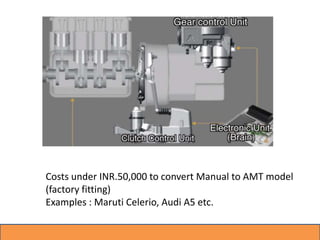
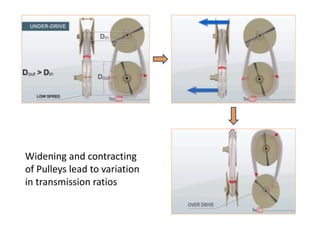
The document summarizes different types of automatic transmissions. It discusses torque converters, planetary gear sets, and four main types of automatic transmissions: traditional, automated manual, continuously variable, and dual clutch. A torque converter replaces a clutch to change gears hydraulically. Planetary gears provide gear reductions like underdrive and overdrive. Automated manual transmissions automate manual transmissions. Continuously variable transmissions use pulleys to provide infinite gear ratios. Dual clutch transmissions use two clutches to switch between gears more quickly.