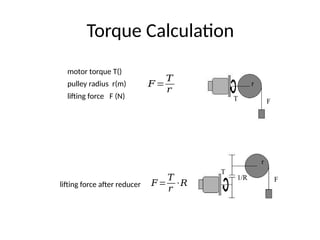
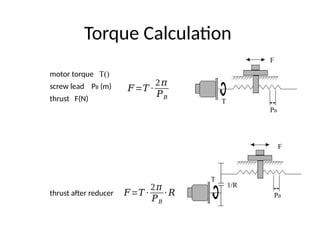
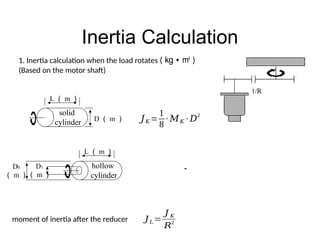
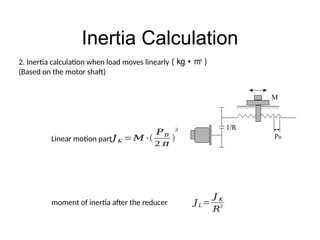
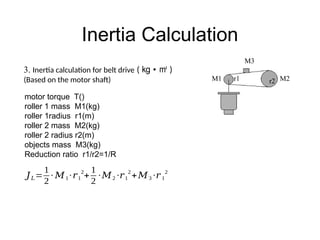
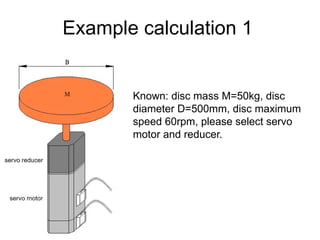
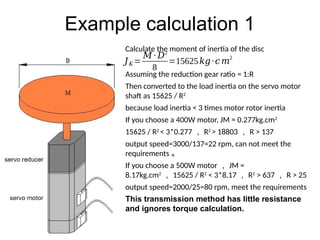
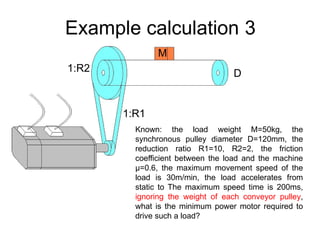
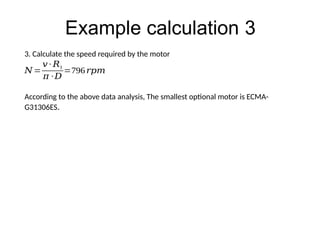
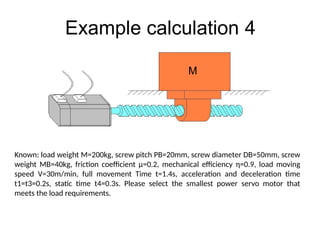
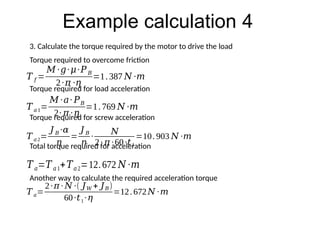
The document provides detailed calculations for torque and inertia in various mechanical systems involving motors, pulleys, and screws. It outlines the principles for servo motor selection and includes multiple example calculations to determine the necessary motor specifications based on load requirements and operational conditions. Key factors affecting motor performance, including load weight, transmission components, and efficiency, are also discussed.