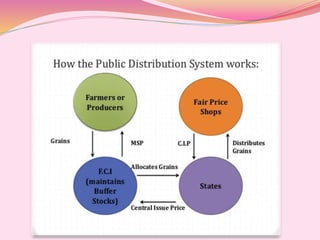
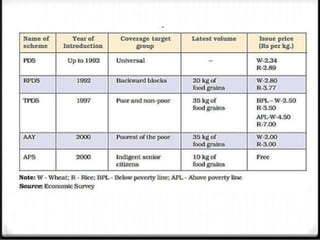
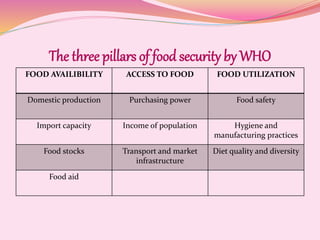
Food security is defined as having access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food. The FAO and WHO work to address food security globally. The FAO leads international efforts against hunger and India is a founding member. The WHO works on health issues and India joined in 1948. Definitions of food security have evolved over time to include availability, accessibility, affordability, and stability. The four pillars of food security are availability, access, utilization, and stability according to the FAO. India faces issues with over 200 million undernourished people and the government has implemented programs to address food security such as PDS, MDM, and employment guarantees.









![Present Scenario of FoodSecurity in India
India is home to more than 230 million undernourished people - 21%
population [FAO Report on The State of Food Insecurity in the World
2008’]
About 1/2 of the population suffers from chronic under-nutrition
especially Children, Women & Elderly (lower income groups)
The rise in food prices between 2005 and 2007 increased poverty by 3%
on an average. Extrapolating these results globally suggest that as a
result of the rise in food prices, total world poverty may have increased
by 73-105 million people [A recent study by World Bank -2008 in 8
countries]
The rising prices have increased 41 million hungry in Asia and 24
million hungry in Sub-Saharan Africa
Among the farmers, 84% are marginal and small farmers operating not
more than 2 hectares of land
States facing problem of food insecurity-Uttar Pradesh (eastern and
south-eastern parts), Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, West Bengal,
Chhattisgarh, parts of Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faonwho-190913093844/85/Fao-n-who-11-320.jpg)