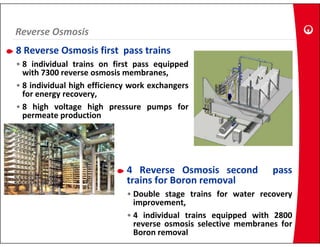
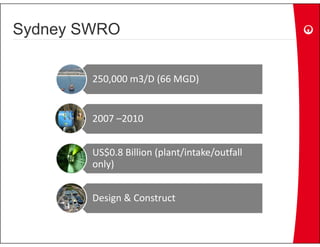
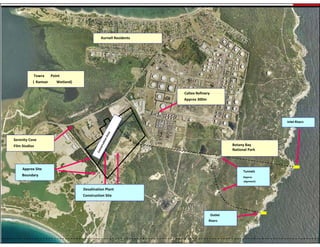
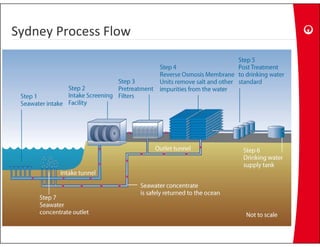
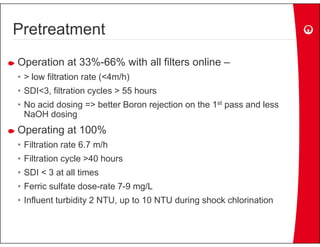
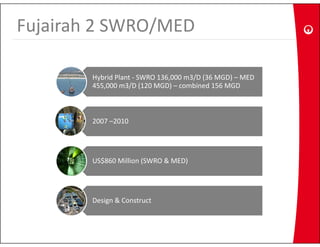
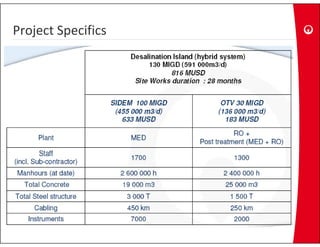
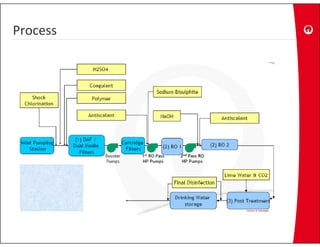
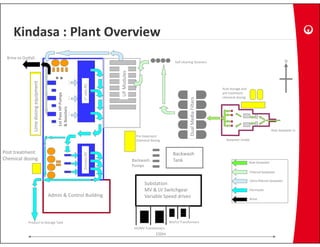
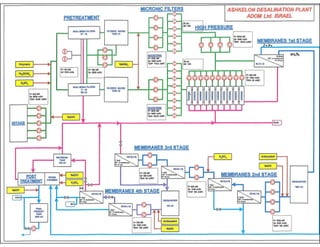
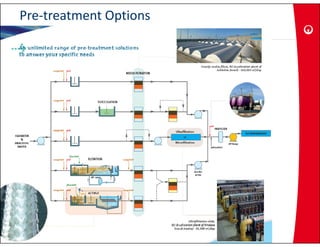
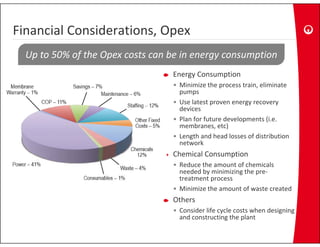
This document provides information on the largest beach well seawater catchment facilities and desalination plant in the world. It includes details such as 32 vertical beach wells split into 3 clusters that can pump 220,000 cubic meters per day. It also describes the pretreatment, reverse osmosis, and post-treatment processes including 5 dual media pressure filters, 8 reverse osmosis first pass trains equipped with 7300 membranes, and 4 reverse osmosis second pass trains for boron removal using 2800 selective membranes. Plant diagrams and a 3D view are also included.