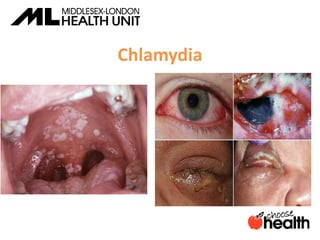
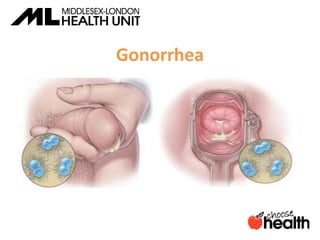
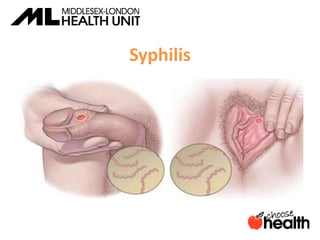
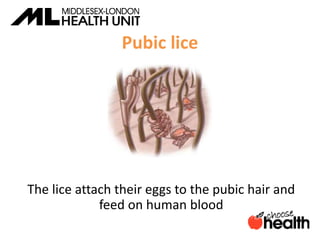
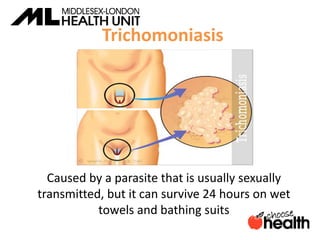
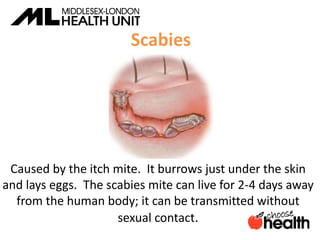
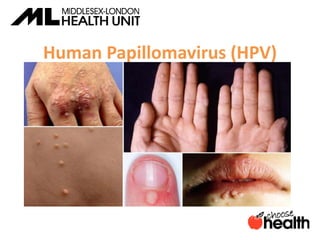
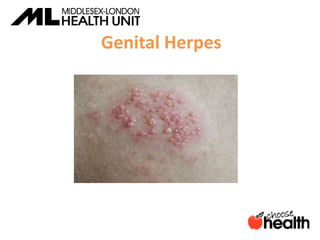
This document provides information about sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including common bacterial, parasitic and viral STIs. It discusses symptoms, testing, and treatment for STIs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, pubic lice, trichomoniasis, herpes, hepatitis, HIV and HPV. The document emphasizes that abstinence is the only 100% effective way to prevent STIs, but practicing safer sex through proper condom or barrier use can help lower risks if one chooses to be sexually active. It encourages open communication with partners and maintaining sexual health through education.