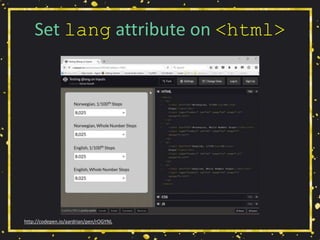
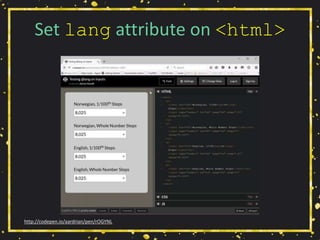
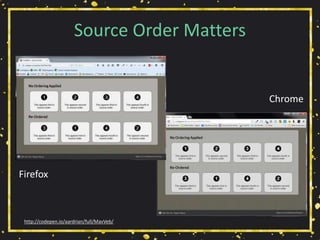
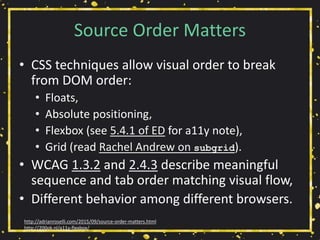
The document presents a workshop by Adrian Roselli on web accessibility (a11y), covering key statistics, user experiences, and practical exercises towards improving site accessibility. It highlights the importance of creating web environments that accommodate individuals with various disabilities, including vision, hearing, mobility, and cognitive impairments. The workshop emphasizes strategies, technical guidelines, and the need for inclusivity in web design through collaborative approaches and user-centered stories.
















































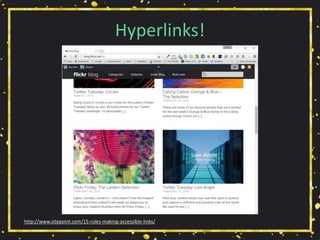









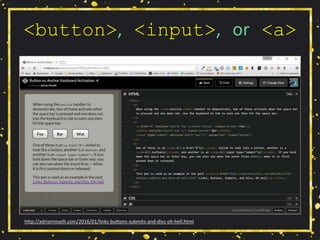
![Use Link Underlines
• You are not Google:
• Users know Google’s layout,
• Users probably don’t visit your site daily.
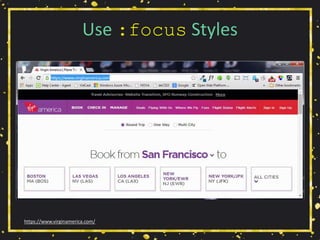
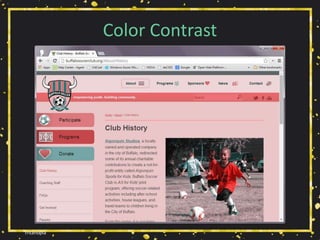
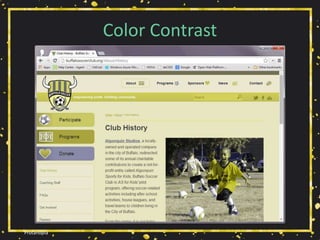
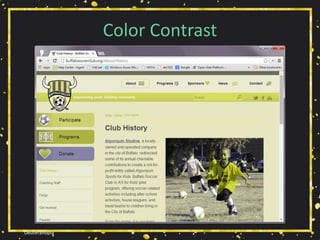
• Relying on color alone will not suffice (WCAG
1.4.1 [A], 1.4.3 [AA]),
• Necessary contrast values:
• 4.5:1 between text and its background for copy,
• 3:1 between text and its background for larger text,
• 3:1 between surrounding text and a hyperlink, plus an
additional visual cue (G183).
http://adrianroselli.com/2014/03/i-dont-care-what-google-did-just-keep.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selfishaccessibility-createupstate2016-160513011725/85/Selfish-Accessibility-for-Create-Upstate-2016-67-320.jpg)









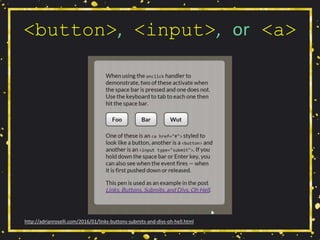


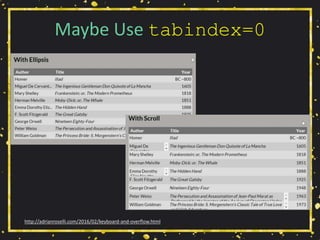
![Maybe Use tabindex=0
• Do you have scrolling content boxes?
• Keyboard users cannot access it.
• Do you have content that displays on hover?
• Keyboard users probably cannot access it.
• A technique:
• <div role="region" aria-label="[if
appropriate]" tabindex="0">
http://adrianroselli.com/2016/02/keyboard-and-overflow.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selfishaccessibility-createupstate2016-160513011725/85/Selfish-Accessibility-for-Create-Upstate-2016-89-320.jpg)