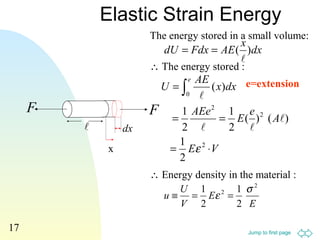
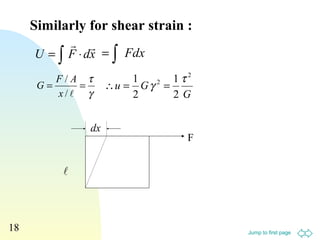
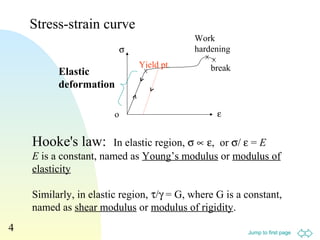
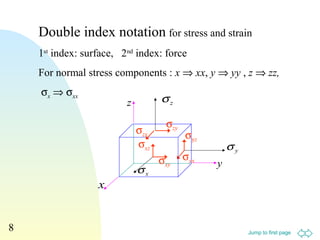
1. The document discusses concepts in mechanics of materials including stress, strain, elastic deformation, stress-strain curves, shear stress, normal stress, Poisson's ratio, and elastic strain energy.
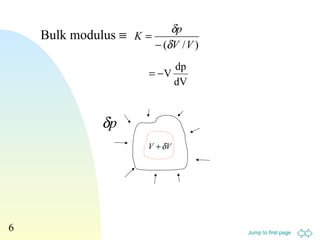
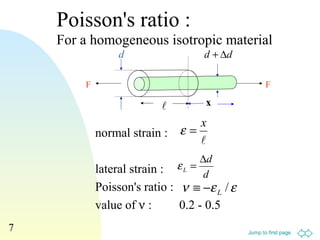
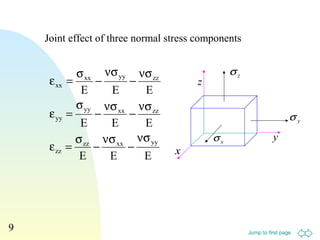
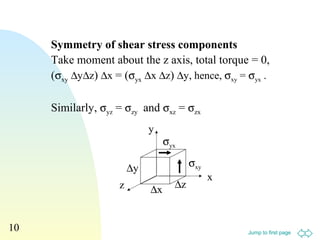
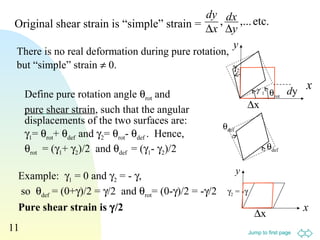
2. Various equations are presented for calculating stress, strain, elastic moduli like Young's modulus, shear modulus, and bulk modulus.
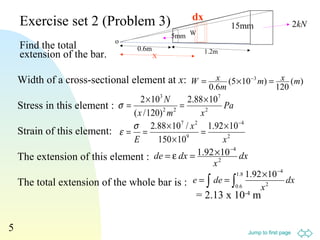
3. Examples are provided to demonstrate relationships between stress and strain components, normal and shear strains, and derivation of equations for elastic moduli.
![Jump to first page
1
dA
dF
A
F
A
==
→ δ
δ
σ
δ 0
lim
Normal stress = [ ] )Pa(pascalm/N
A
Force 2
≡σ
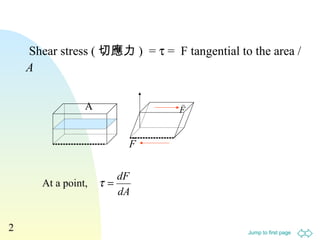
Chapter 2 Mechanics of Materials
Example: Estimate the normal stress on a shin bone ( 脛骨
)
AF
F
F
F
F
F
Tensile stress (+)
F
F
Compressive stress (-)
At a point:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shear-140719032103-phpapp02/85/Shear-1-320.jpg)
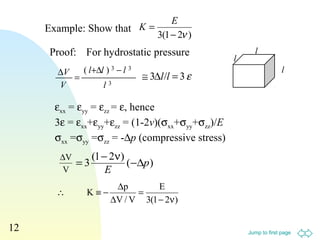
![Jump to first page
13
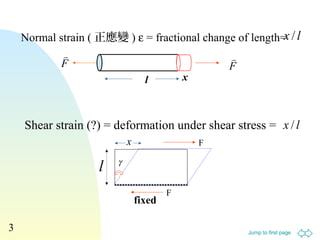
Point C moves further along x- and y-direction by distances
of AD(γ/2) and AD(γ/2) respectively.
εnn = [(AD . γ/2)2
+ (AD . γ/2)2
]1/2
/ [(AD)2
+ (AD)2
]1/2
= γ/2
True shear strain: εyx = γ/2
Therefore, the normal component of strain is equal to the
shear component of strain:
εnn = εyx and εnn = γ/2
Example : Show that εnn = γ/2
2/γ x
y
A
C’
C
D
D’2
γ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shear-140719032103-phpapp02/85/Shear-13-320.jpg)
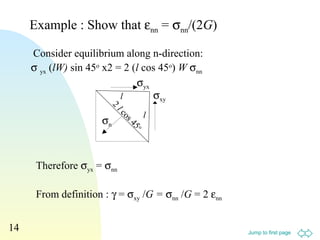
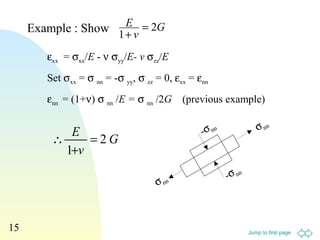
![Jump to first page
16
Ex. 12 kN forces are applied to the top
& bottom of a cube (20 mm edges), E =
60 GPa, ν = 0.3. Find (i) the force
exerted by the walls, (ii) εyy
z
y
12kN
x
(ι) εxx = 0, σyy = 0 and
σzz= -12×103
N/(20×10-3
m)2
= 3×107
Pa
εxx = (σxx- v σyy- v σzz) /E
0 = [σxx- 0 – 0.3×(- 3×107
)]/60×109
∴ σxx = -9×106
Pa (compressive)
Force = Aσxx = (20×10-3
m)2
×(-9×106
Pa) = -3.6 ×103
N
(ii) εyy = (σyy- v σzz- v σxx) /E
= [0 – 0.3×(- 3×107
) – 0.3×(- 9×106
)]/60×109
= 1.95×10-4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shear-140719032103-phpapp02/85/Shear-16-320.jpg)