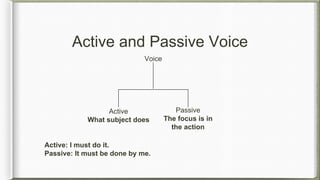
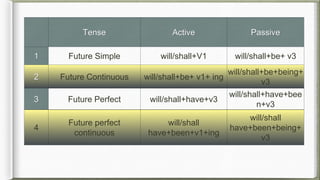
The document explains the differences between active and passive sentences, providing definitions and examples for transforming various tenses. It outlines the rules for constructing passive voice, including cases where the doer is unknown and how to handle imperative sentences. Additionally, it includes practice sentences and their passive forms, as well as notes on when to use specific prepositions.