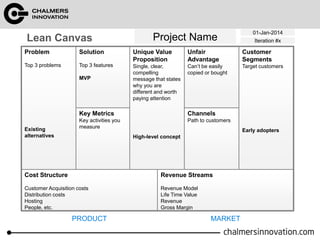
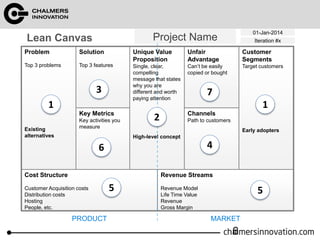
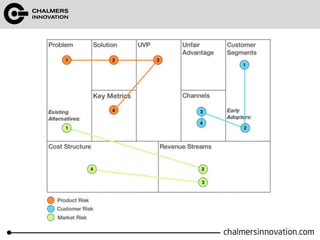
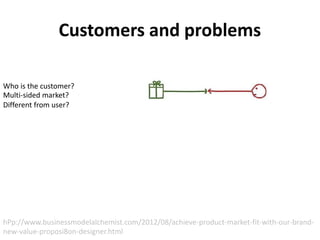
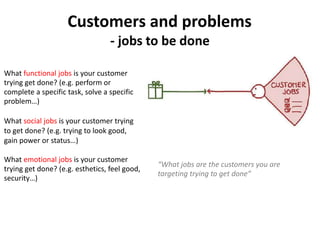
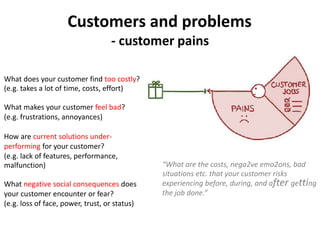
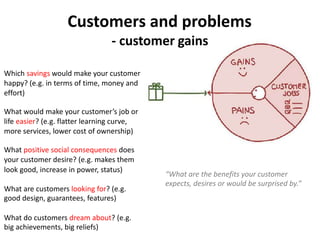
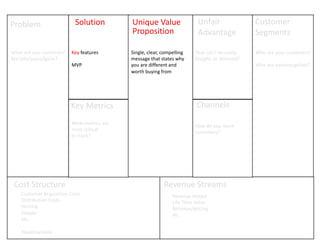
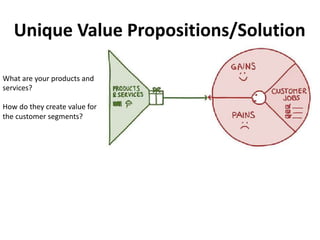
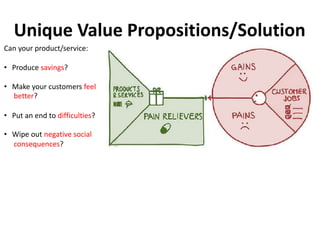
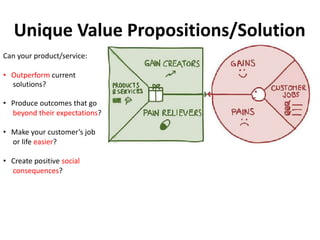
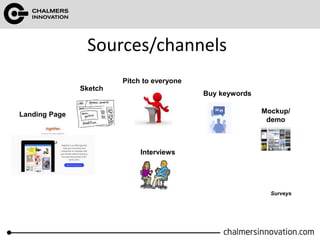
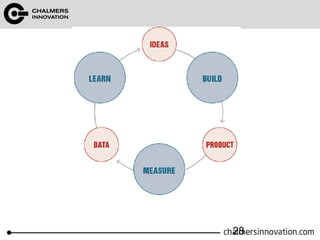
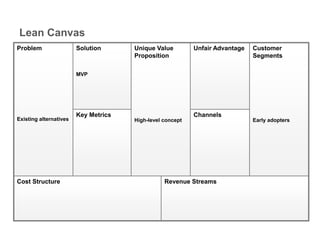
The document discusses the Lean Canvas and Value Proposition Canvas tools for startups. It explains that these tools help startups focus on understanding customer problems and developing solutions to those problems, rather than wasting time on full business plans. The Lean Canvas is used to map out key aspects of a startup idea including the customer segments, problems, solution, unique value proposition, channels, revenue streams, and costs. Understanding the customer's "jobs to be done" as well as their pains and gains is essential. The value proposition should communicate how the solution creates value by addressing these customer needs. Examples are provided and a workshop is outlined to help validate hypotheses.