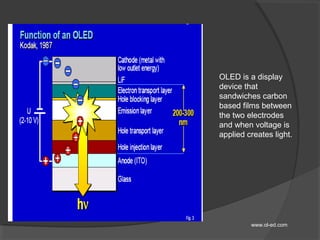
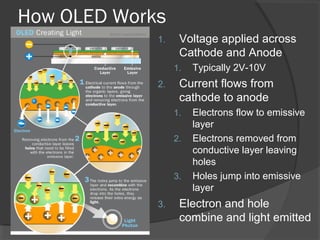
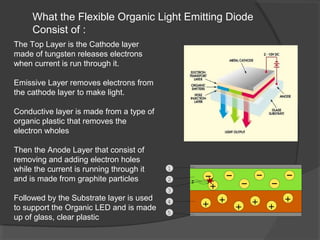
OLED (organic light-emitting diode) is a light-emitting diode that uses organic compounds which emit light in response to an electric current. It consists of a cathode, an emissive layer, a conductive layer, and an anode, sandwiched between two electrodes. When voltage is applied, electrons flow to the emissive layer where they combine with holes to emit light. OLEDs have advantages over LCDs like being thinner, more flexible, requiring less power, and producing higher resolution and faster switching speeds. However, OLEDs also have shorter lifetimes and are more expensive than LCDs.