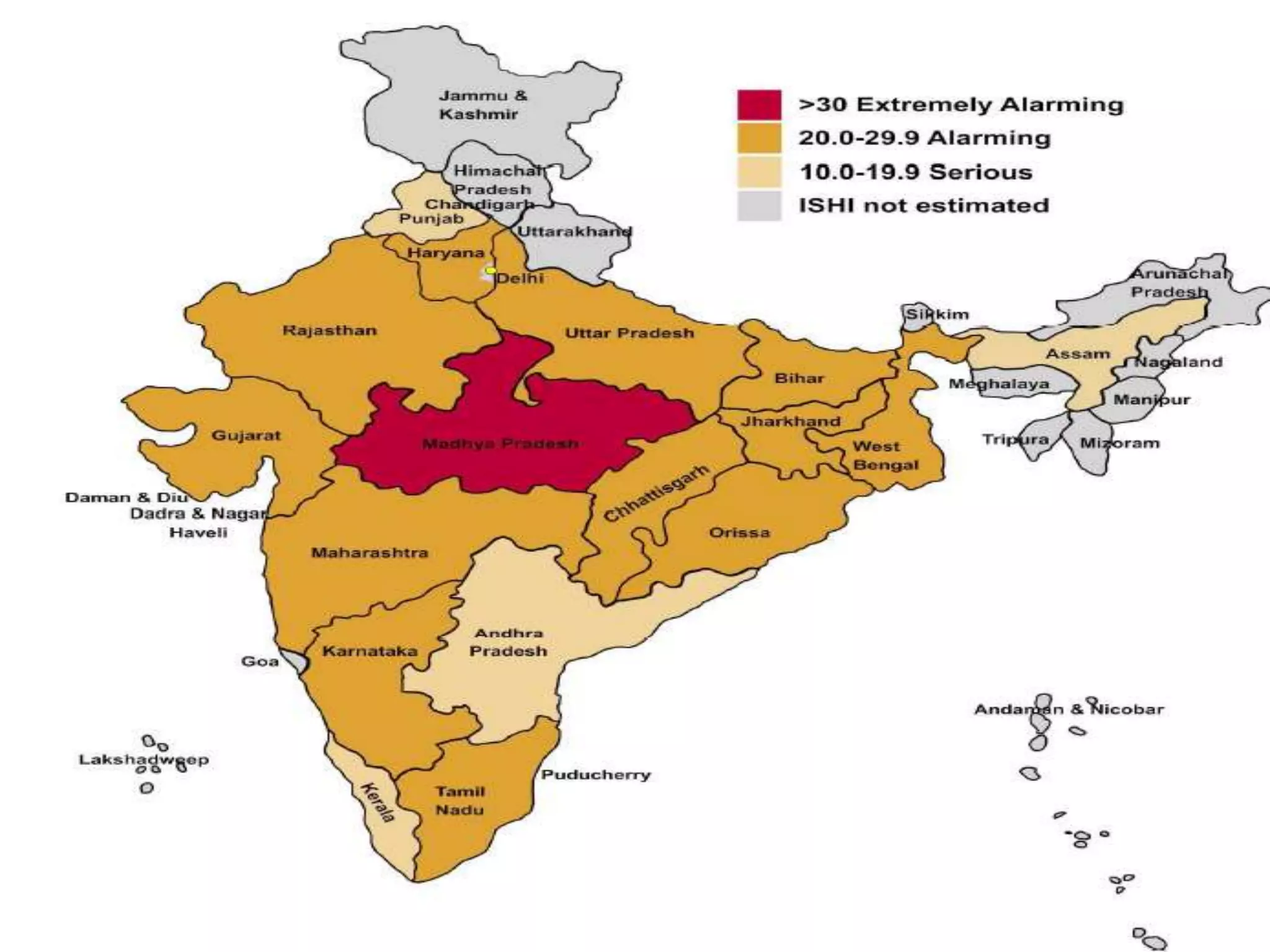
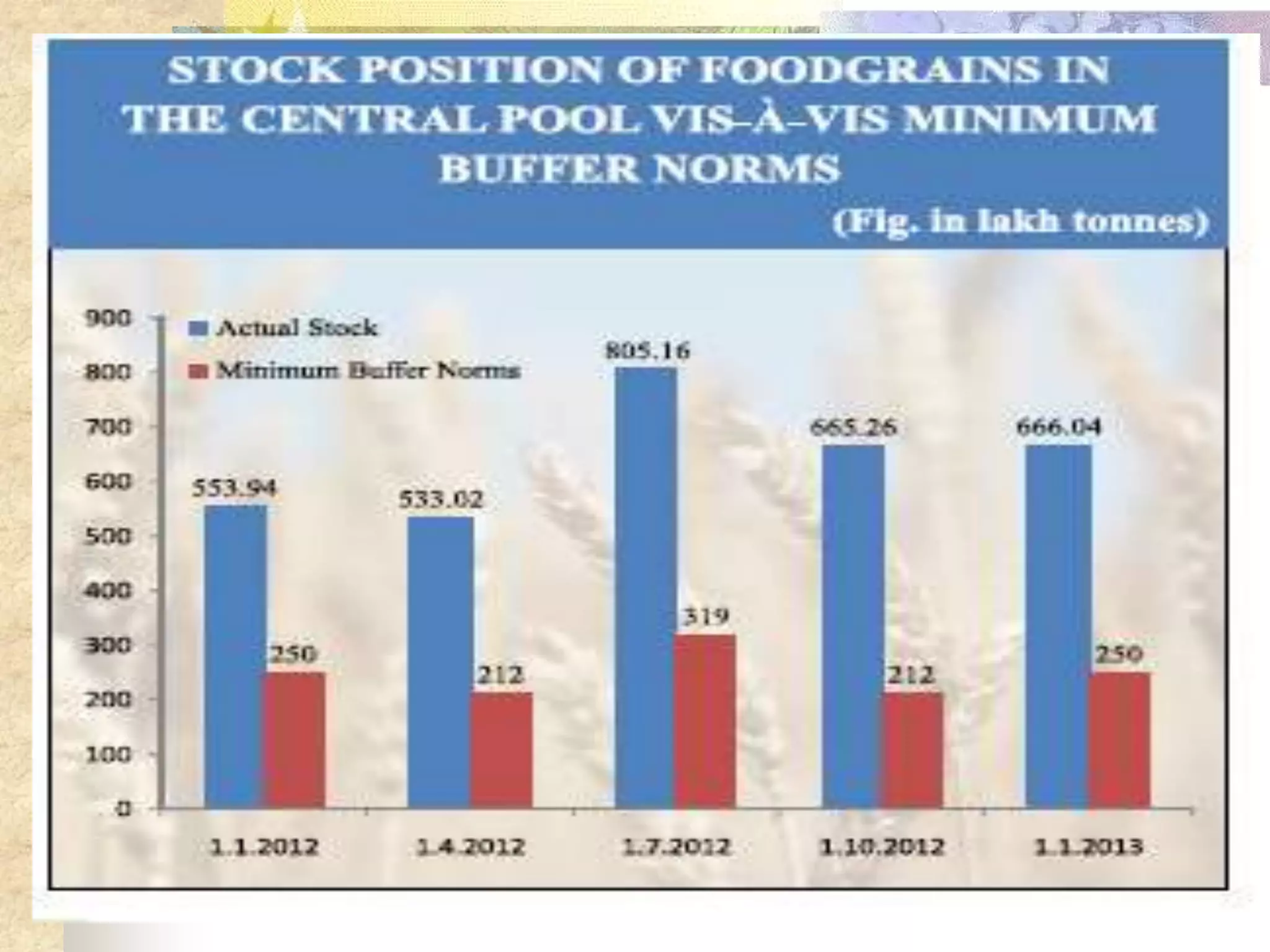
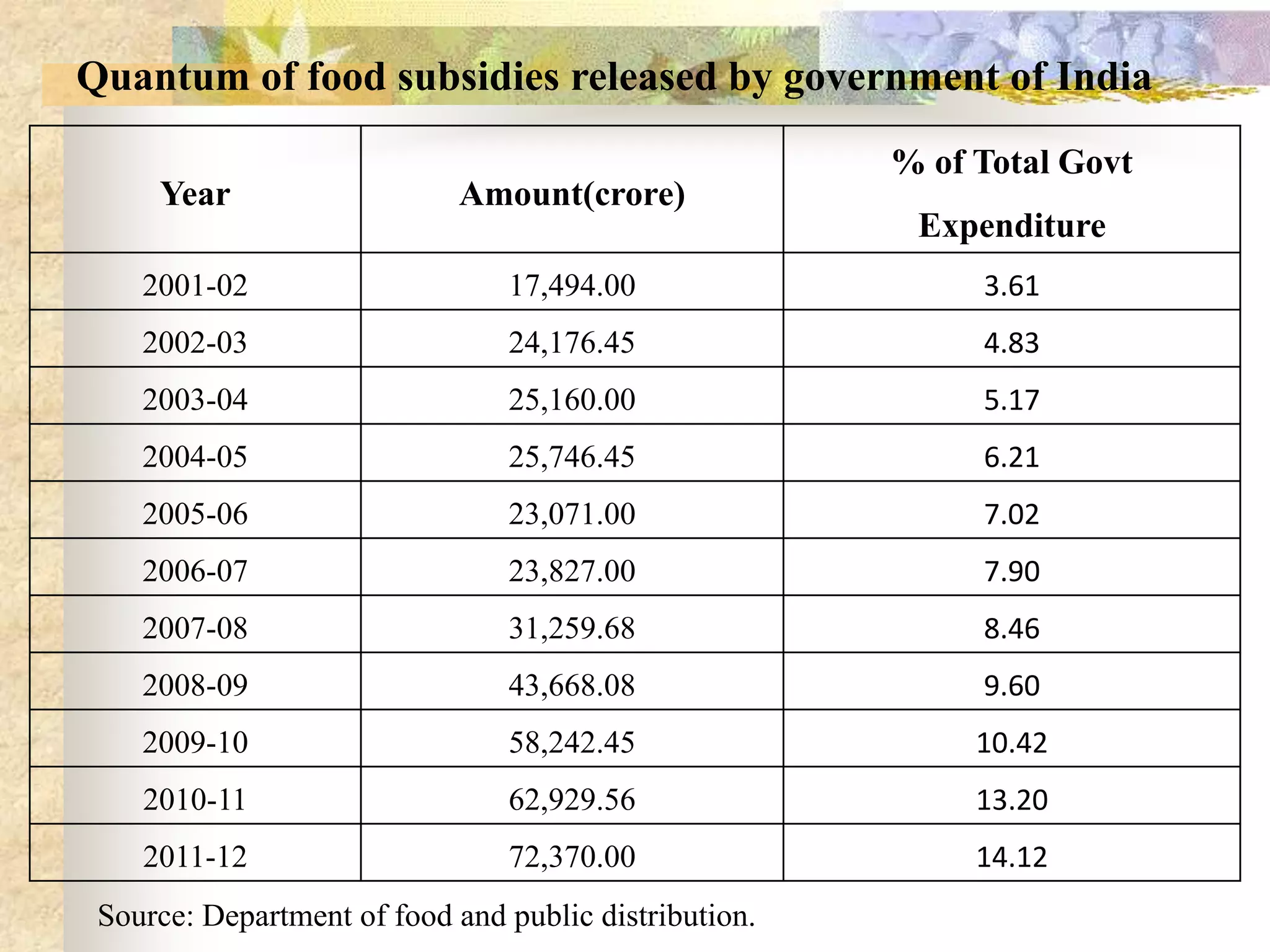
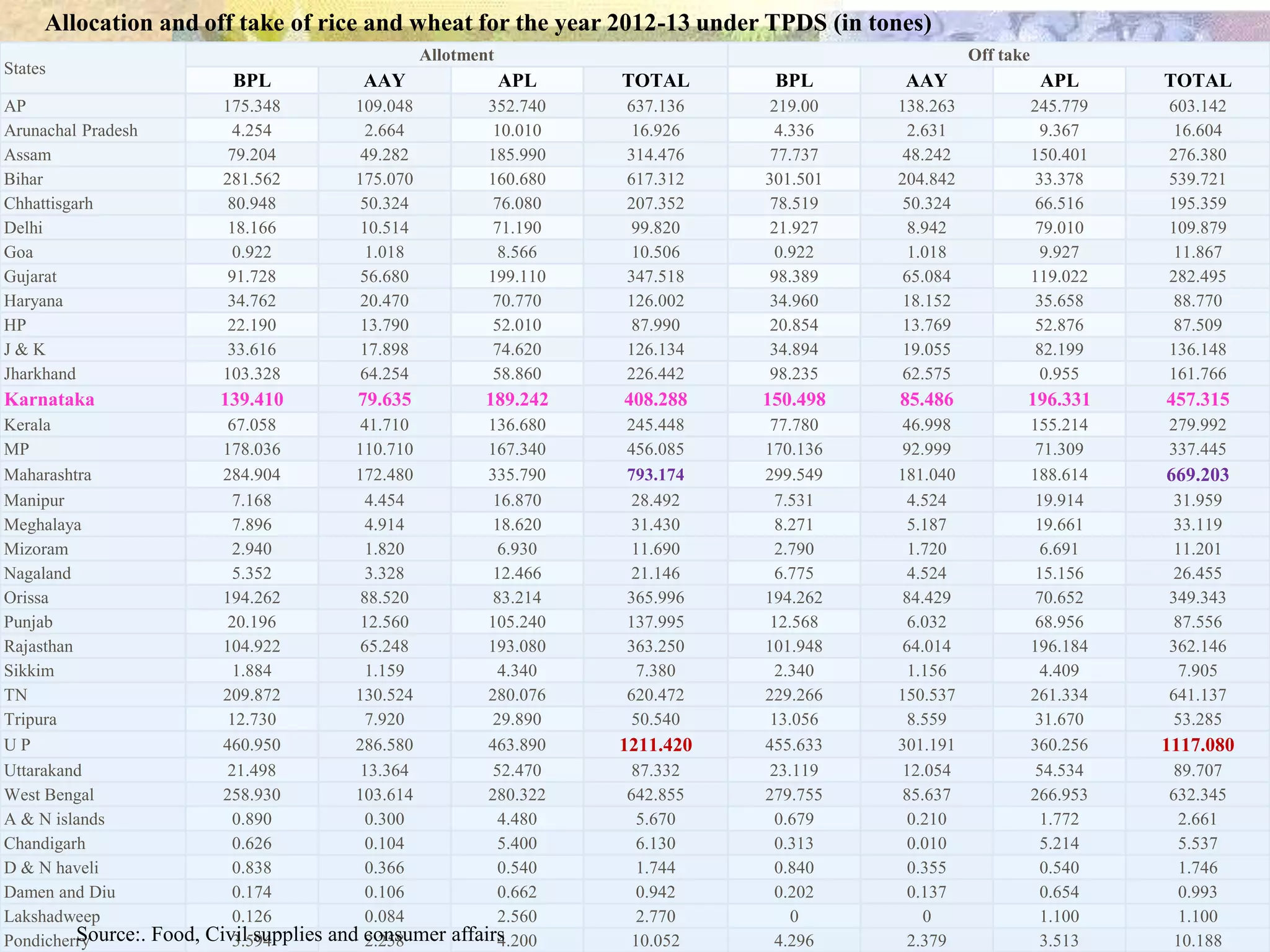
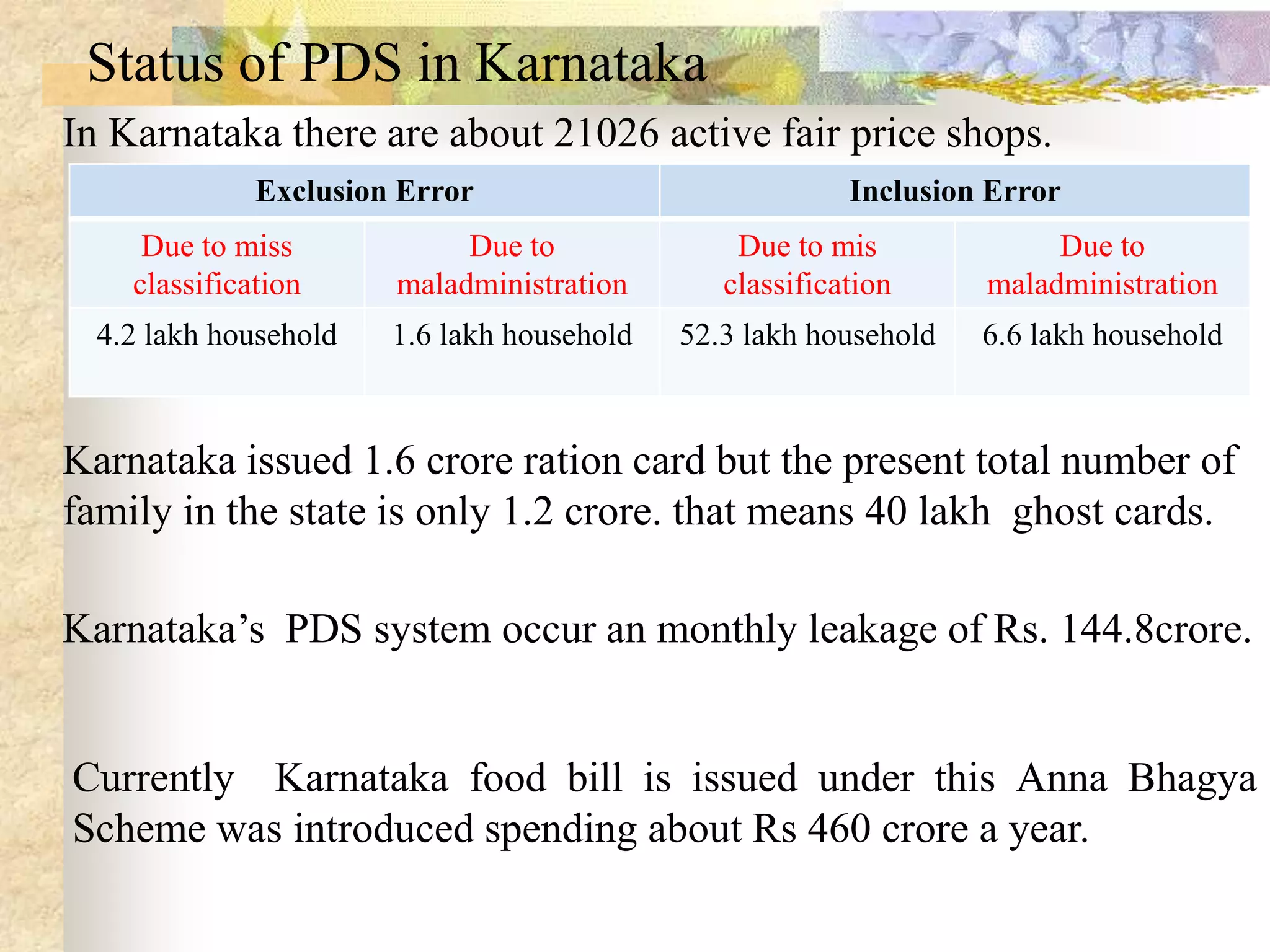
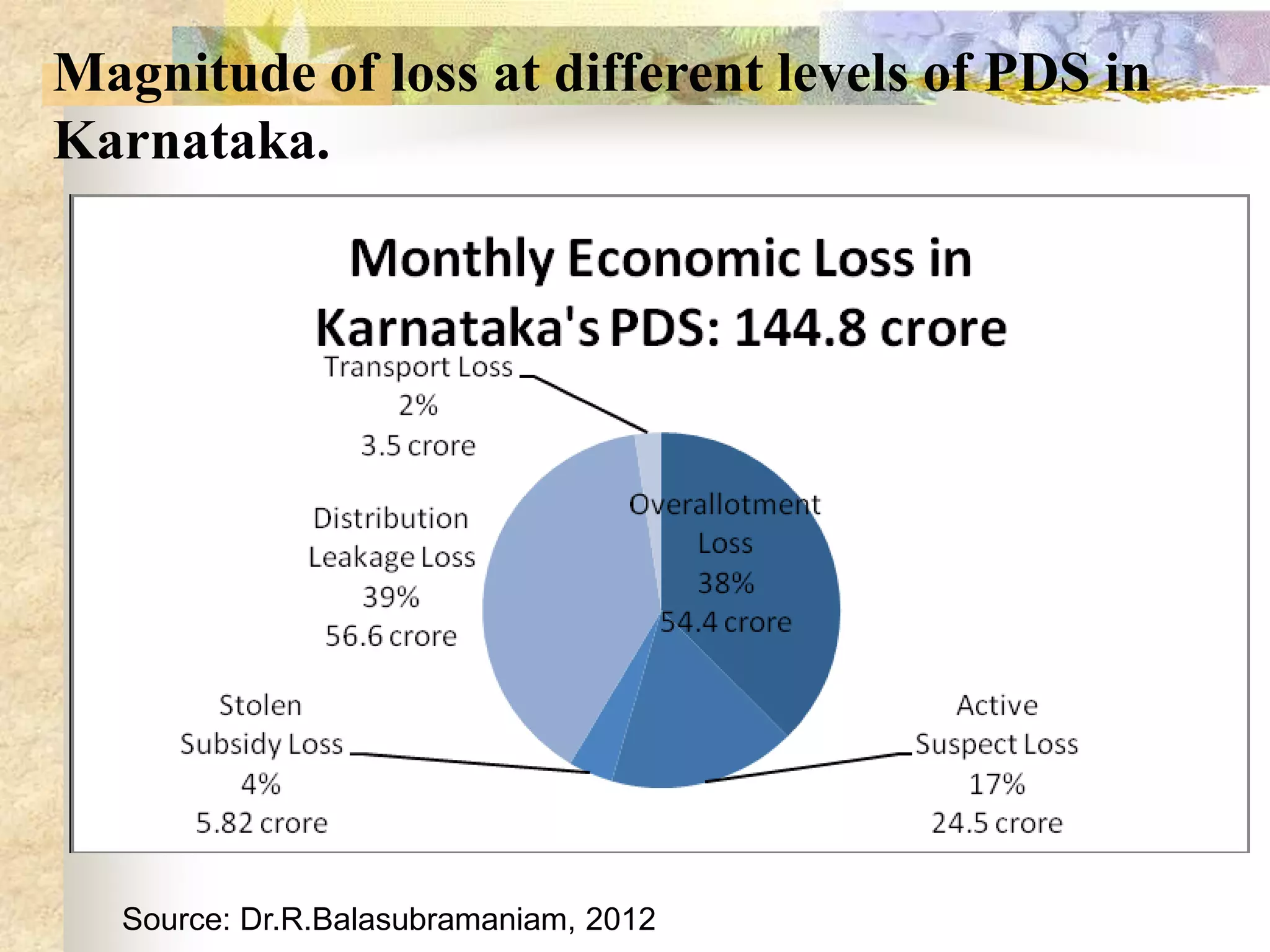
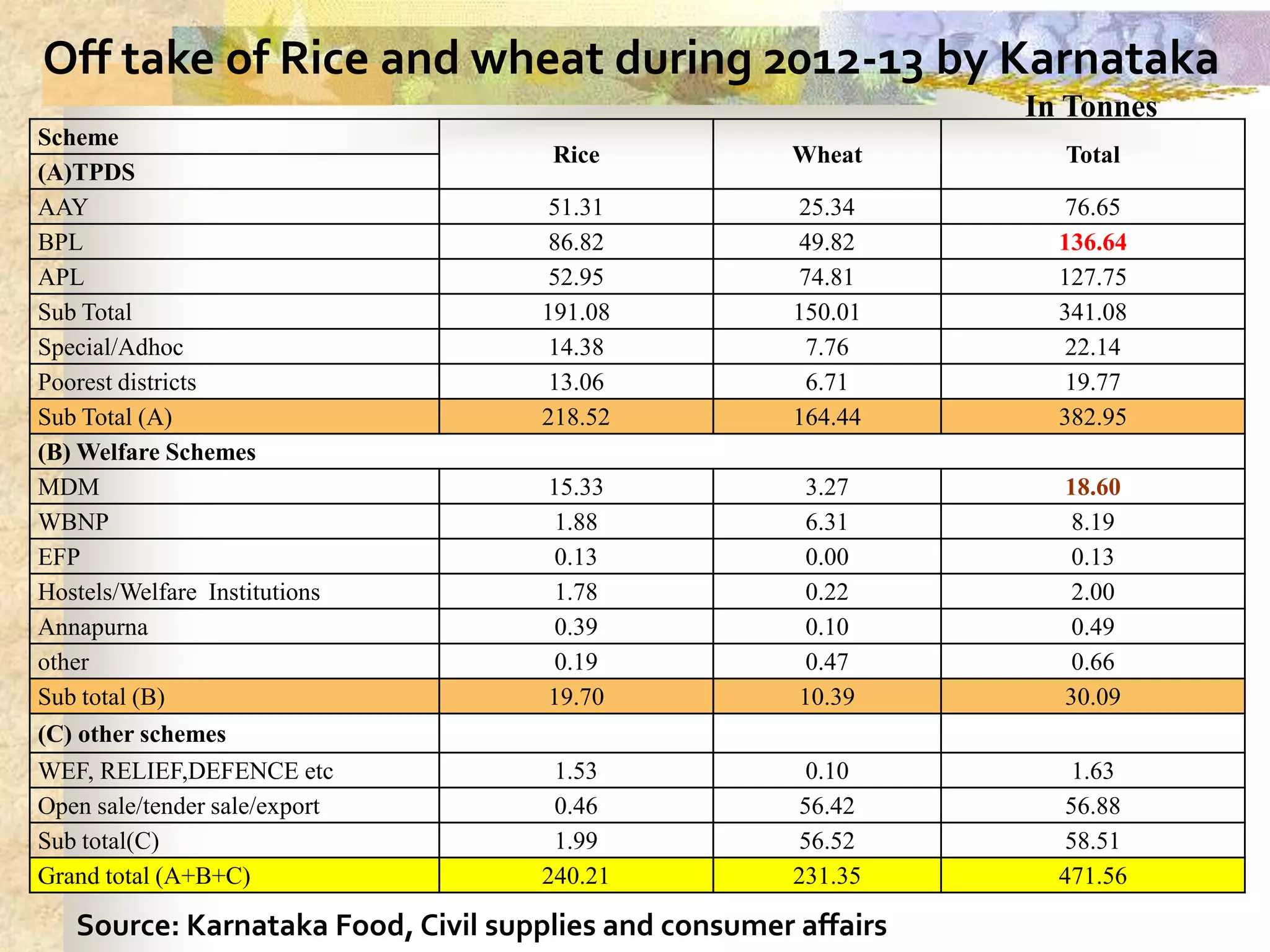
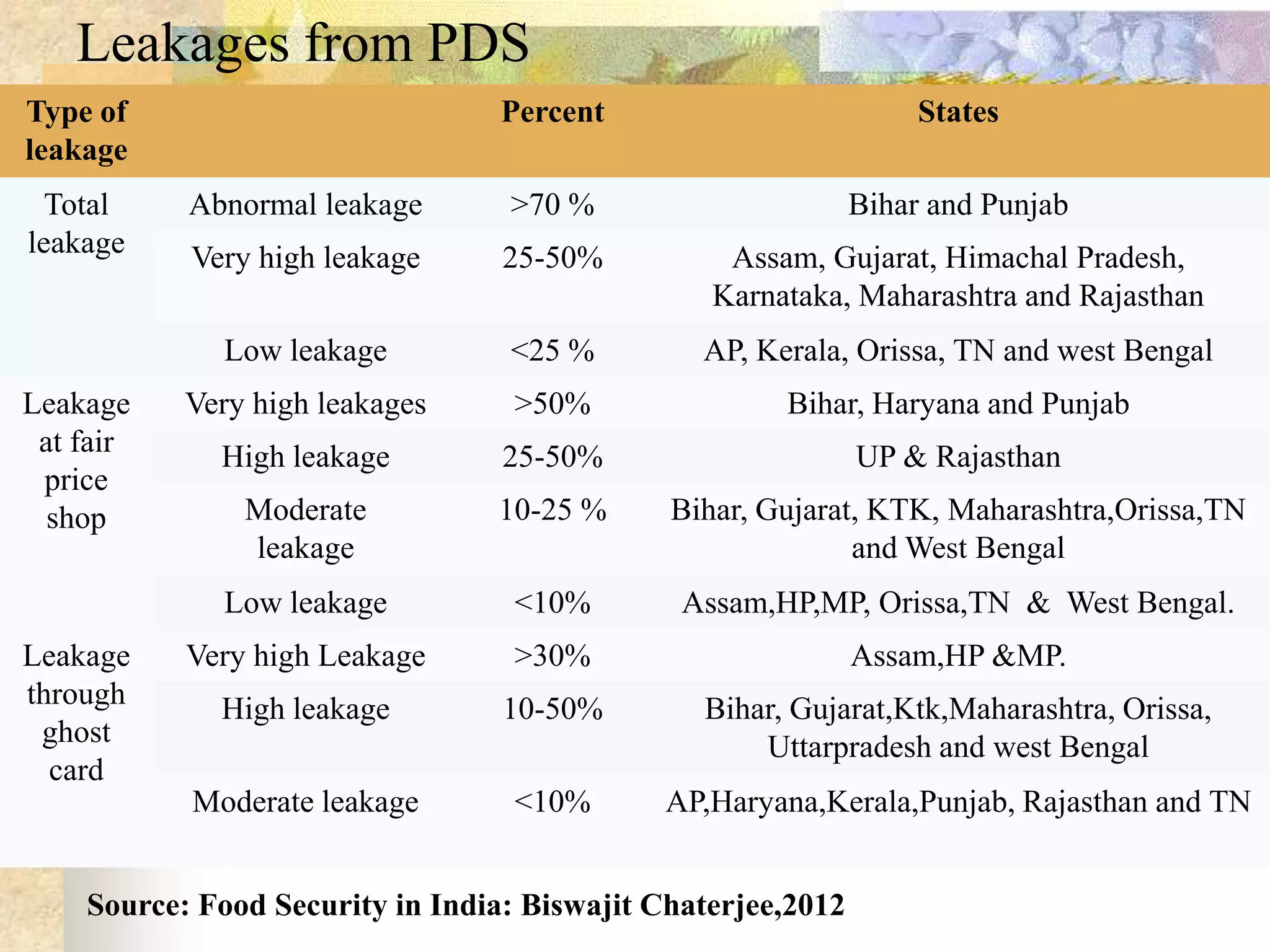
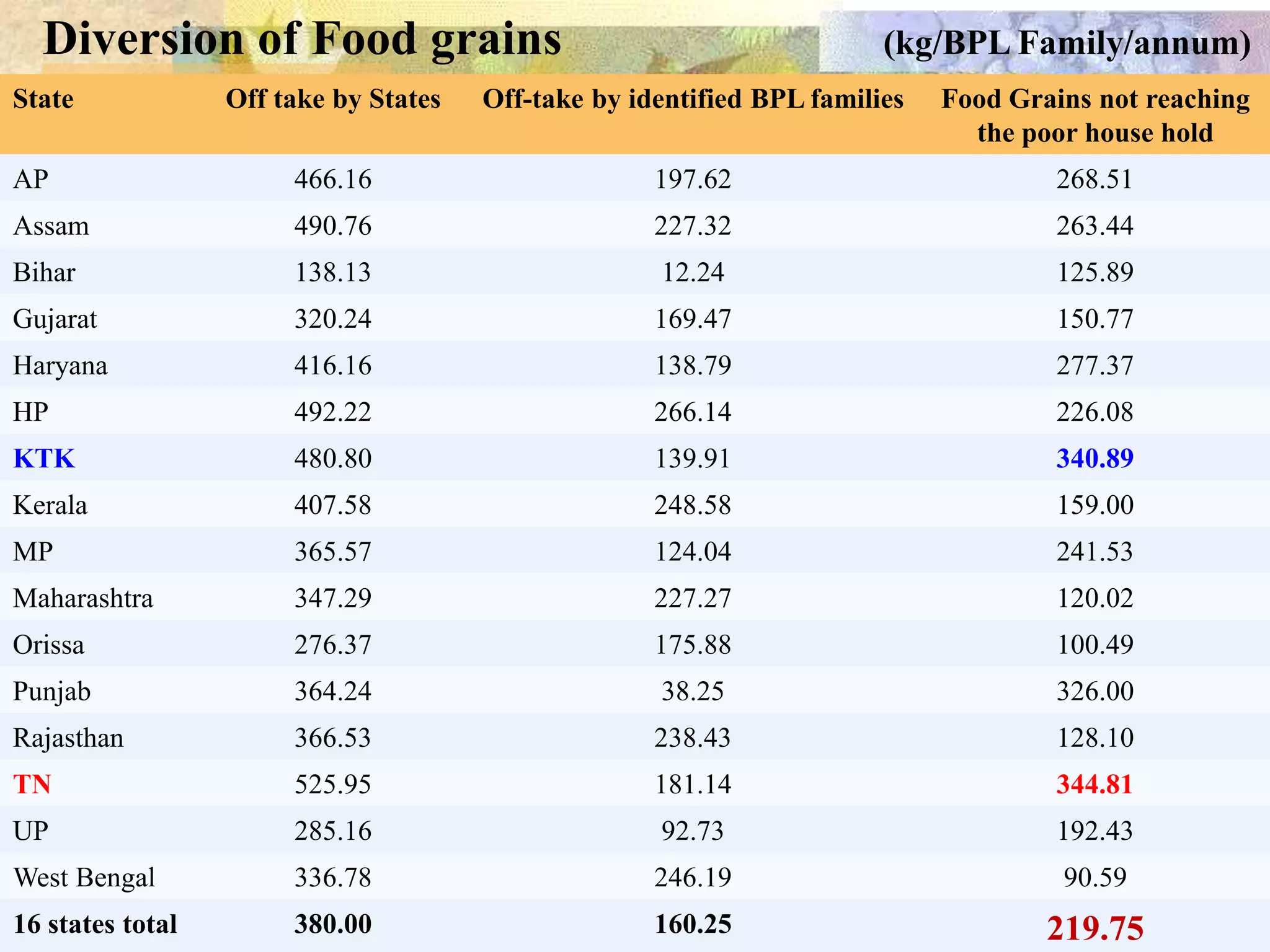
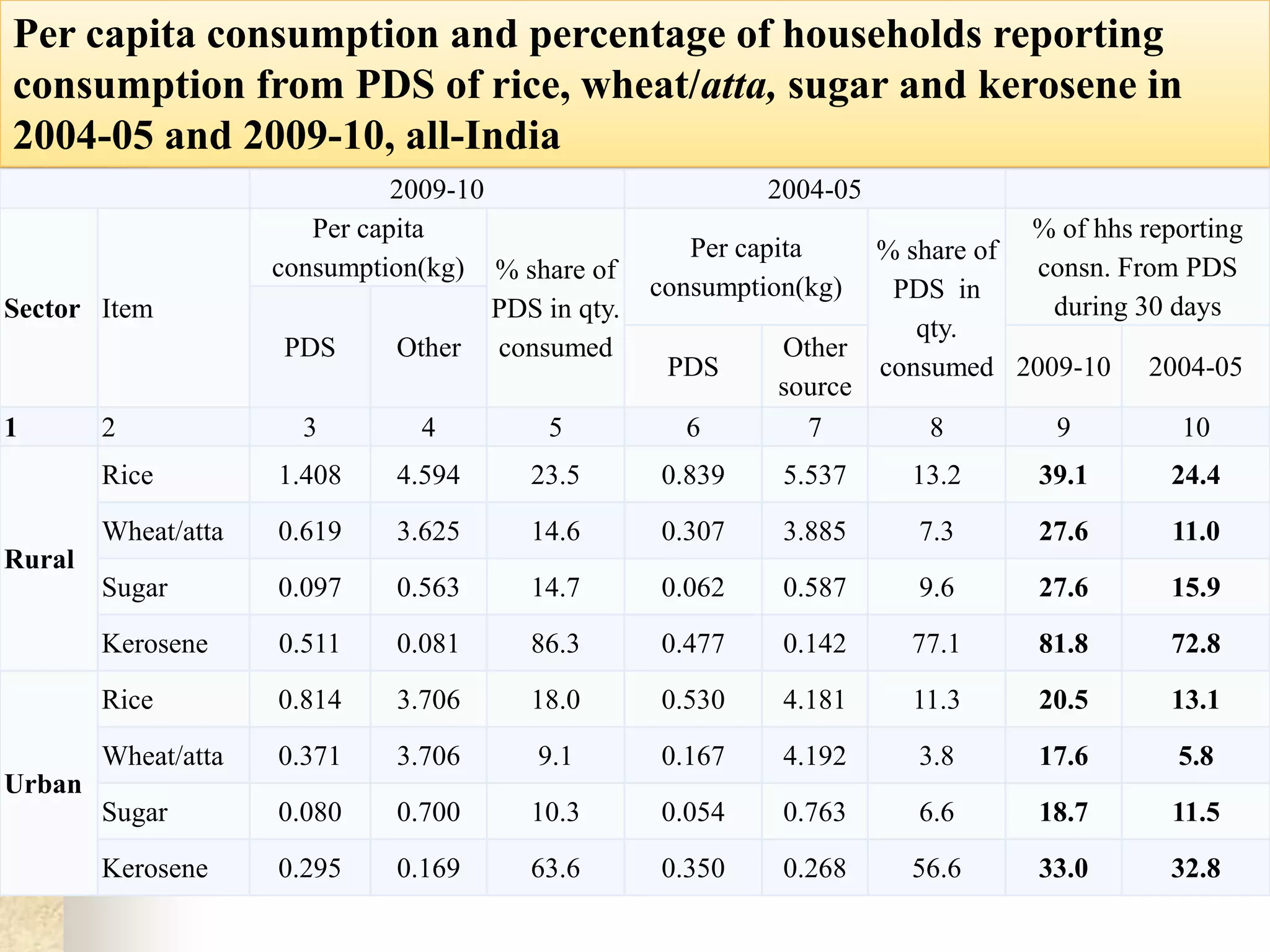
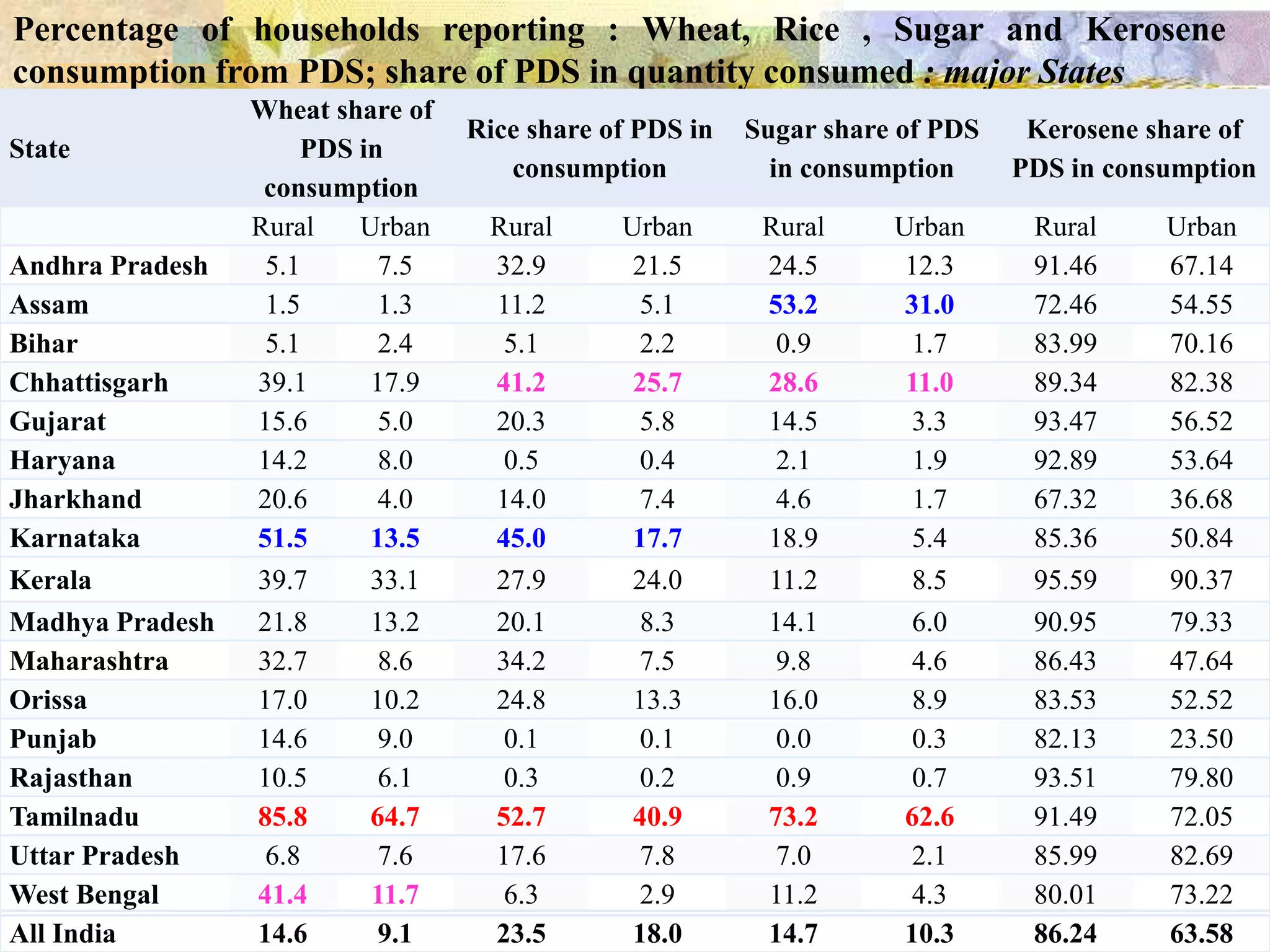
- India achieved national food self-sufficiency 35 years ago but about 35% of its population remains food insecure due to low incomes and high food prices. The Public Distribution System meets less than 10% of grain consumption by the poor.
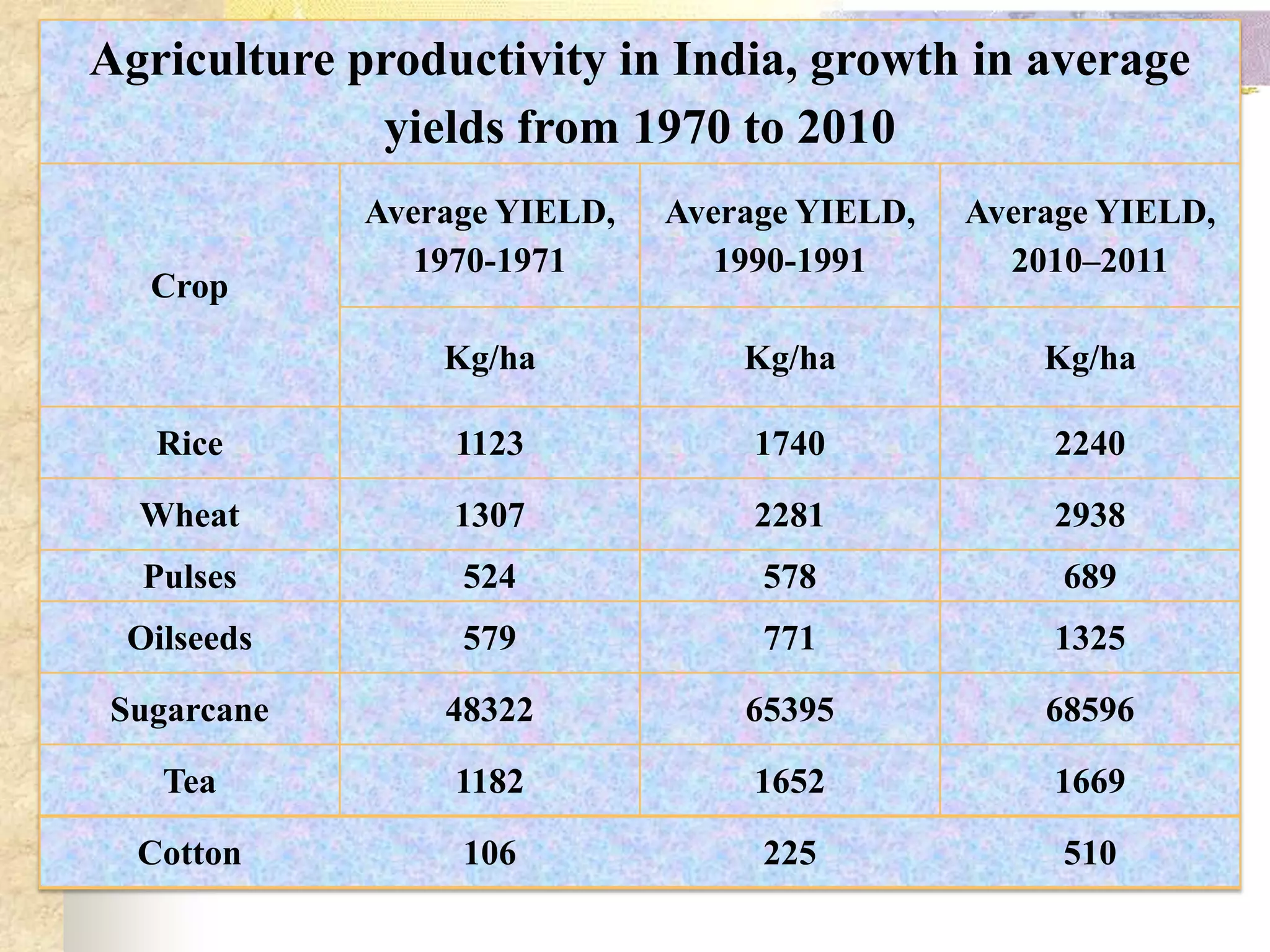
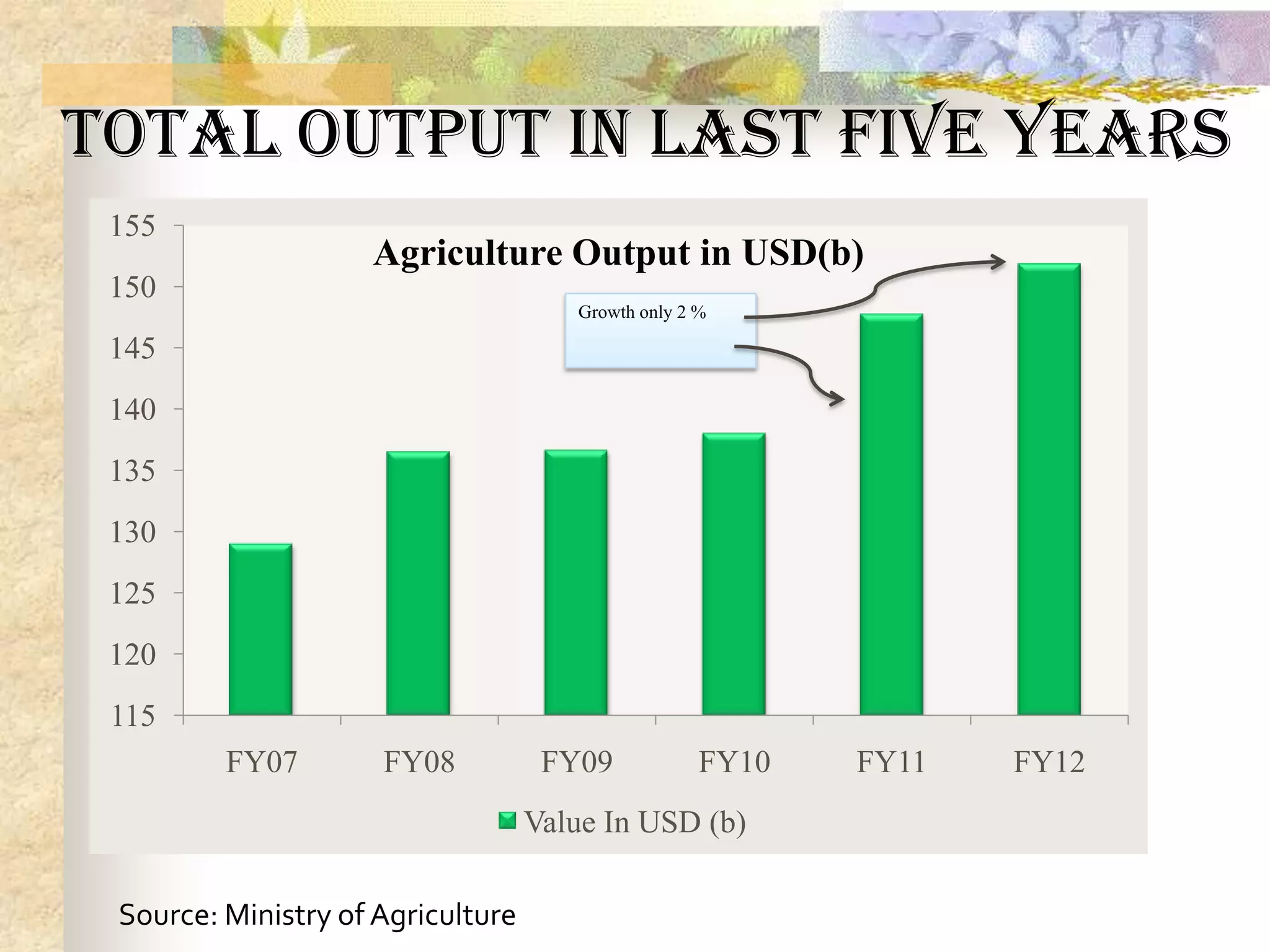
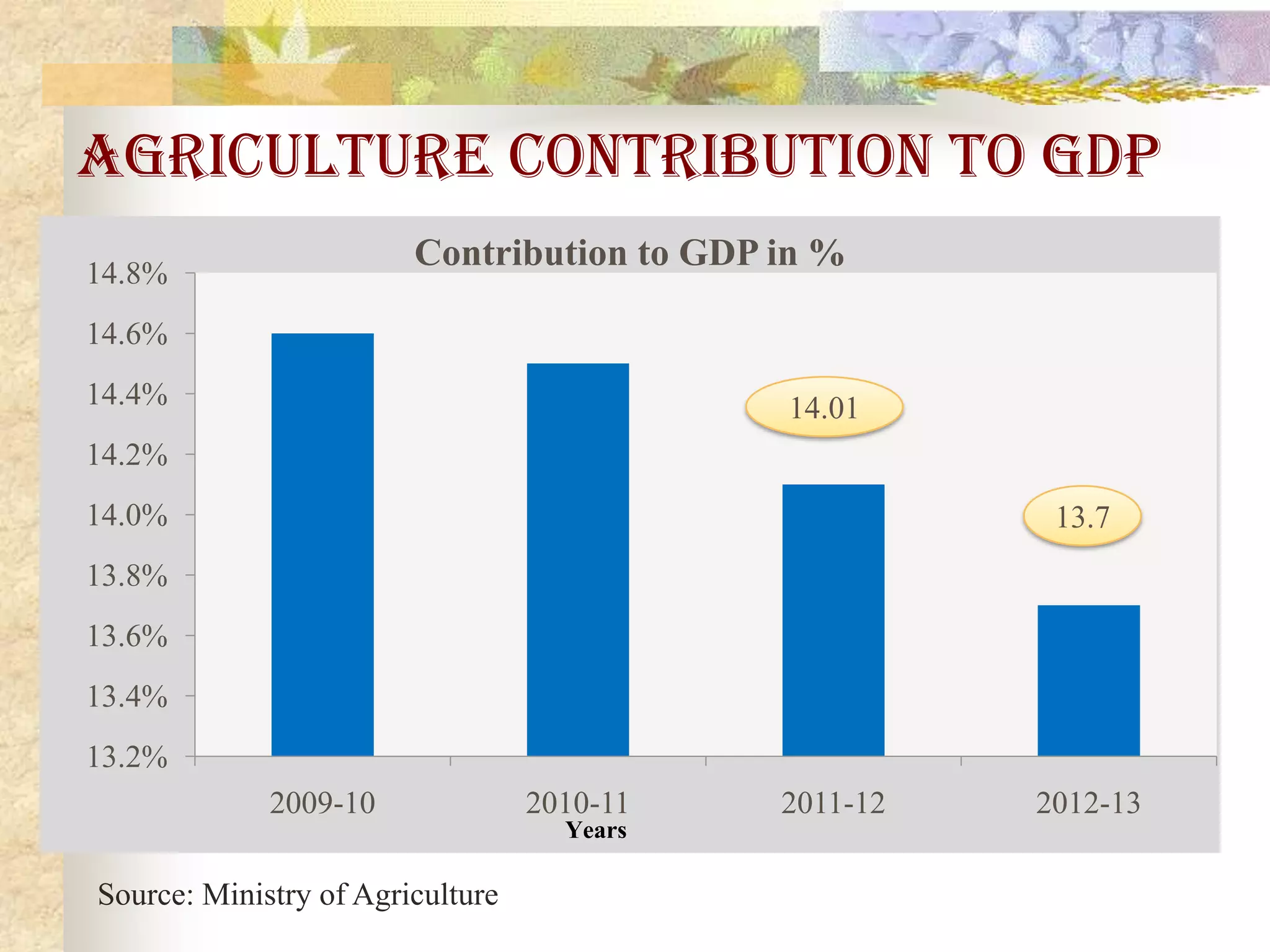
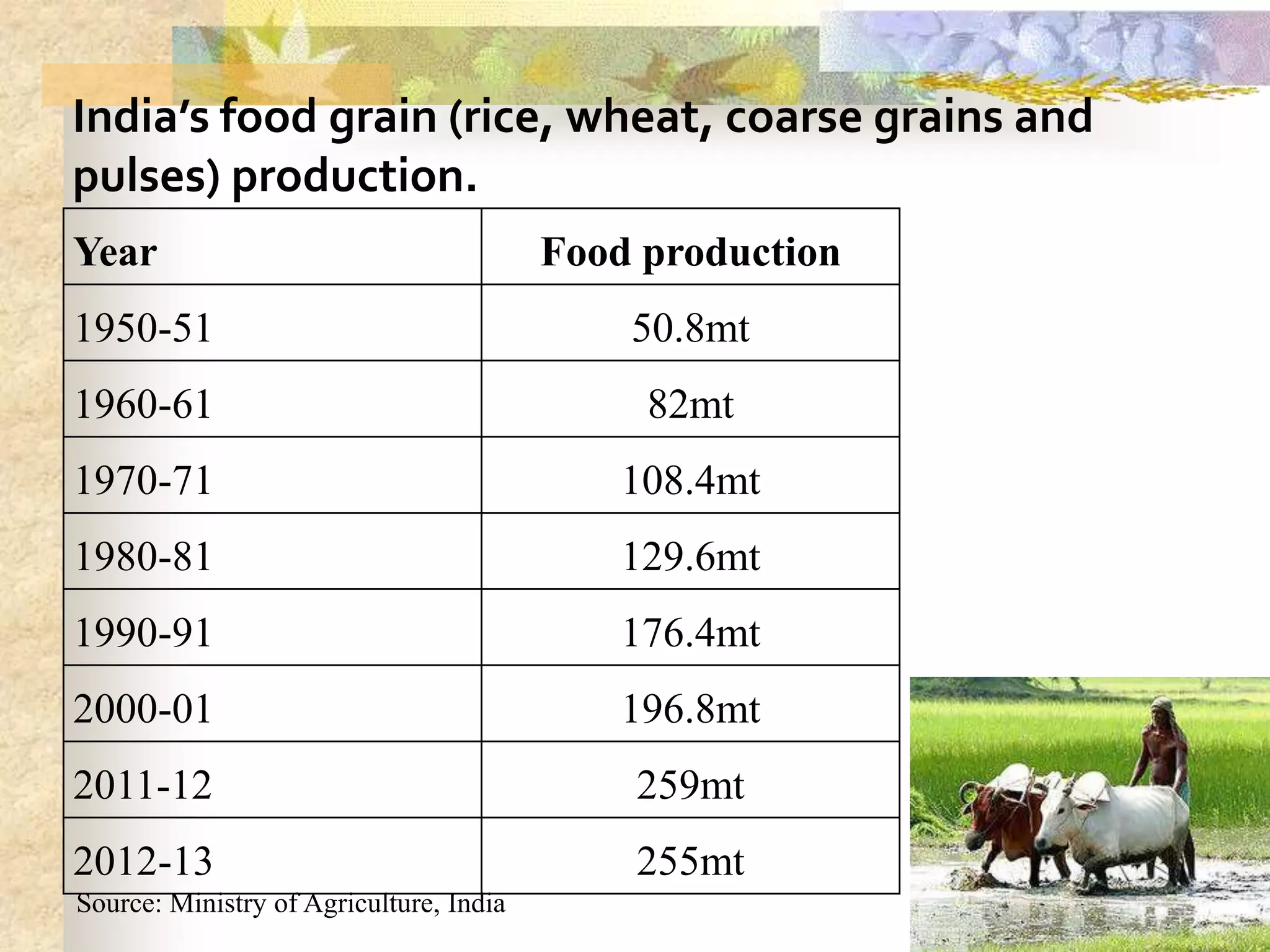
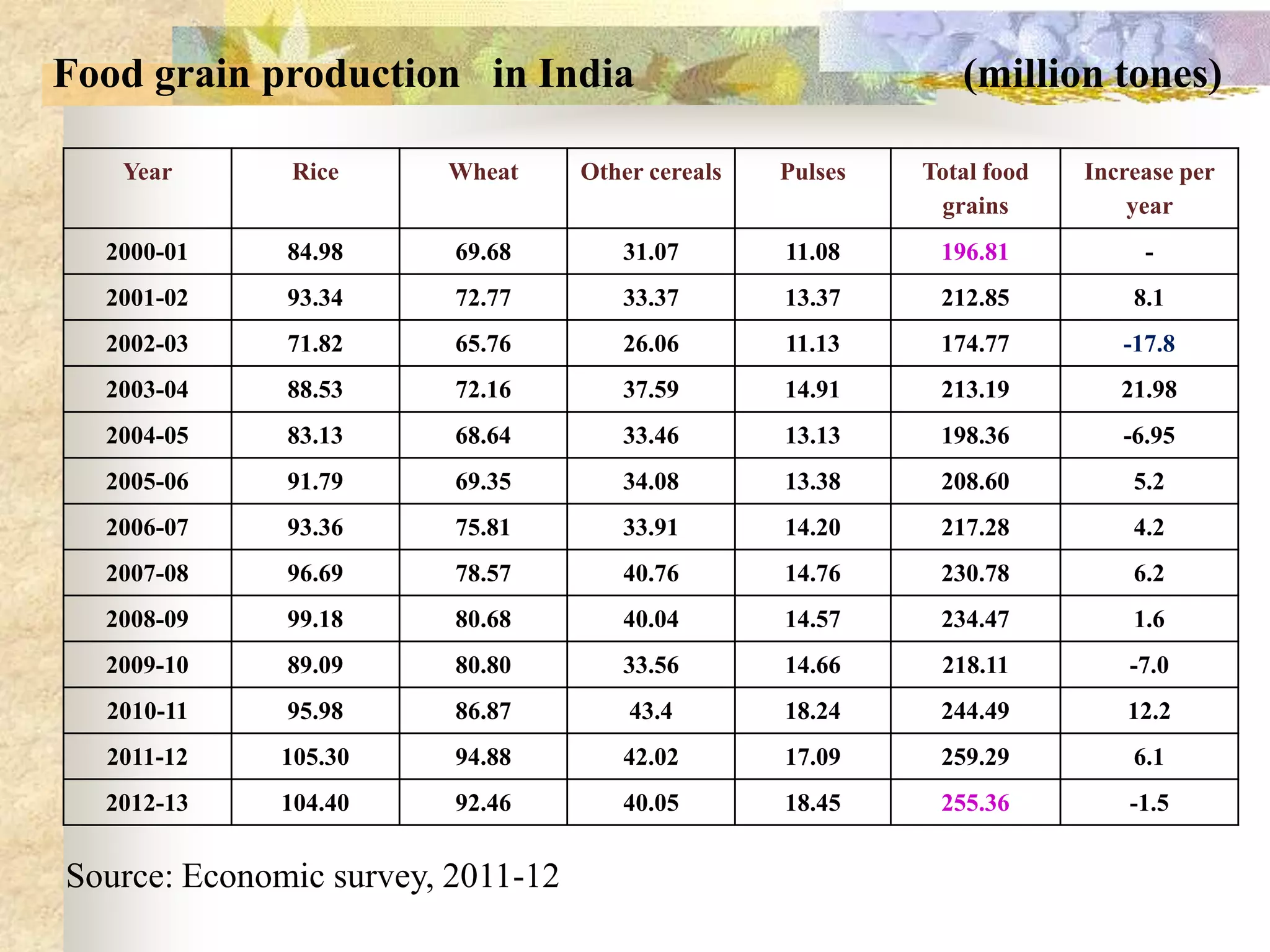
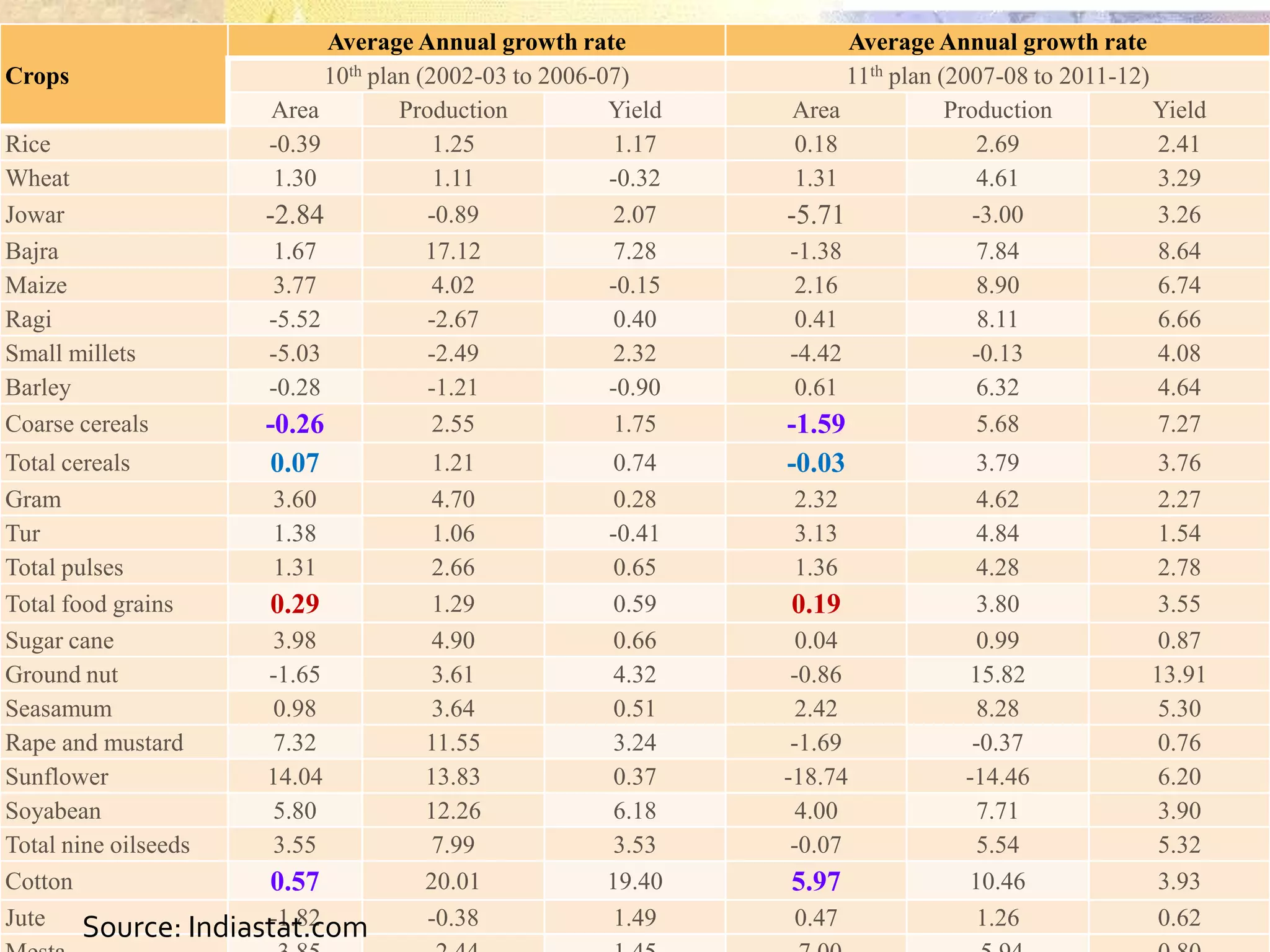
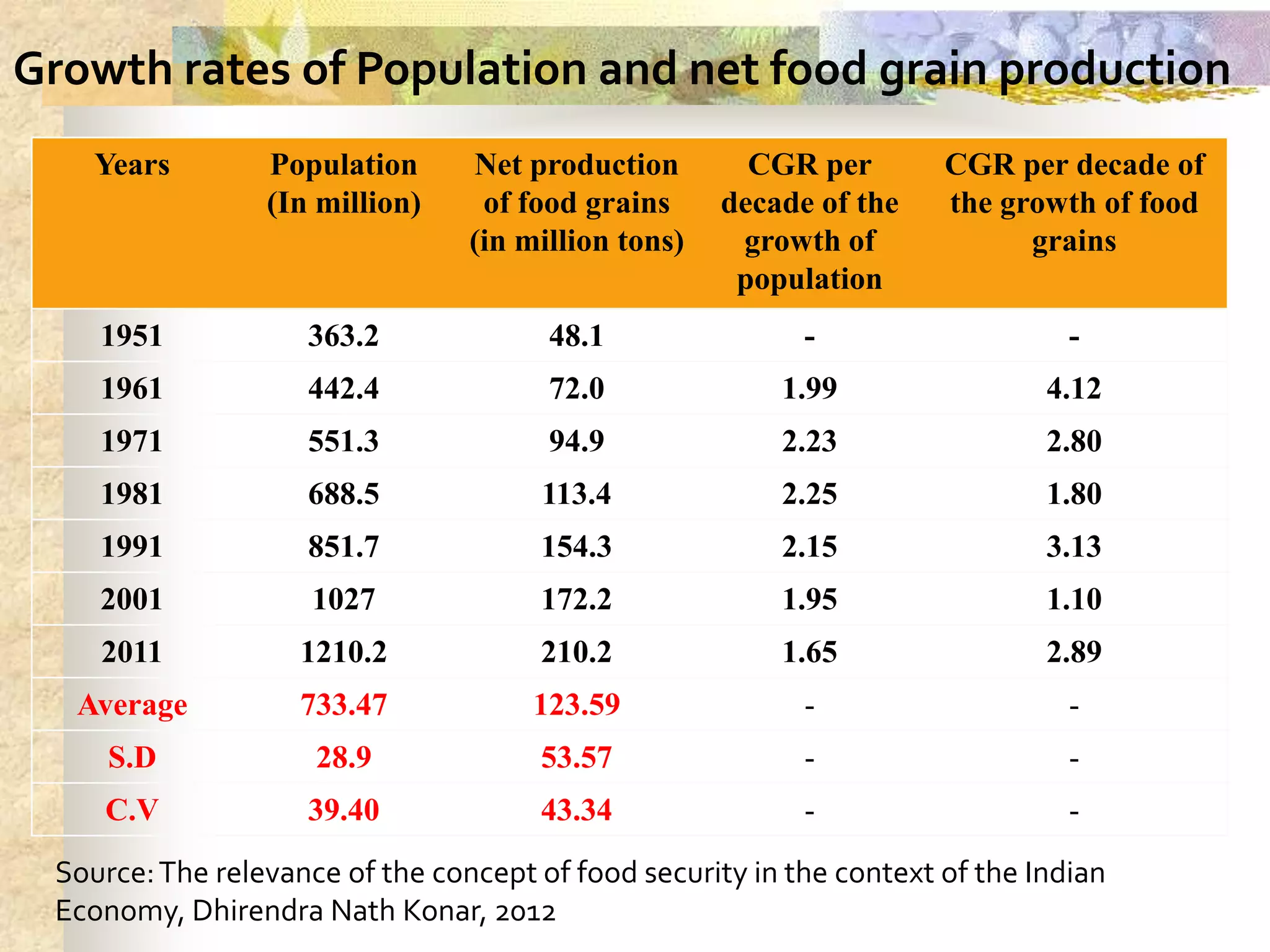
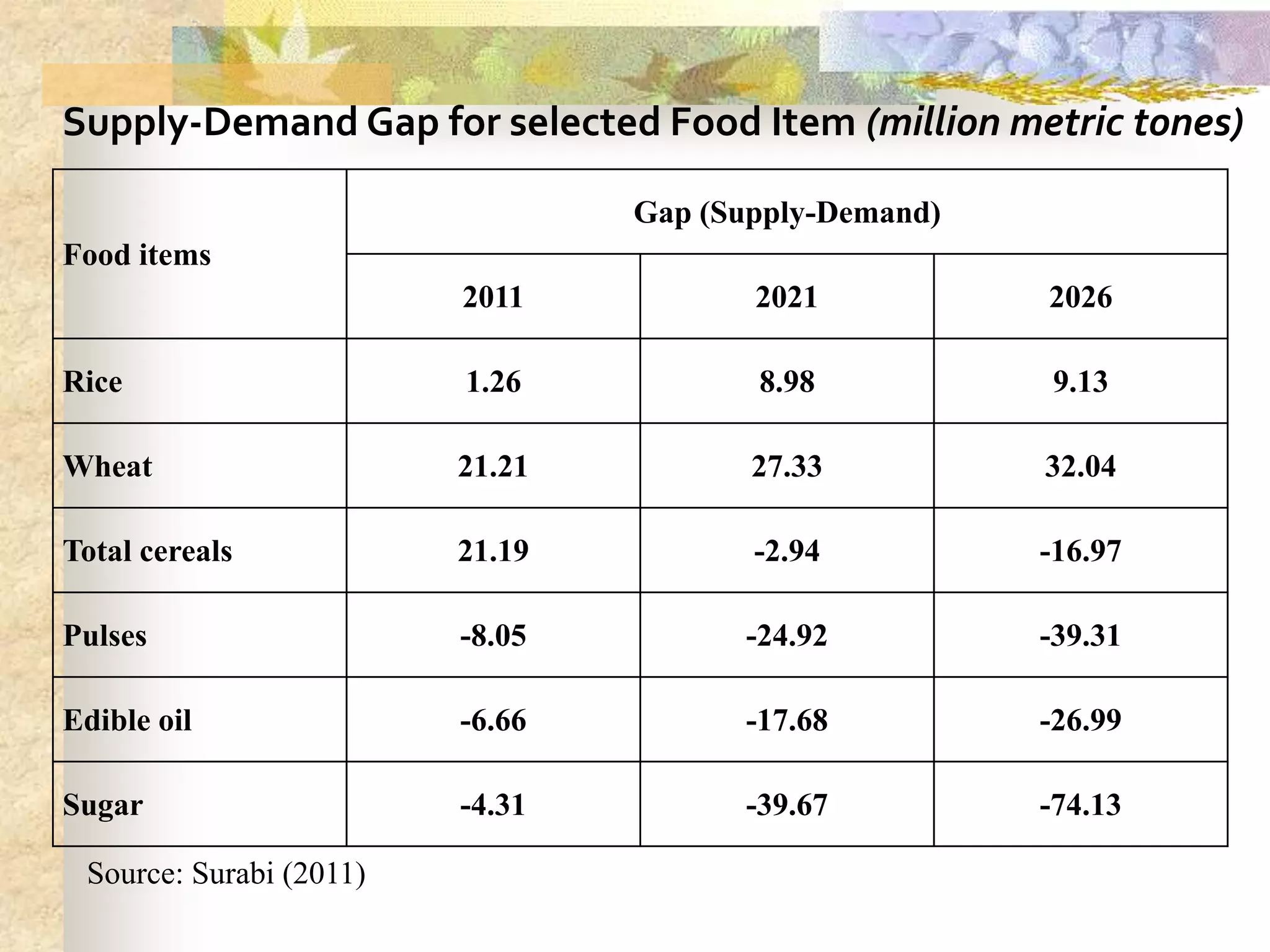
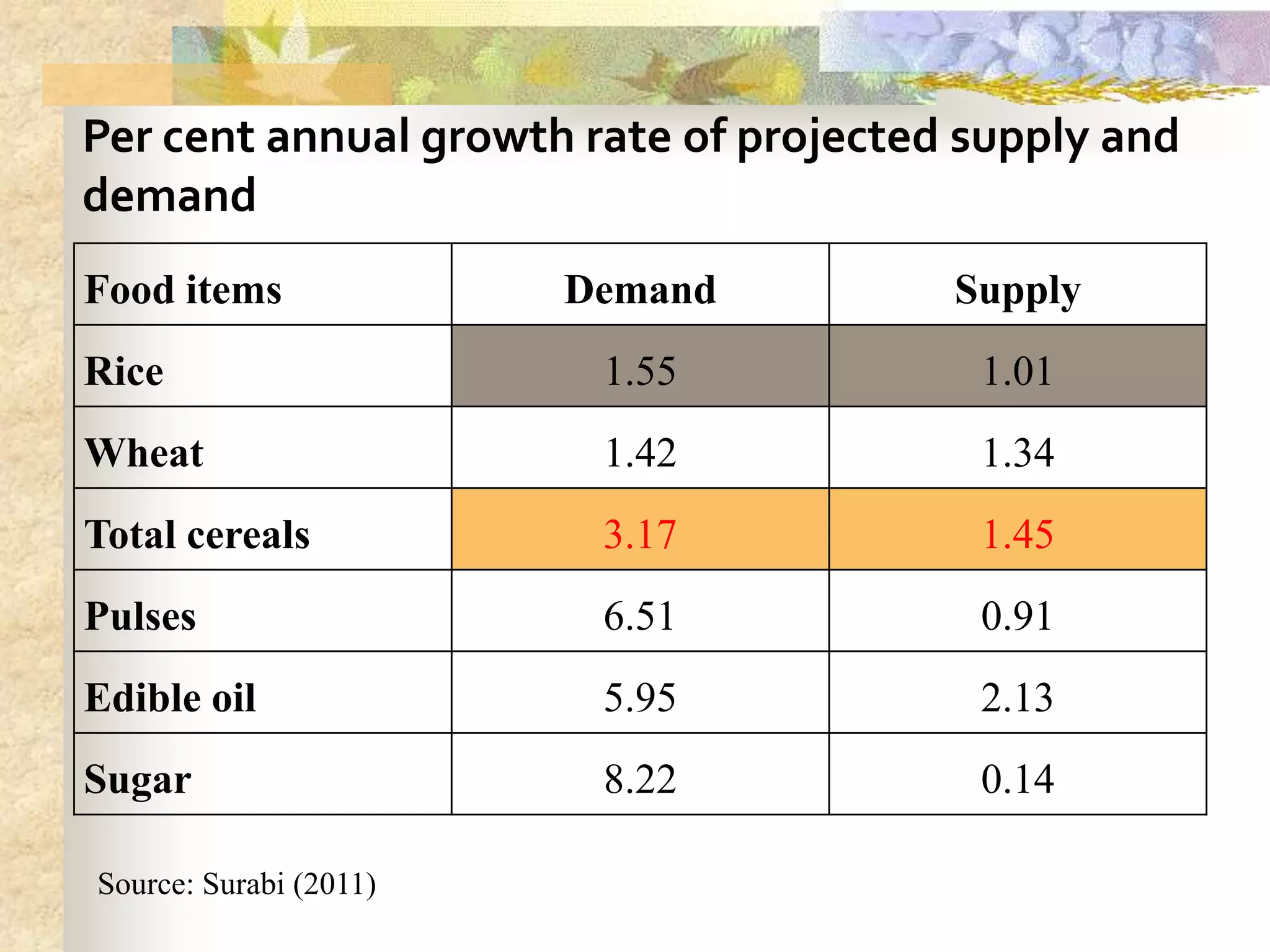
- Agriculture is the backbone of the Indian economy, contributing 16% to GDP. India is a major global producer of many crops but agriculture growth has slowed in recent years. Food grain production has increased significantly since the 1950s but demand is projected to outpace supply.
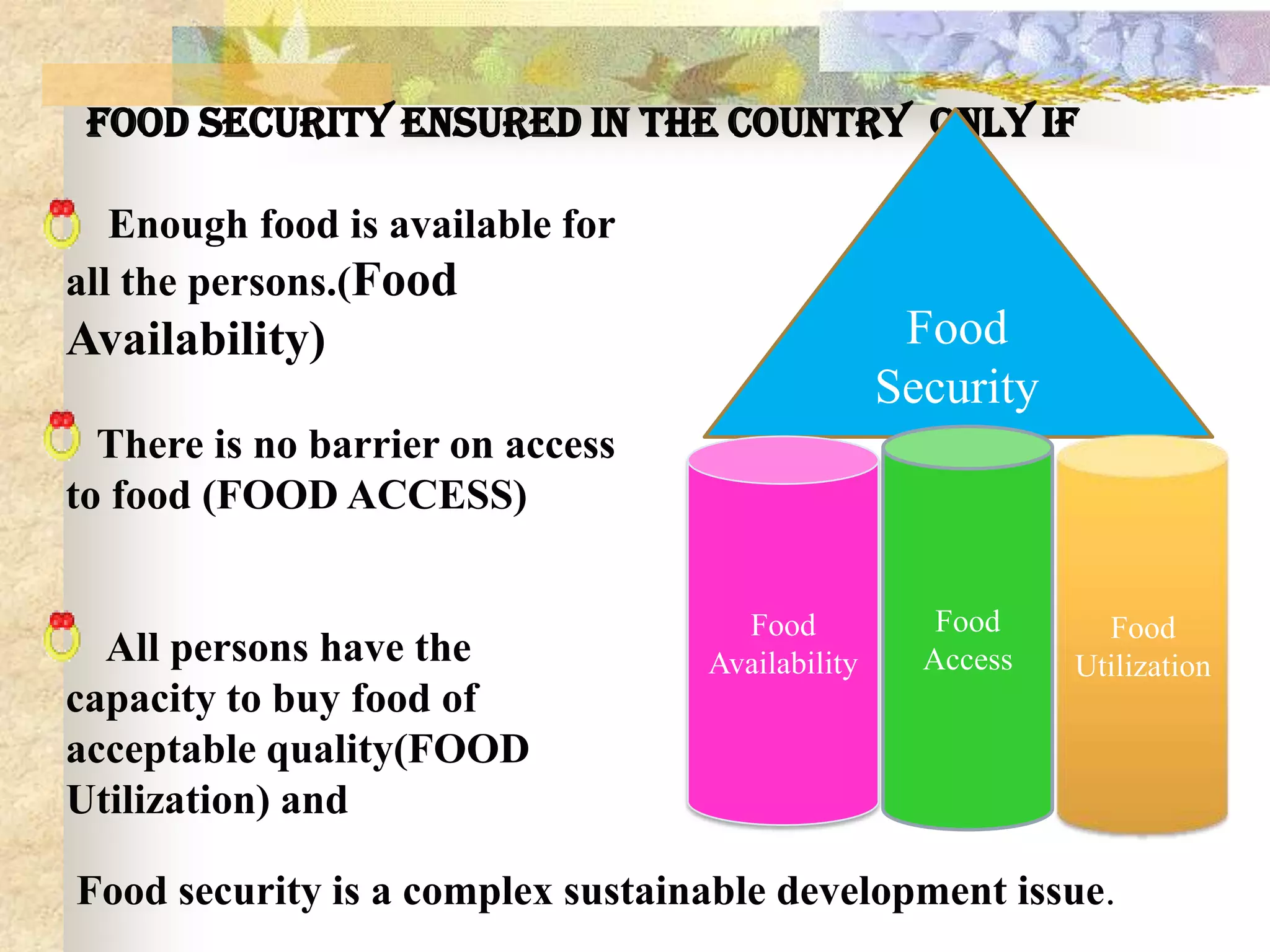
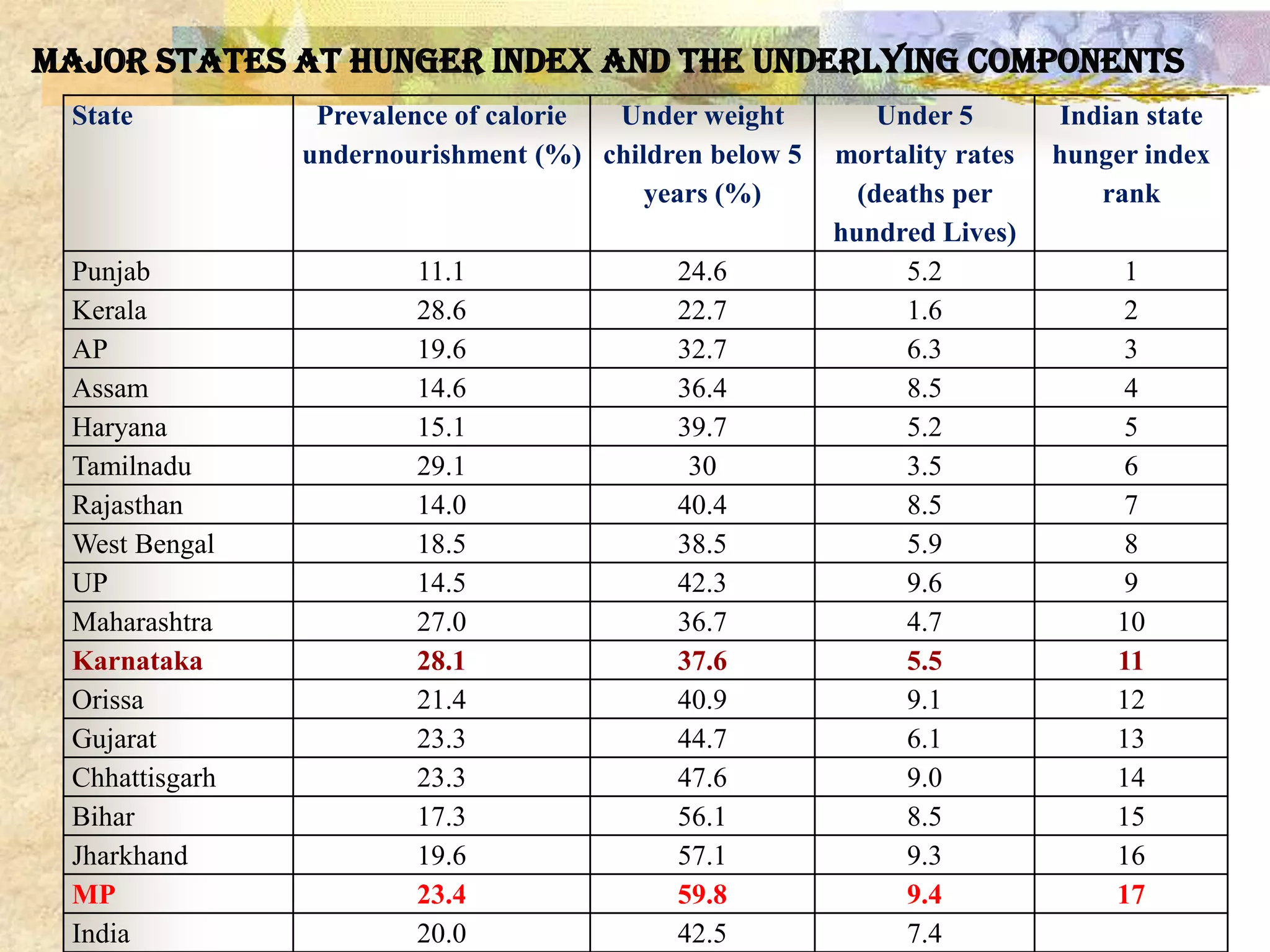
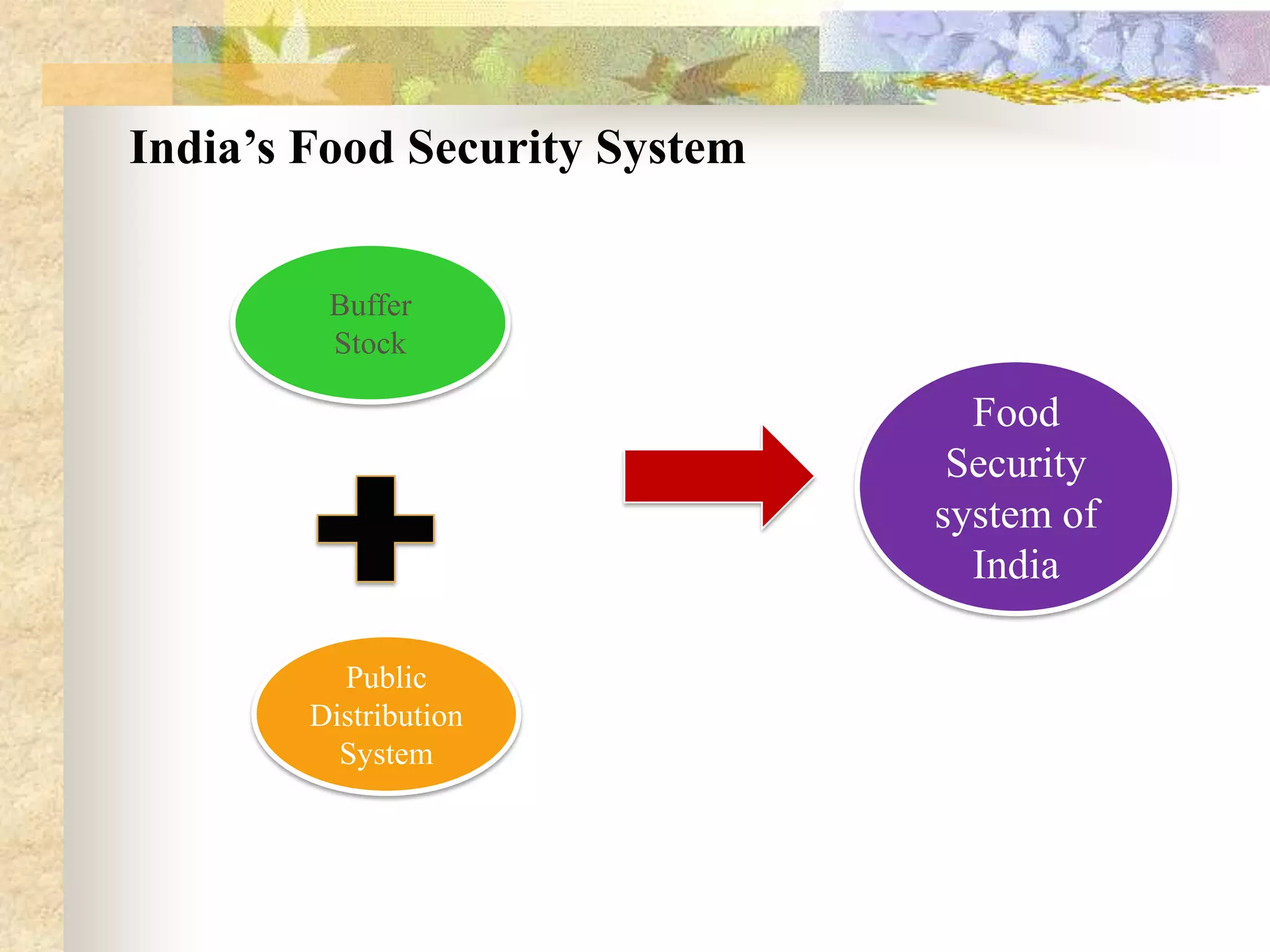
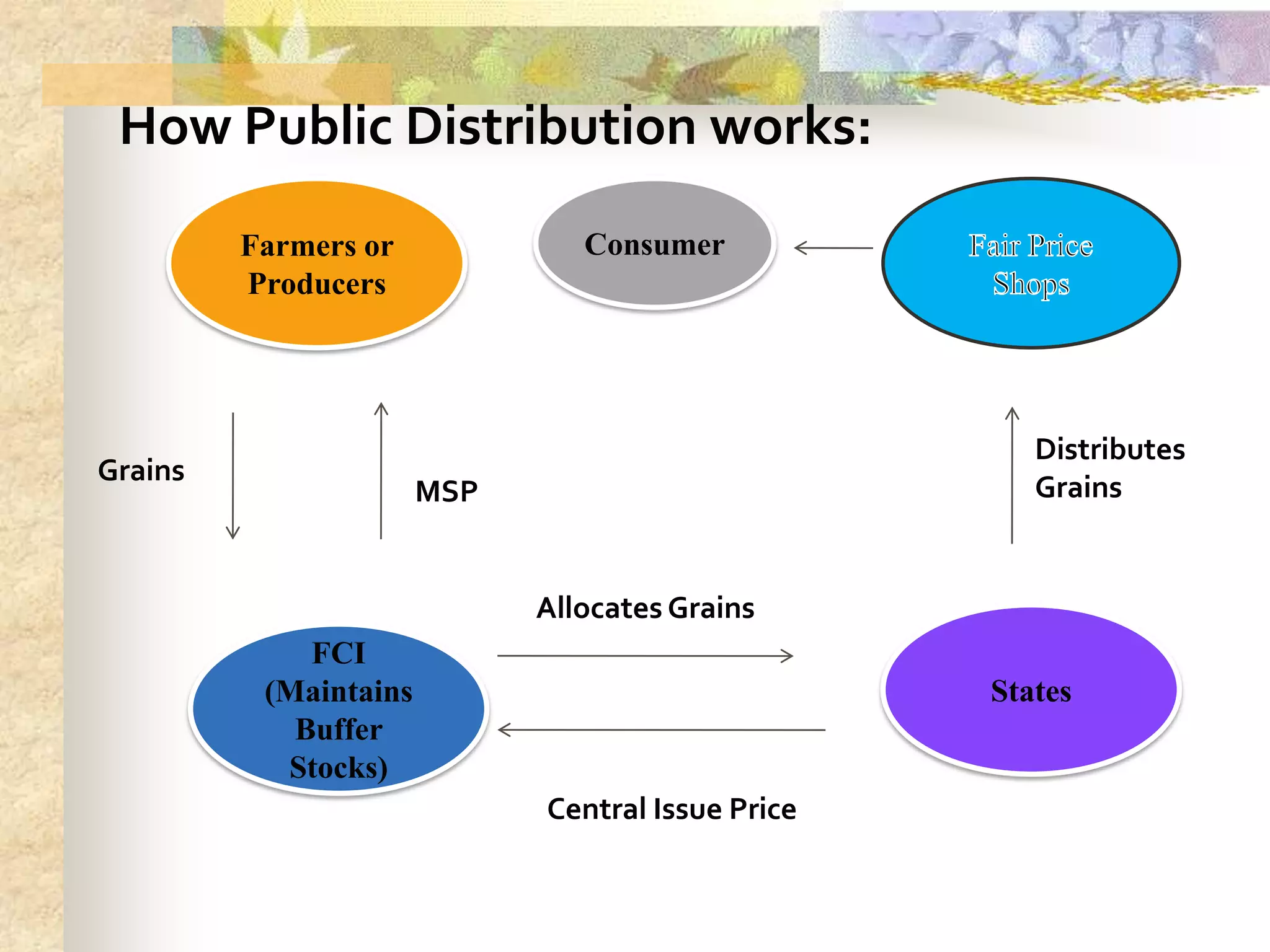
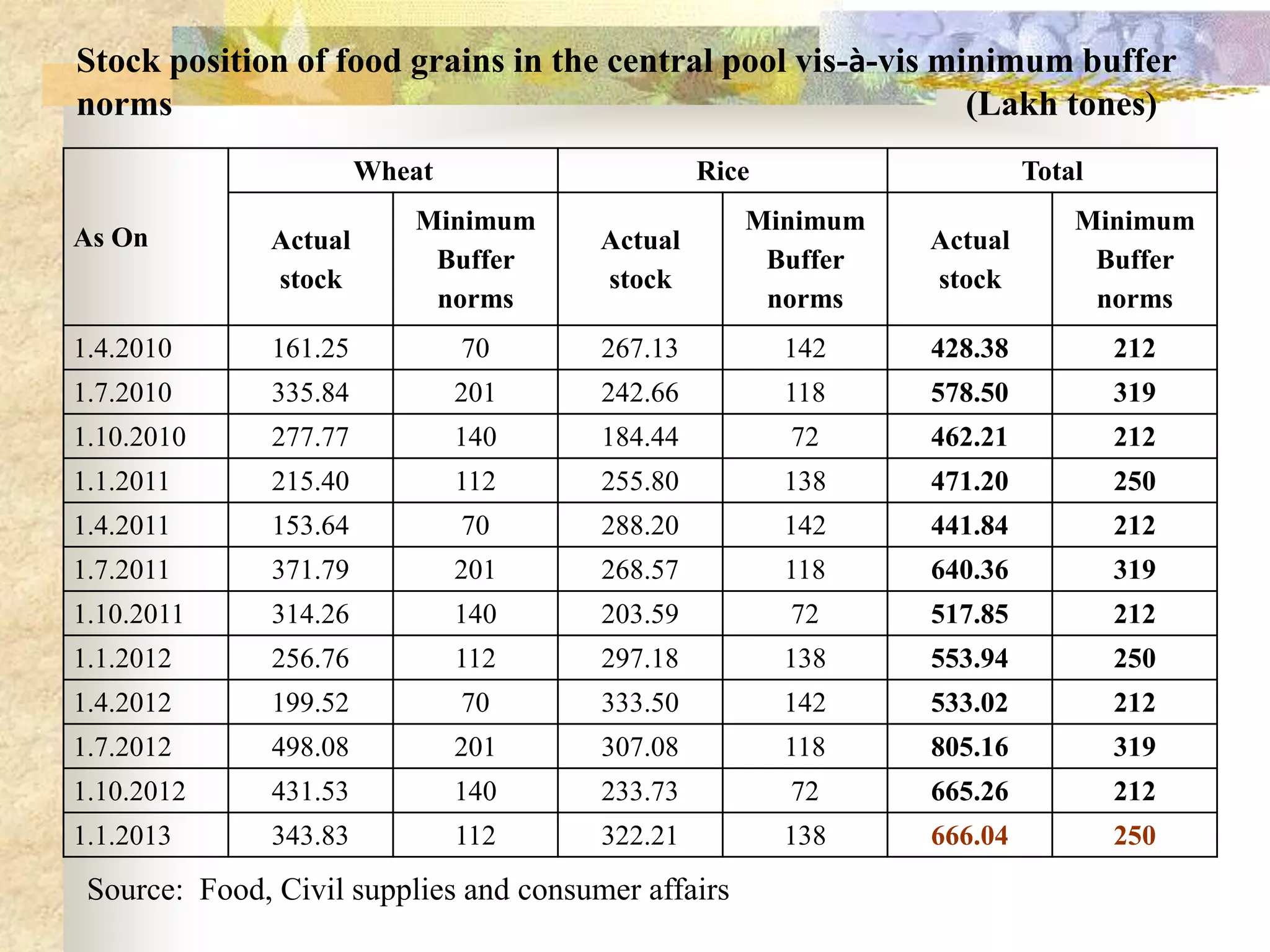
- Ensuring food security requires sufficient food availability, access, and utilization. Various government schemes aim to achieve food security through food procurement, distribution through PDS, and employment programs but India still has high levels