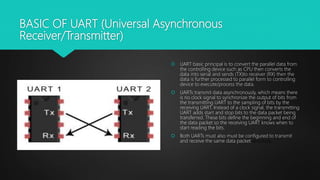
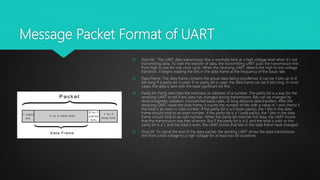
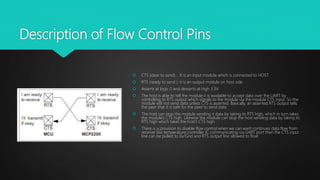
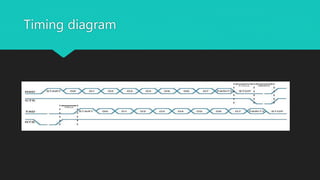
This document provides an overview of UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) serial communication. It describes the basic principles of UART including message packet formatting, baud rate, flow control pins, and modes of operation. The timing diagram and steps for performing UART communication are outlined. Advantages of UART include using only two wires for transmission and not requiring a clock signal. Disadvantages include limited data frame size and baud rates needing to be closely matched.