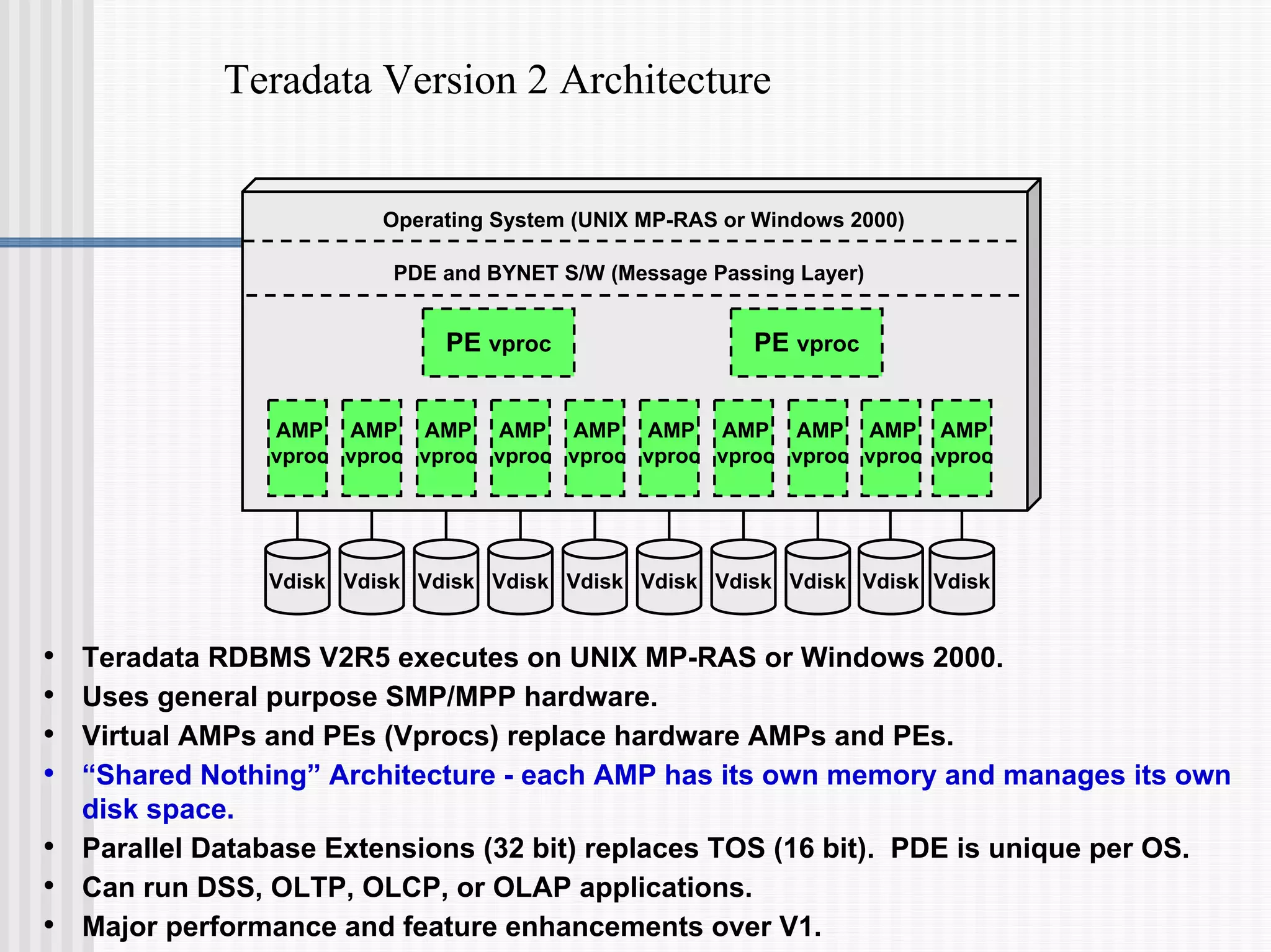
- Teradata Version 2 introduced a software-based architecture where physical AMPs and PEs were replaced with virtual processors (vprocs). This allowed Teradata to run on general purpose hardware and different operating systems.
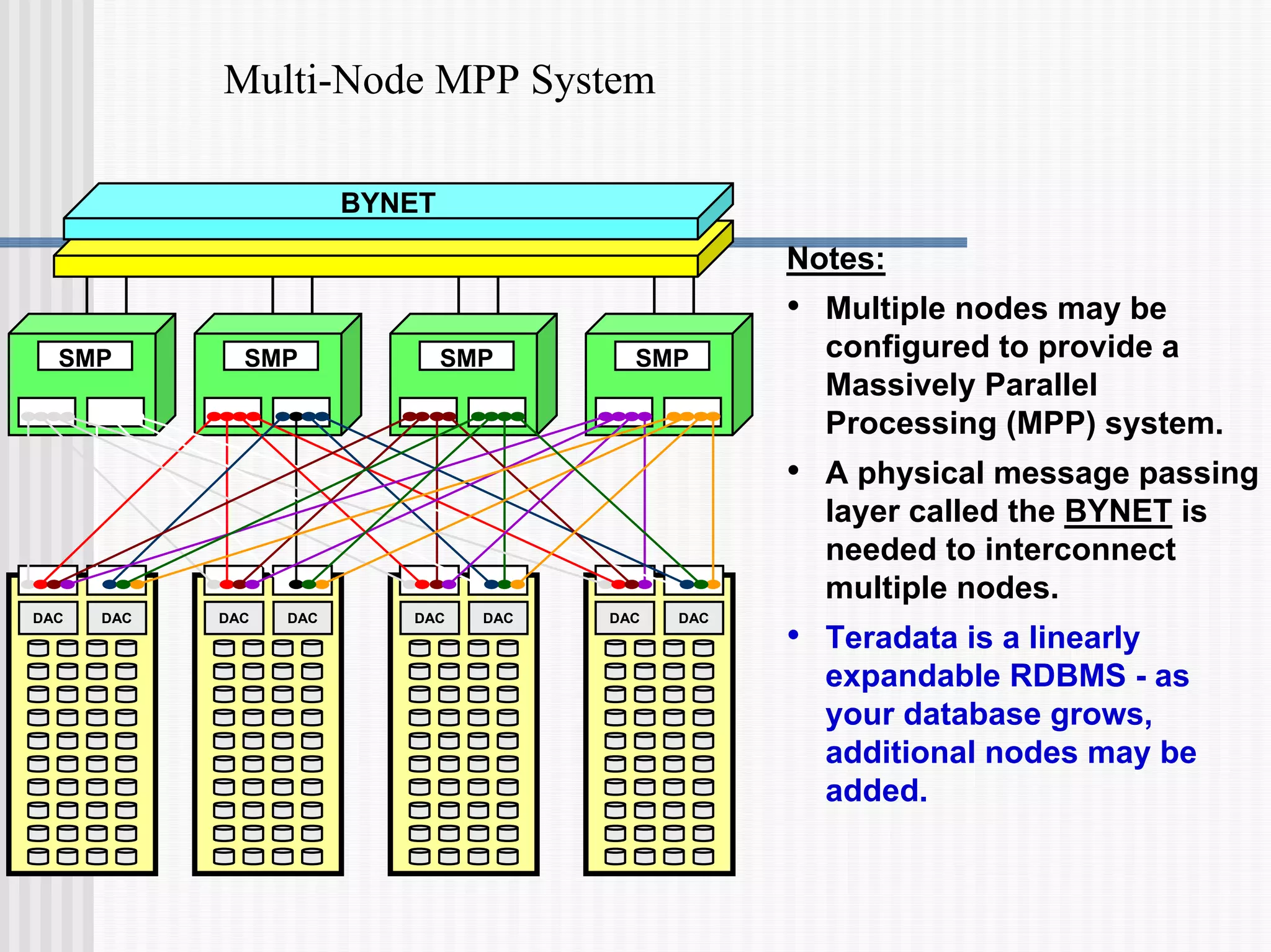
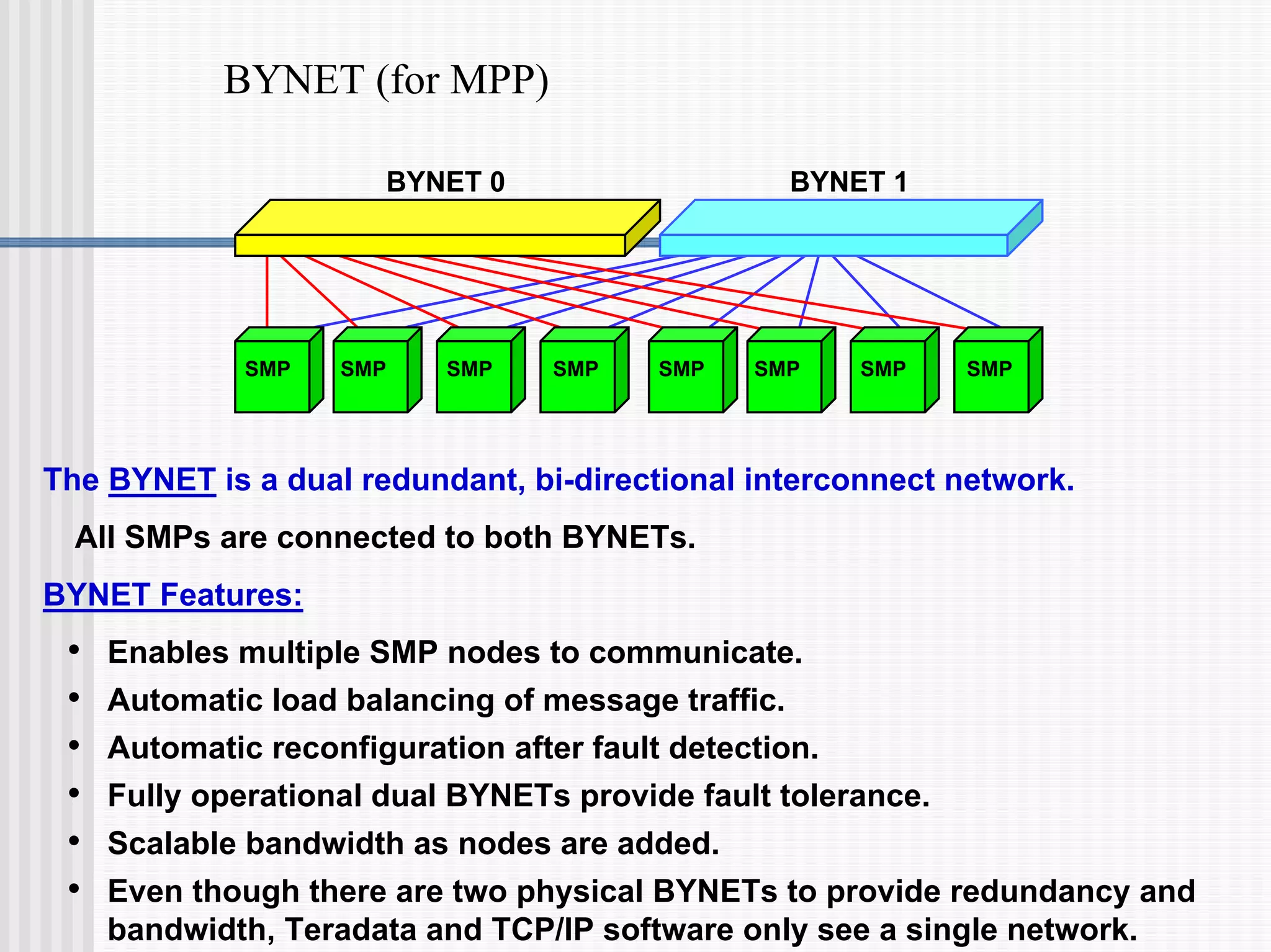
- Teradata uses a "shared nothing" architecture where each AMP has its own memory and disk space. Multiple nodes can be connected with a physical BYNET interconnect to form a massively parallel processing (MPP) system.
- A clique is a group of nodes that share disk arrays, providing protection against node failures by allowing vproc migration to remaining nodes.