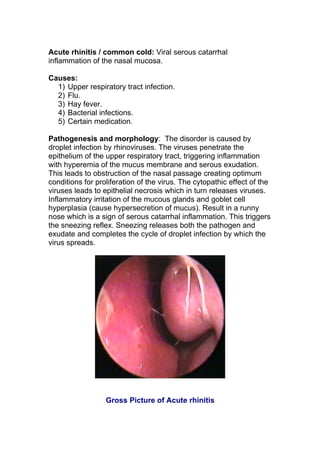
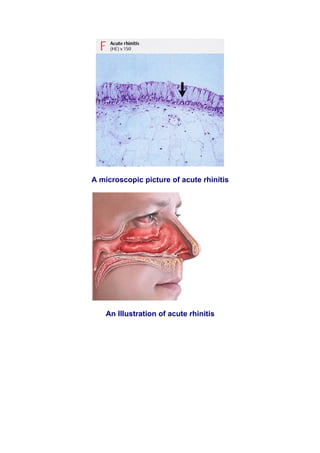
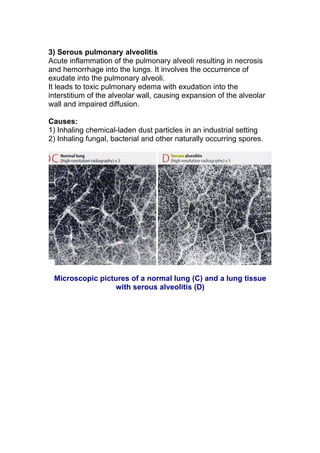
Serous inflammation is characterized by the effusion of non-viscous serous fluid rich in proteins but lacking white blood cells or neutrophils. This fluid dilution noxious agents and is produced by mesothelial cells lining body cavities. Examples include skin blisters, inflammation of body cavities like the pericardium and peritoneum, rheumatoid arthritis, and acute rhinitis or the common cold. Serous pulmonary alveolitis involves the accumulation of exudate in the pulmonary alveoli due to inhaled particles or spores.