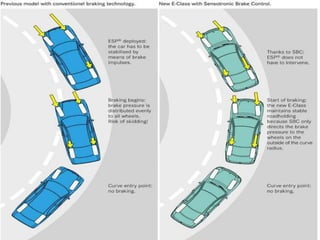
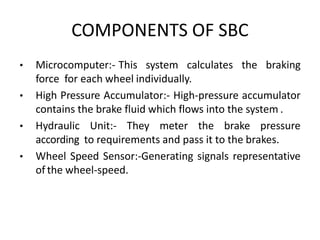
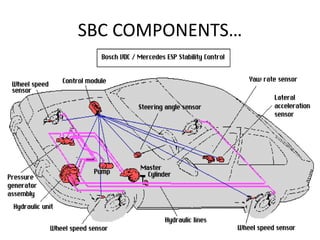
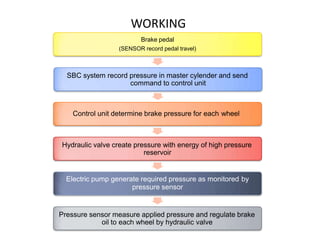
Sensotronic Brake Control (SBC) is an electronically controlled braking system that allows for faster and more precise braking than conventional hydraulic braking systems. SBC uses electronic sensors and controllers to monitor brake pedal input and wheel speeds and individually modulate brake pressure to each wheel. This provides for improved emergency braking, driving stability, braking comfort, and features like soft stops and hill hold. While SBC is more complex and expensive than traditional brakes, it paves the way for advanced driver assistance technologies and fully autonomous vehicles.