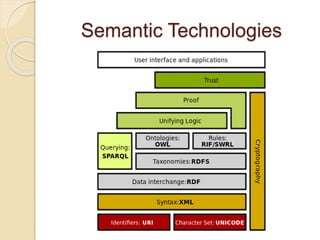
The document discusses the evolution of the web from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0 and the problems with representing meaning. It introduces semantic web as representing things rather than just documents using semantic annotations in formats like RDFa, microformats and microdata. Linked data allows complex queries across a web of data by embedding semantic annotations and using common schemas like Schema.org. Major companies are now building knowledge graphs to represent structured data from sources on a linked open web.