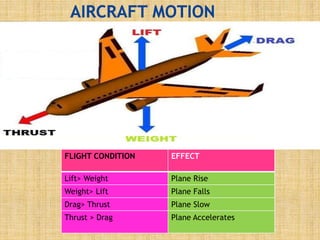
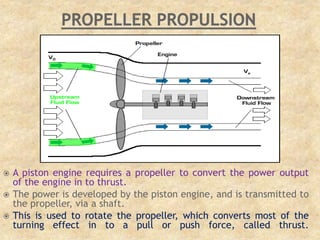
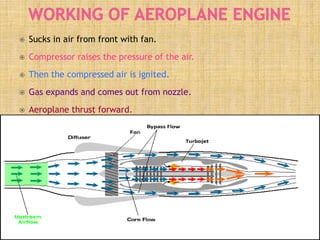
The document provides an overview of aeroplane propulsion systems, focusing on the principles, components, and types of propulsion, including jet, rocket, and propeller systems. It highlights the importance of thrust, lift, and drag, as well as the basic parts of jet engines such as fans, compressors, combustion chambers, turbines, and nozzles. The document emphasizes Newton's laws of motion as the foundational principles governing the operation of these propulsion systems.