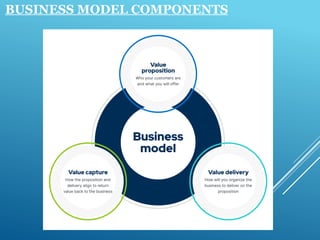
The document outlines the concept of a business model, highlighting its role as a profit-making plan that defines products, target markets, and costs involved. It details various types of business models such as retailers, manufacturers, and fee-for-service, while emphasizing the importance of gross profit and evaluation methods. Additionally, it covers components of effective business models, including vision, customer targets, pricing, and the distinction between business models and business plans.