This document defines and explains basic concepts in set theory, including:
- A set is a collection of distinct objects considered as a single object. Set theory was developed in the 19th century and is now fundamental to mathematics.
- German mathematician Georg Cantor created set theory and proved that real numbers are more numerous than natural numbers. He defined cardinal and ordinal numbers.
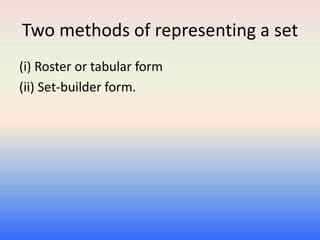
- Sets can be represented through rosters or the set-builder form. A set is finite if it has a definite number of elements, infinite otherwise. Two sets are equal if they contain the same elements.












![Intervals
• The set of real numbers
• { y : a < y < b} is called an open interval and is
denoted by (a, b).
• The interval which contains the end points
also is called closed interval and is denoted by
[ a, b ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sets-200603064149/85/Sets-14-320.jpg)











