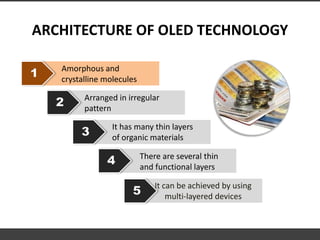
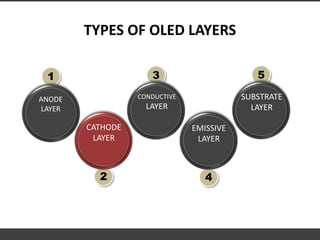
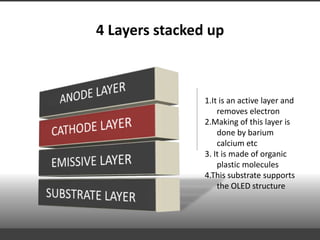
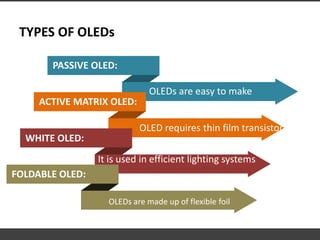
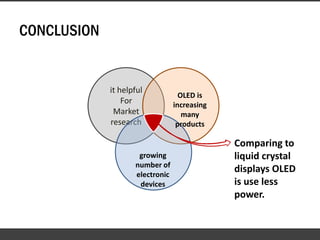
This document provides information about organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs). It discusses the basic principles and architecture of OLED technology. The key components of an OLED including the anode layer, cathode layer, conductive layer and emissive layer are described. The document also outlines how OLEDs work and the different types, including passive OLEDs, active matrix OLEDs, white OLEDs, and foldable OLEDs. Finally, some applications of OLED display technology are listed such as in TVs, cell phones, computers and more.