This document provides an introduction to search engine marketing, covering both organic (SEO) and paid search (PPC). It discusses the key components of SEO including keyword research, content optimization, and link building. For paid search, it explains how paid listings work on search engines using an auction system and how advertisers can structure campaigns into ad groups and keywords. The goal is to own the top organic and paid search results to maximize traffic through the "golden triangle" of search engine results.











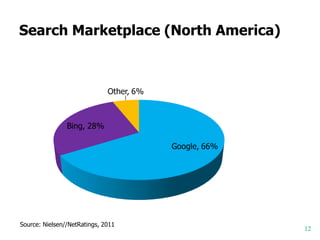














![Example of Keyword Matching
28
match type...
With this
punctuation...
To trigger your ad on... Example
broad match none
synonyms, related searches, and
other relevant variations
Candy bars
broad match modifier +keyword
close variations but not synonyms
or related searches
+Candy Bar +Chocolate
phrase match "keyword"
a phrase and close variants of
that phrase
”Candy Bars" Chocolate
exact match [keyword] an exact search of that term [Chocolate Candy Bar]
negative match -keyword
Excludes searches with the
negative term
-Vanilla
Broad
Phrase
Exact
Source: Google](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sem101-130516143253-phpapp02/85/Sem-101-28-320.jpg)


![3. Exact Match
Exact Match is the most targeted option
• You ad will appear only when the specific term in a specified
order is typed in by a person searching
– Example: [candy bar] would only appear if only those two words were
typed and only in that order.
• Use brackets to define the words
• Your ad will not show if there are other terms in the query
– Example: Your ad won't show for Vanilla Candy Bars
• You will receive less impressions but you'll likely generate
higher click through rates because users searching for the
terms may want precisely what you have to offer.
– Less Volume, Highest CTR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sem101-130516143253-phpapp02/85/Sem-101-31-320.jpg)
