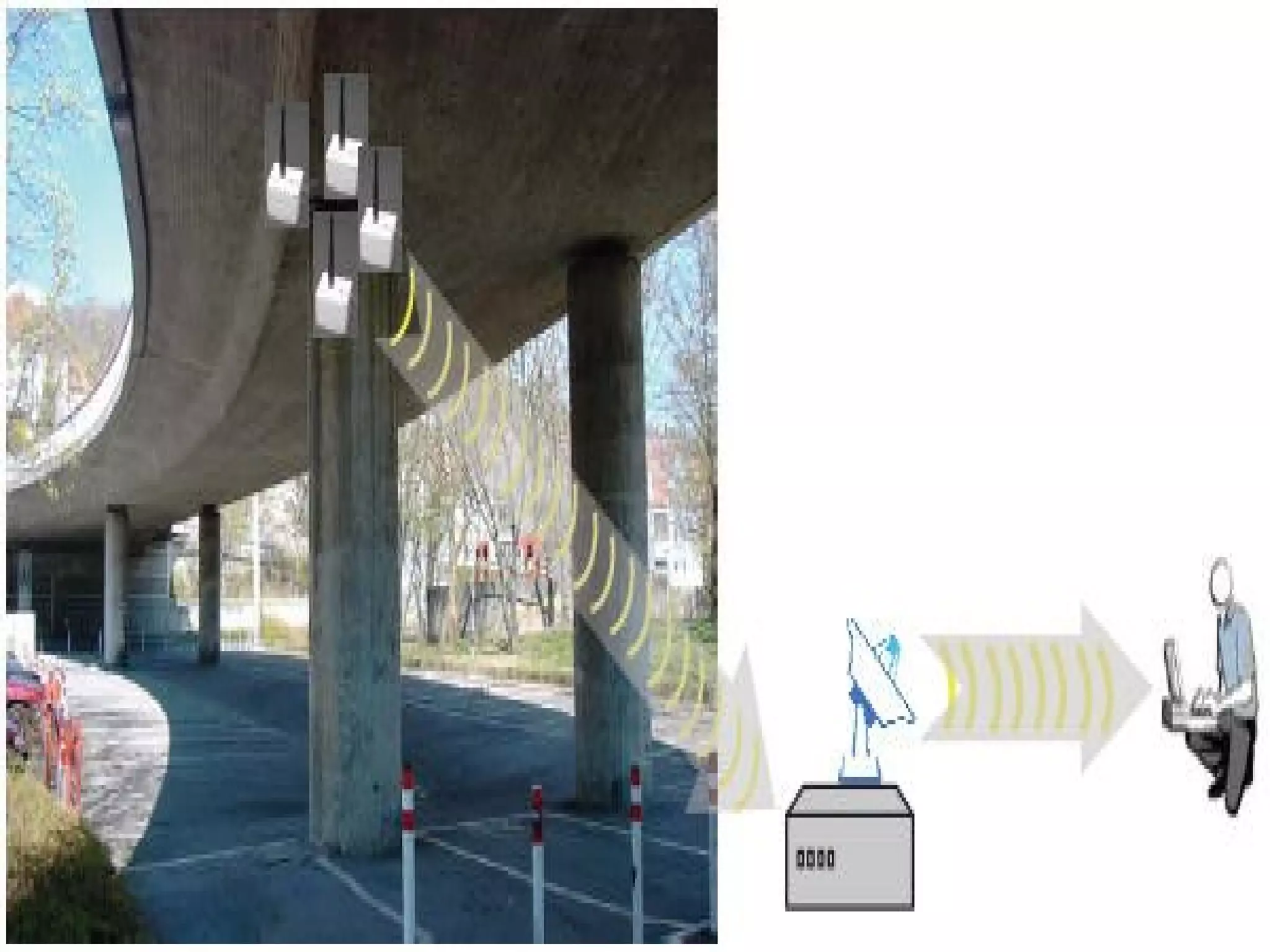
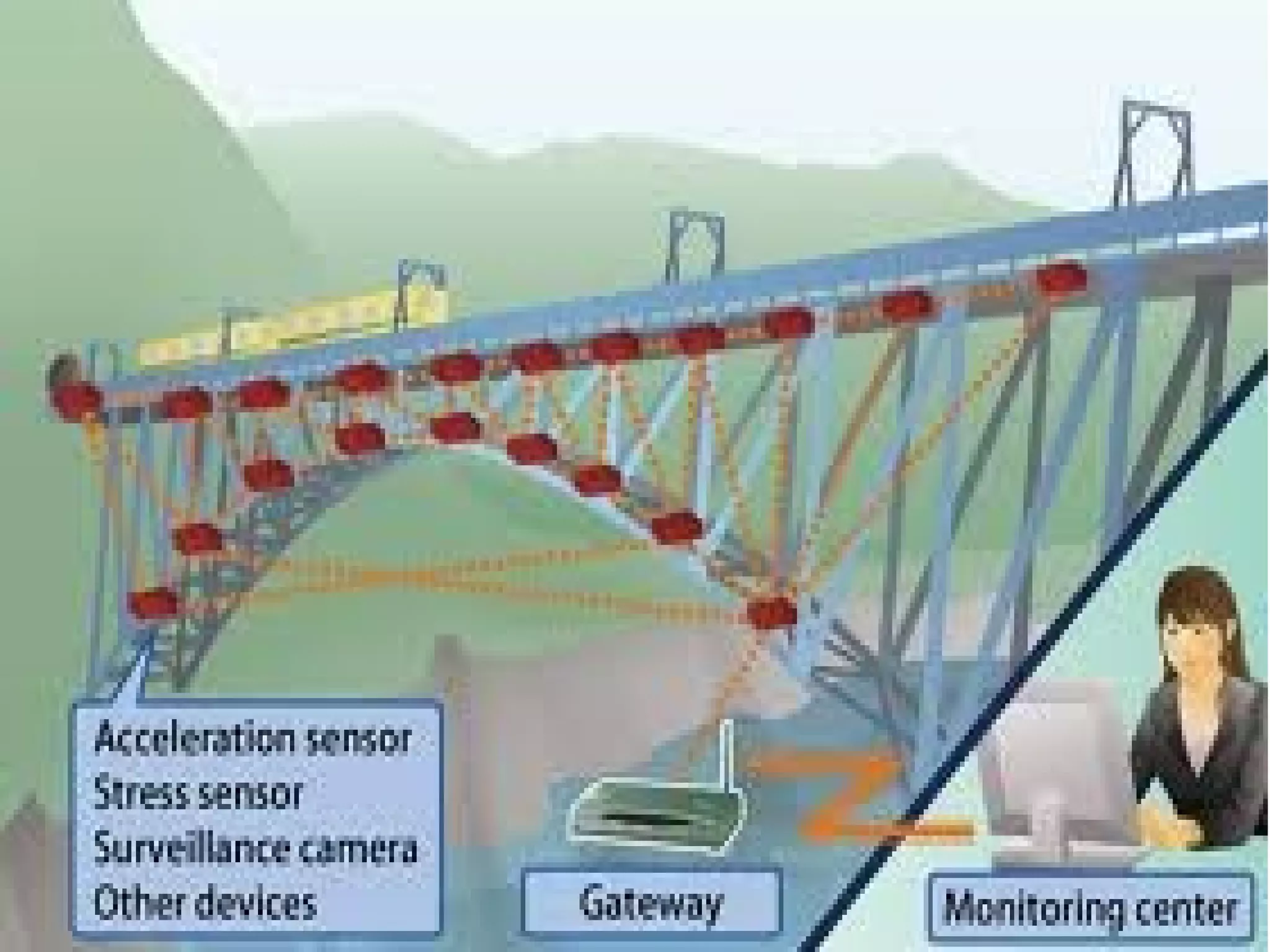
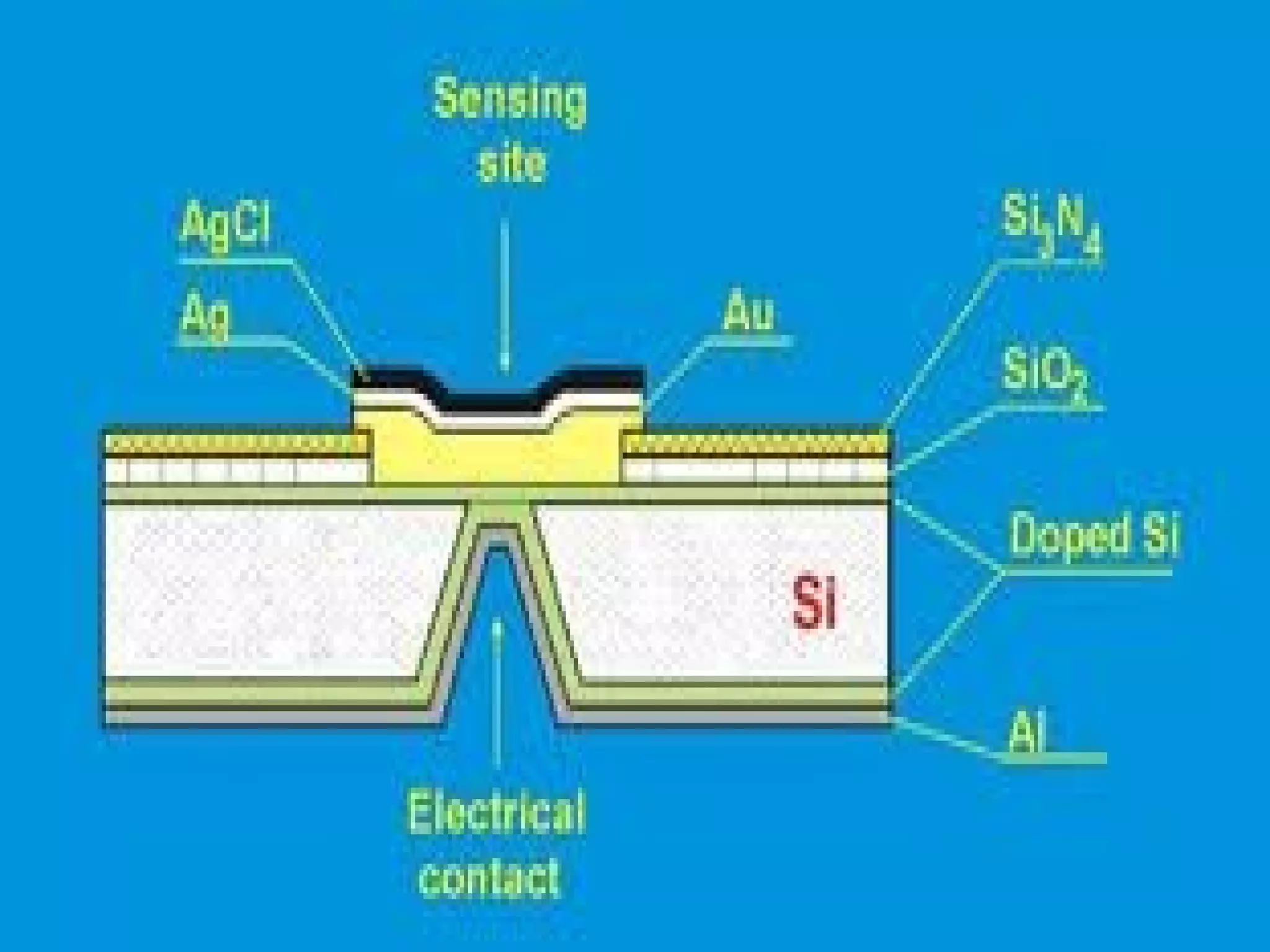
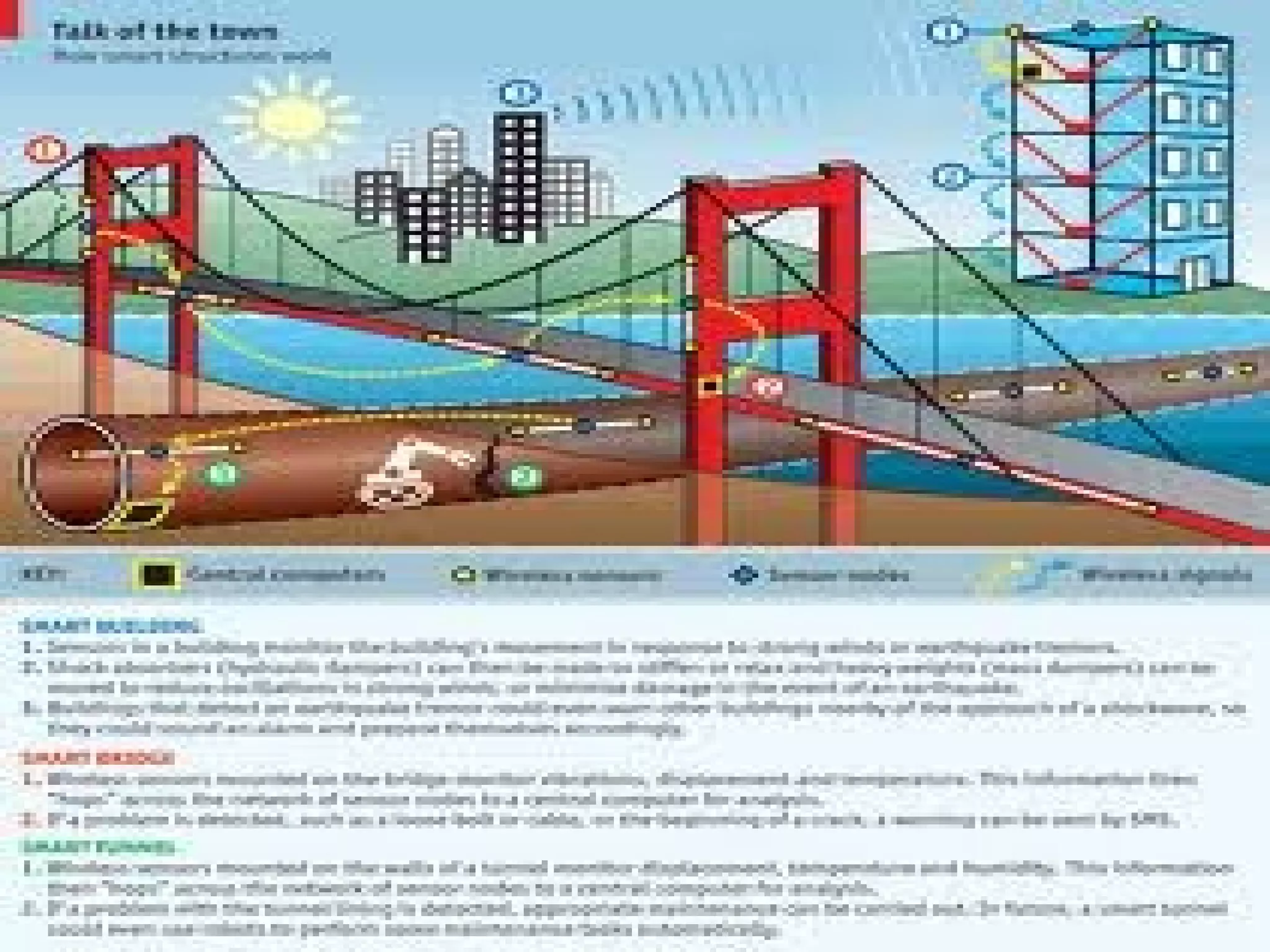
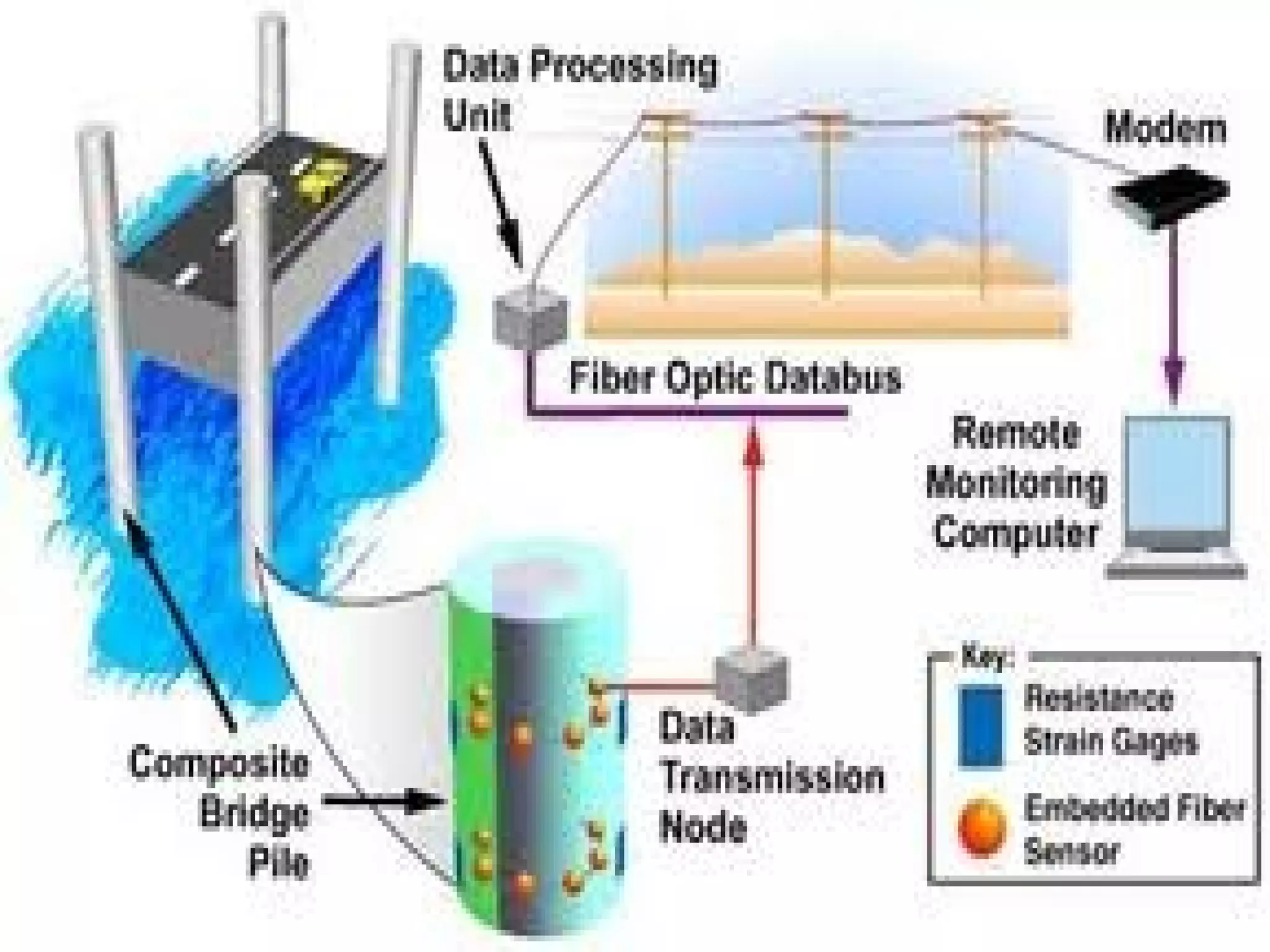
Structural health monitoring (SHM) involves implementing a strategy to detect and characterize damage in engineering structures. It uses sensors to measure structures, data acquisition systems to collect sensor readings, and data processing techniques like feature extraction and statistical modeling to determine whether damage is present. SHM is important as it improves structural safety and functionality by enabling timely warning of failures and more cost-effective maintenance through condition-based monitoring and assessment.