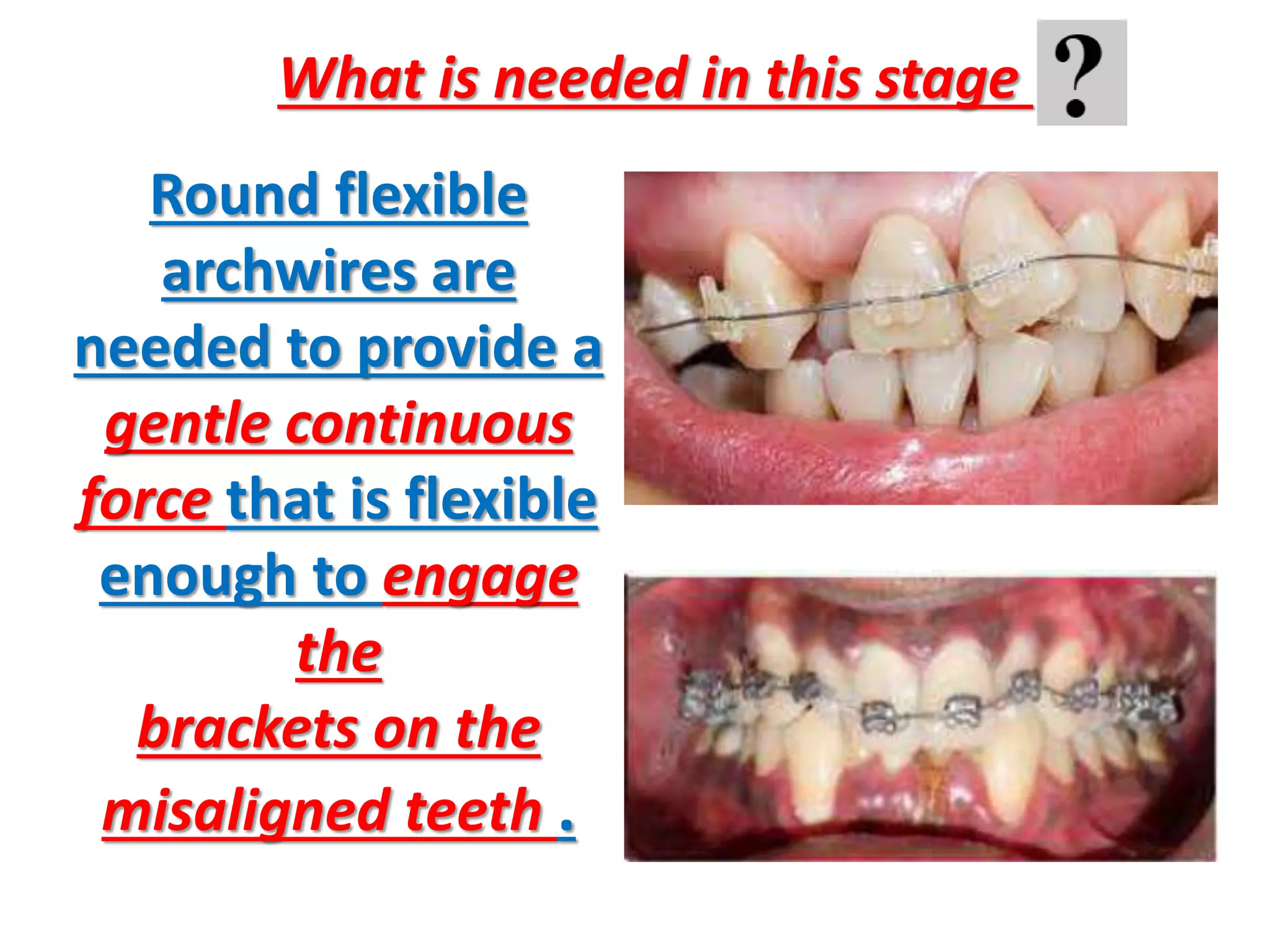
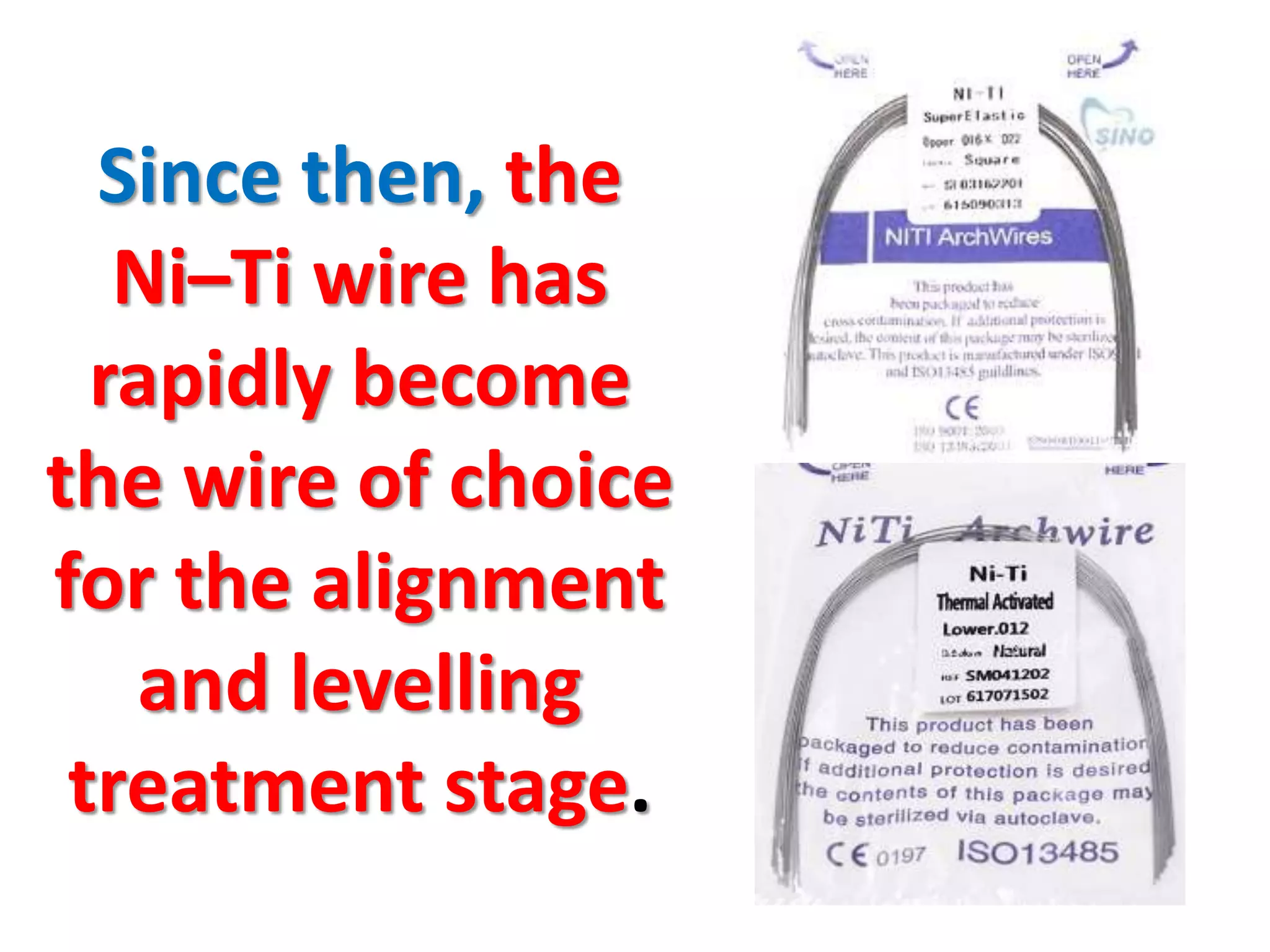
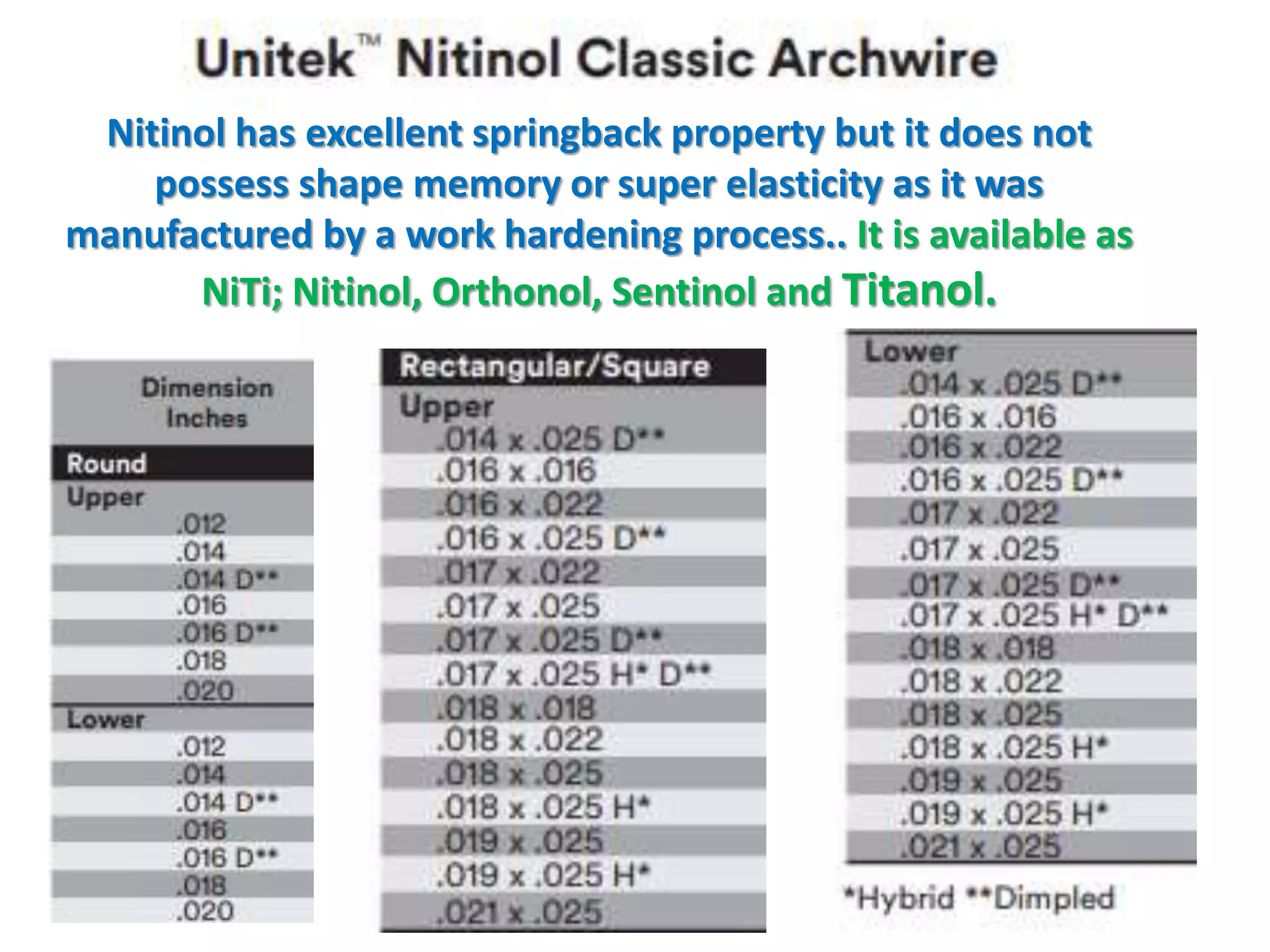
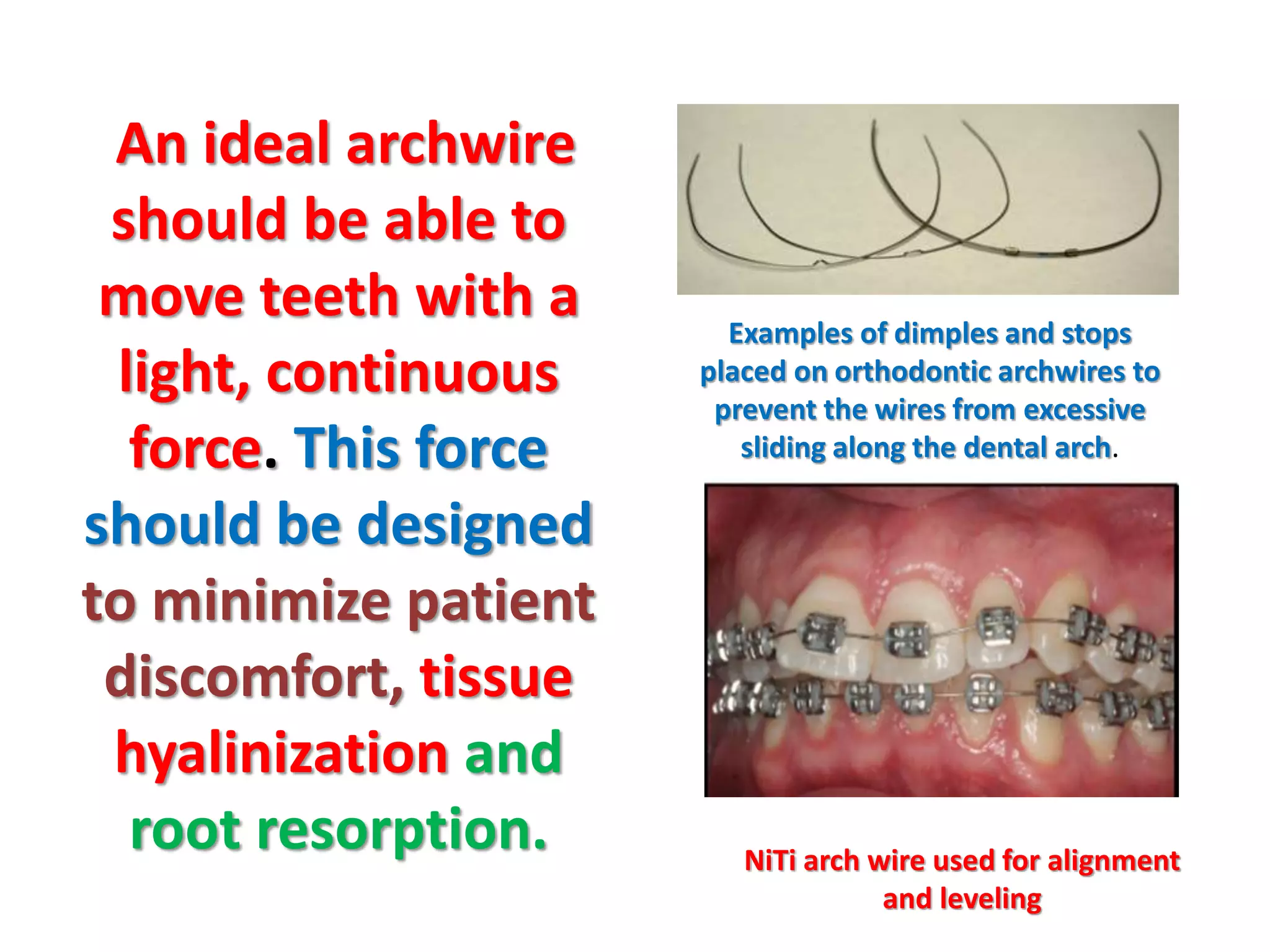
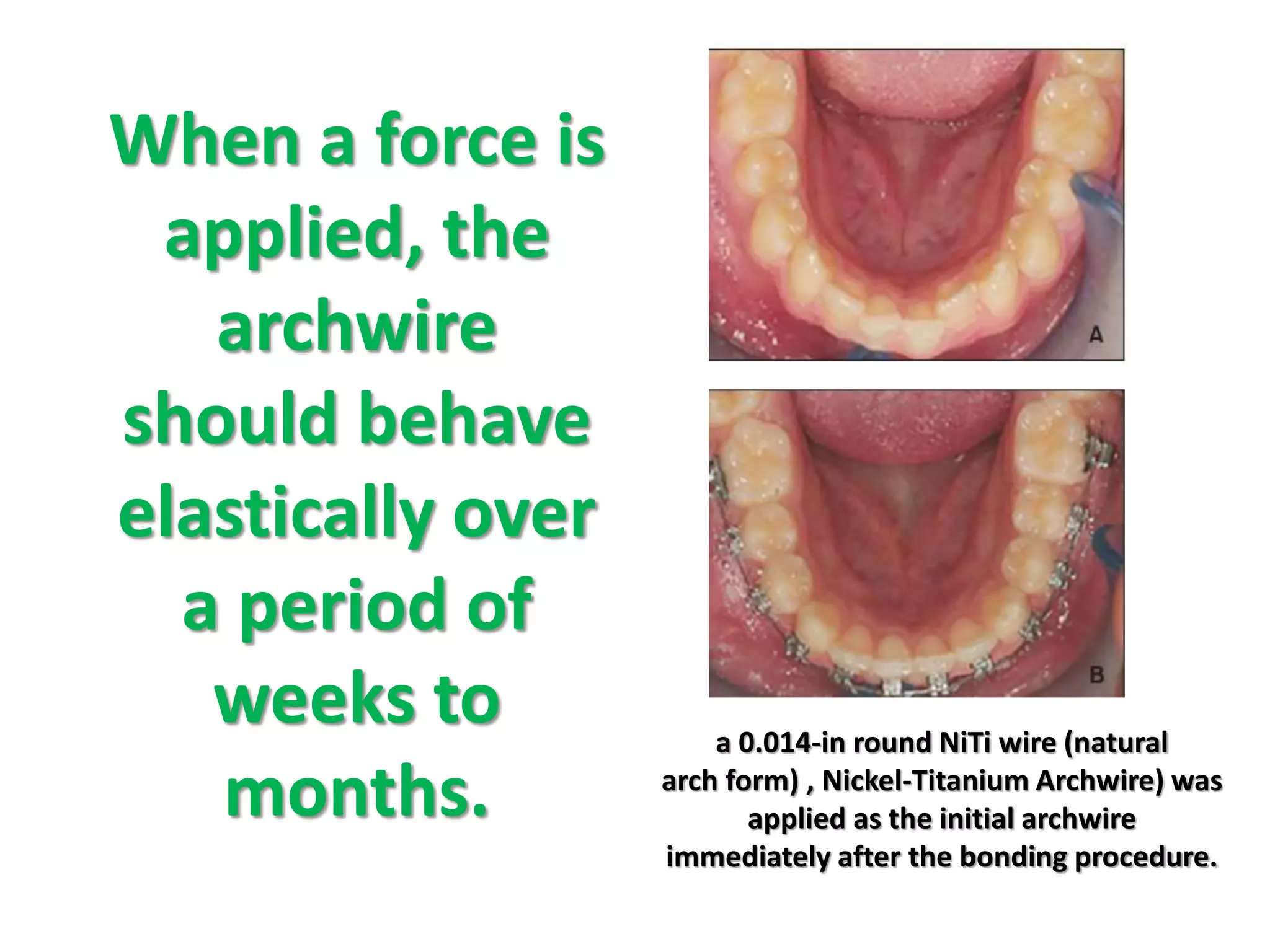
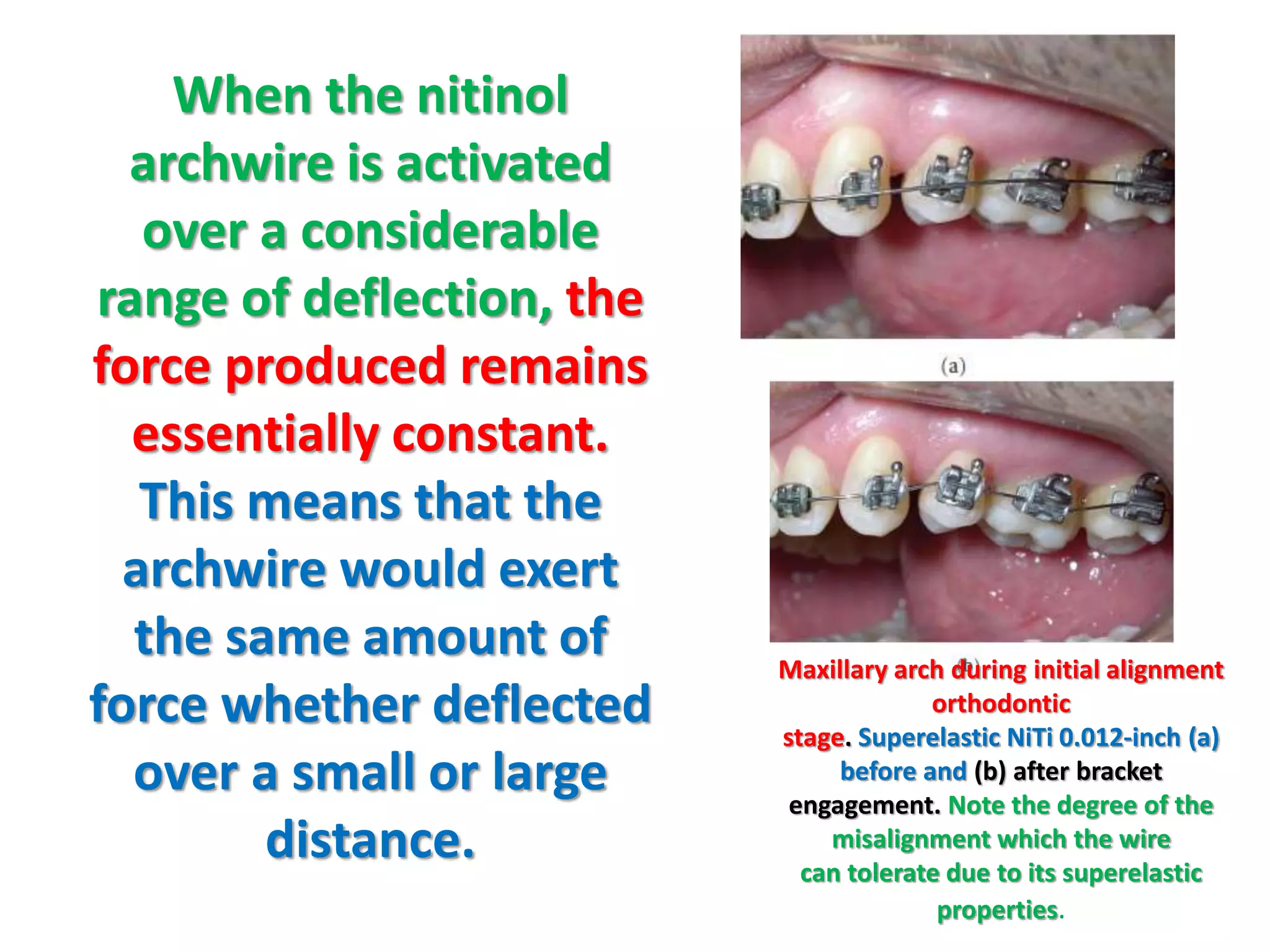
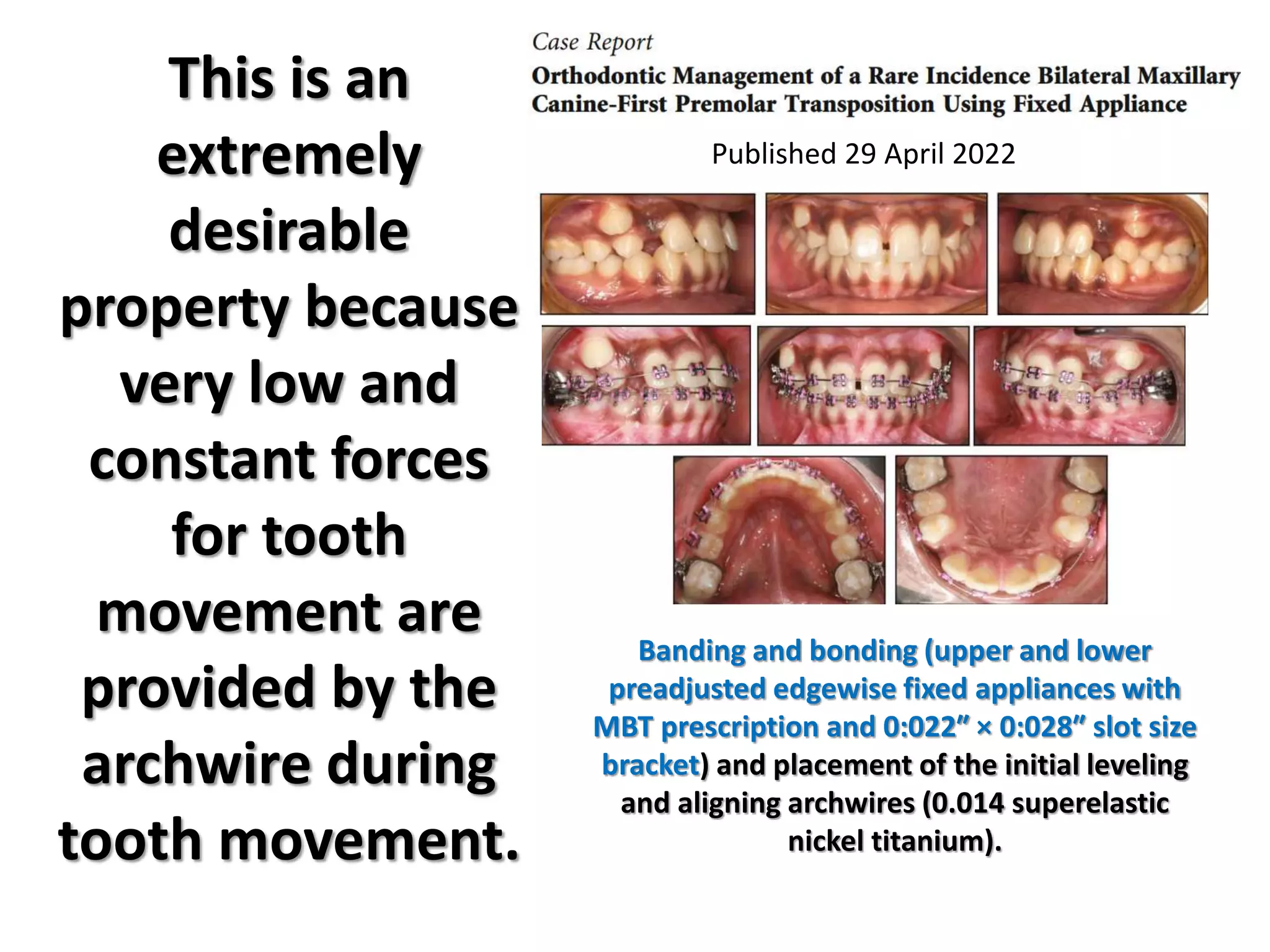
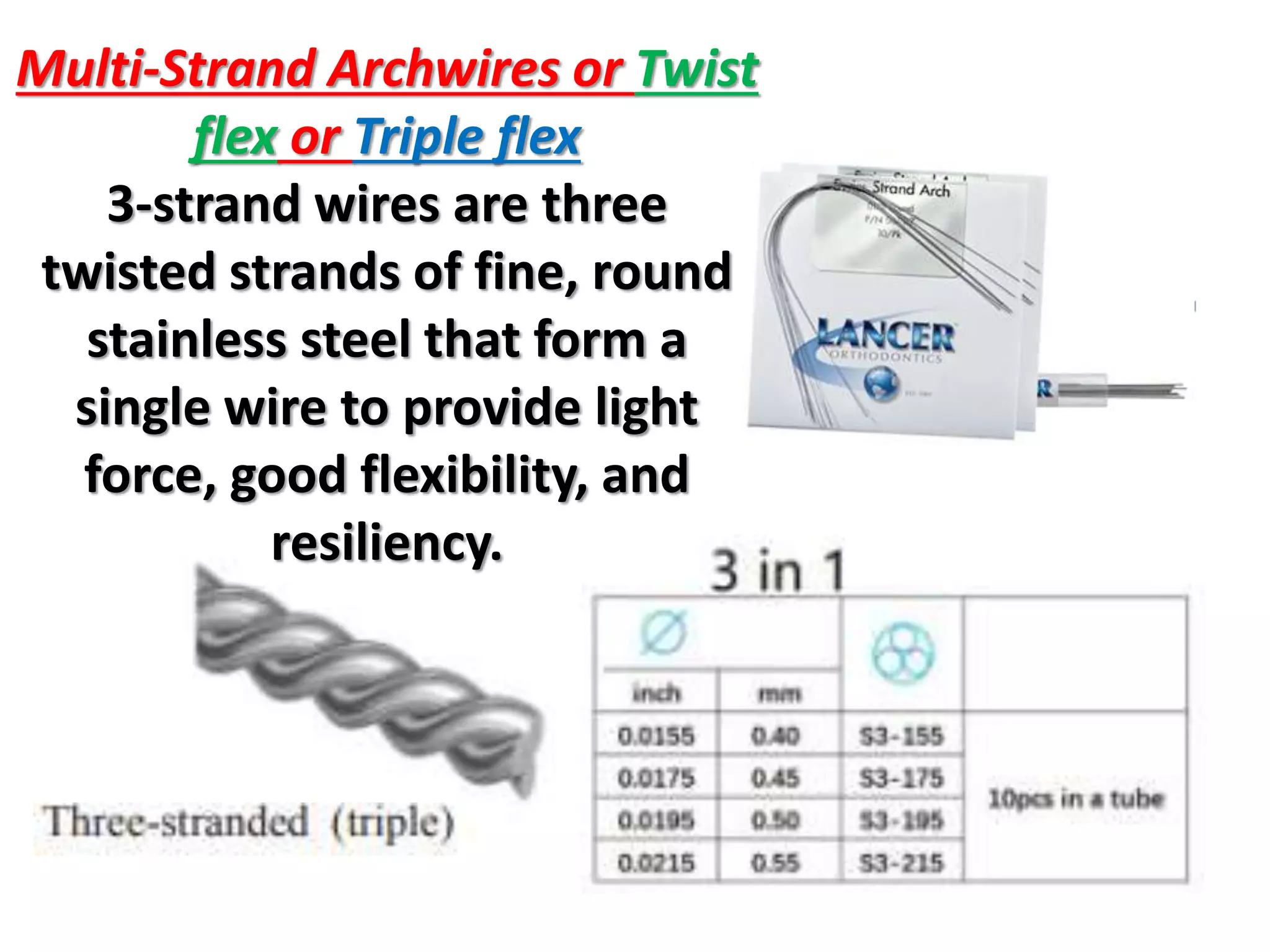
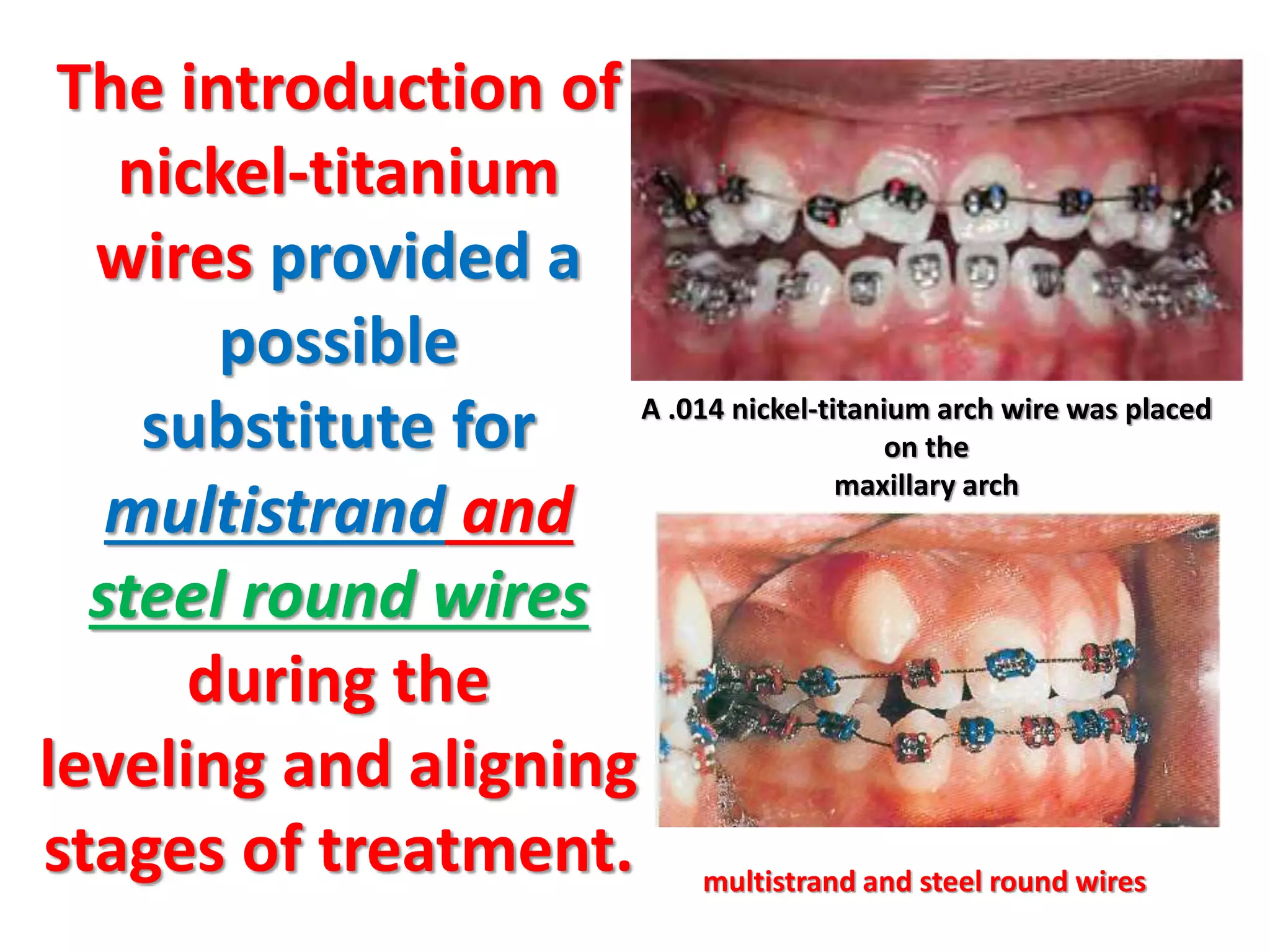
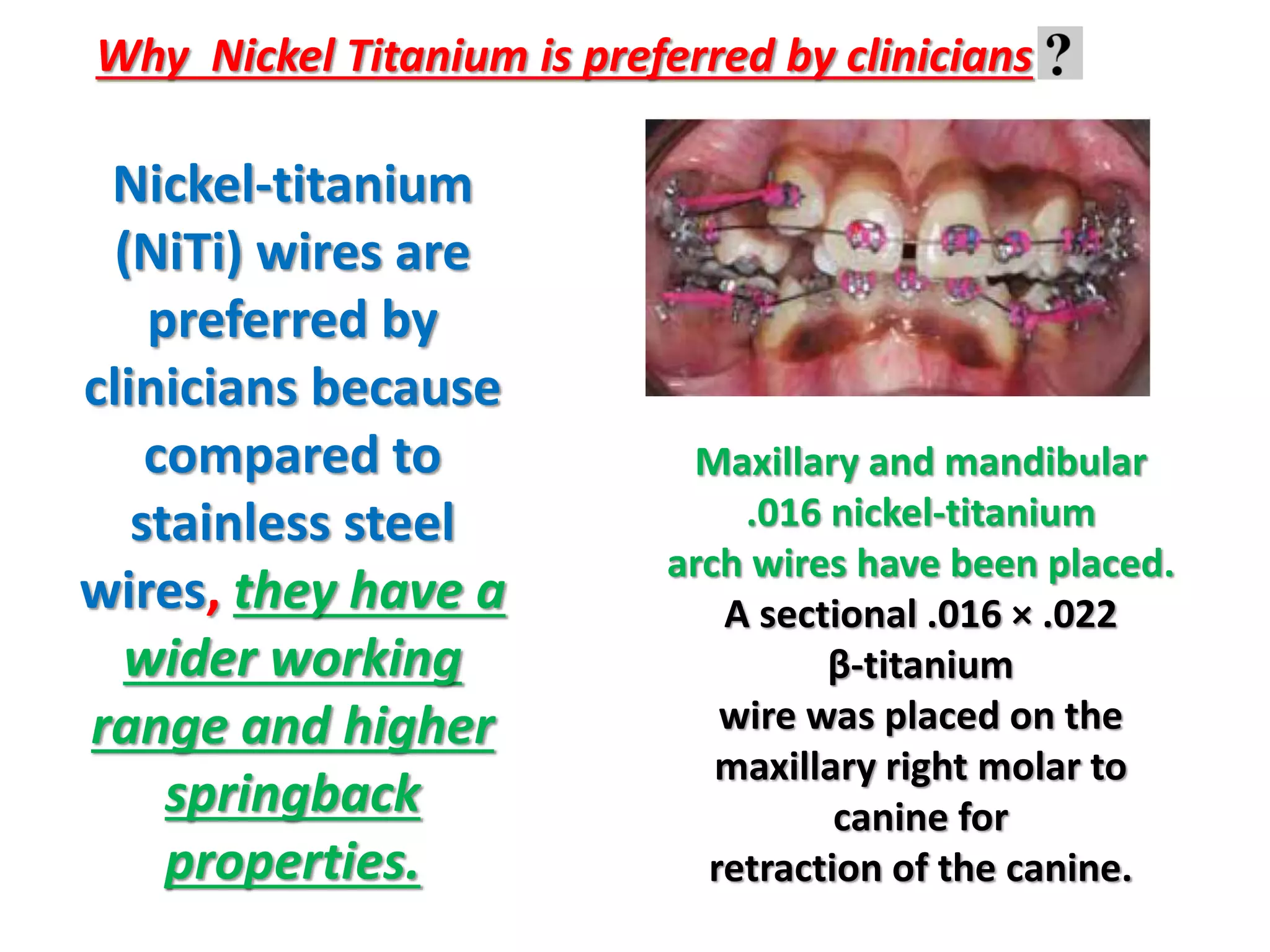
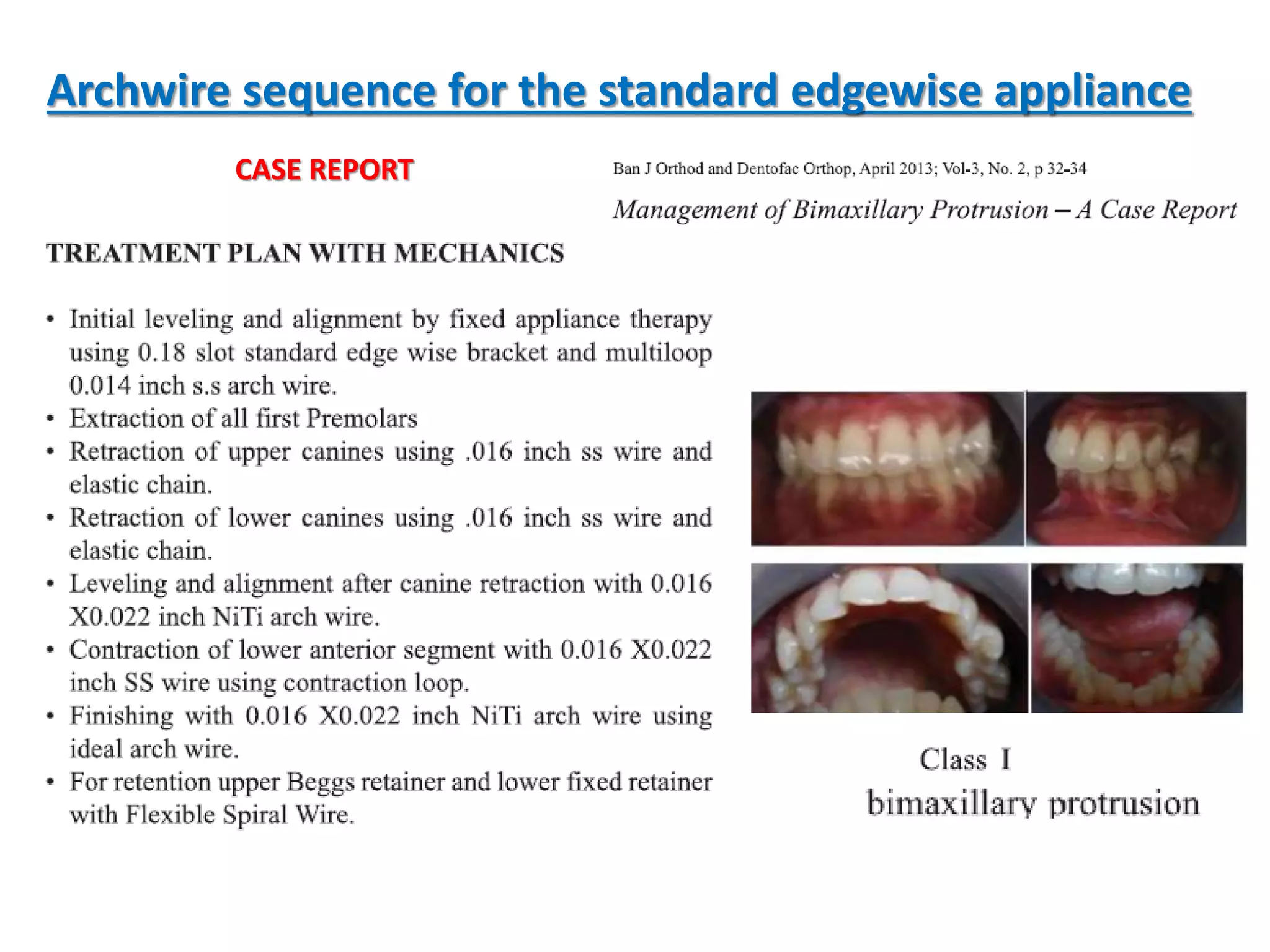
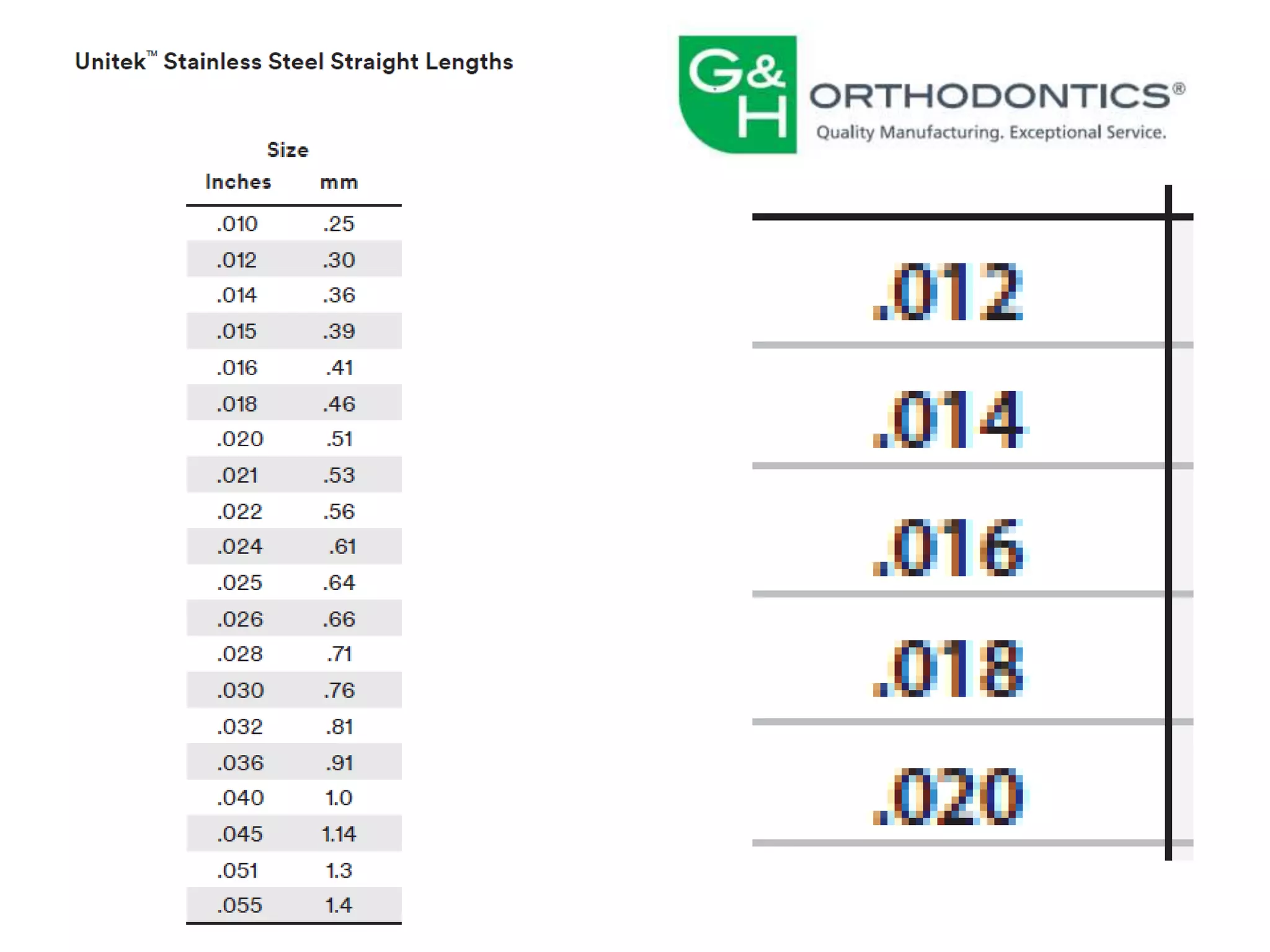
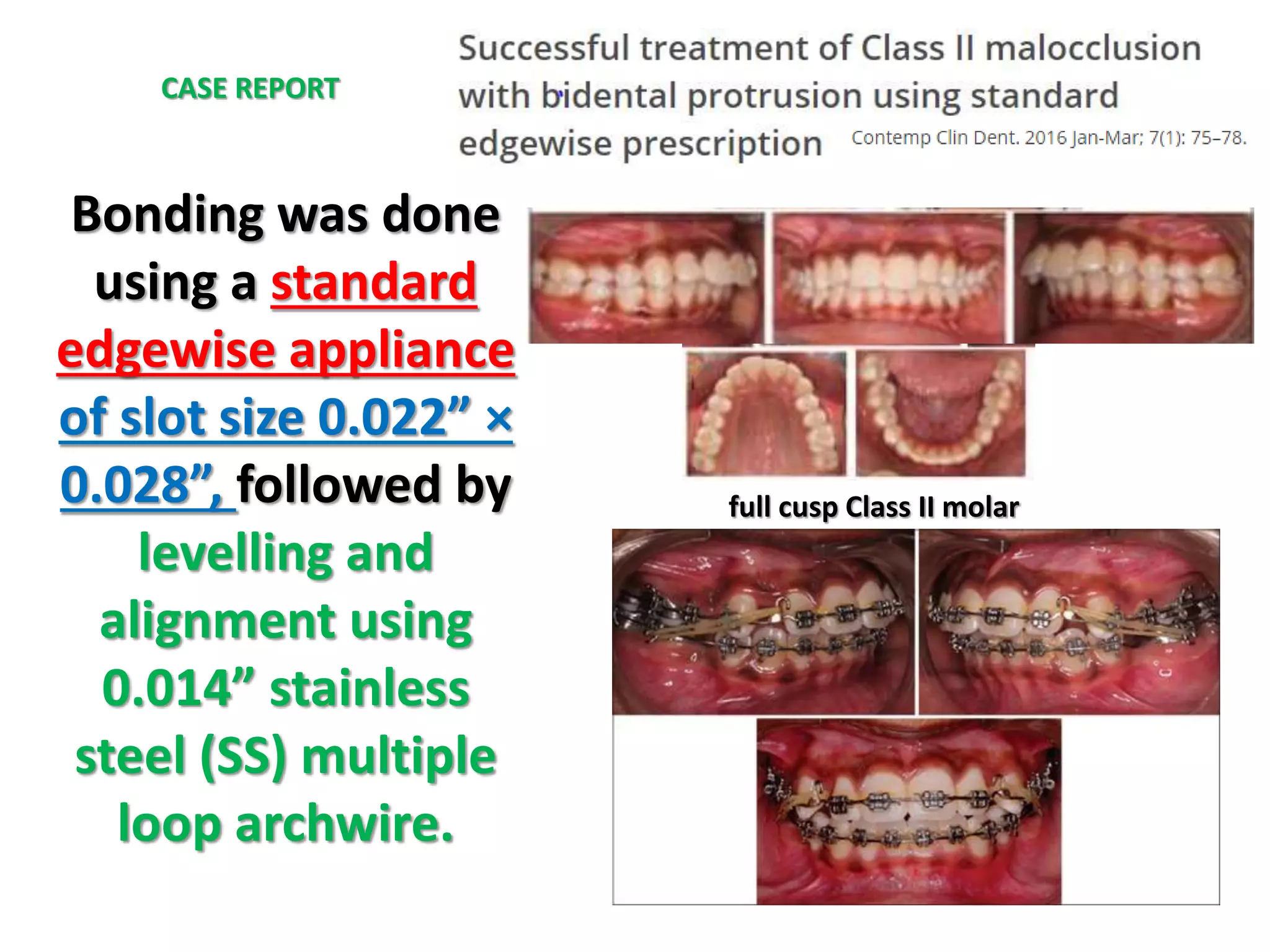
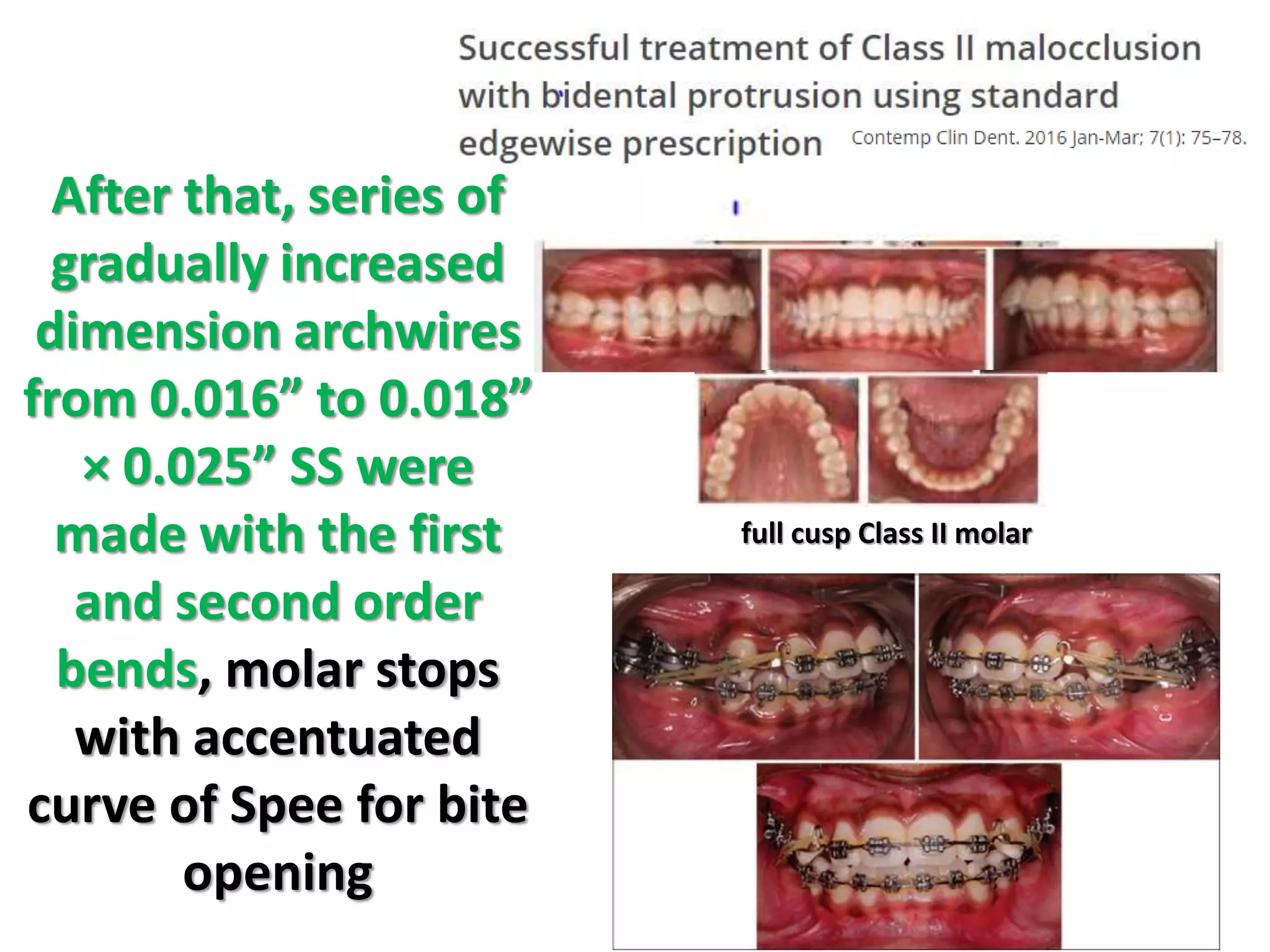
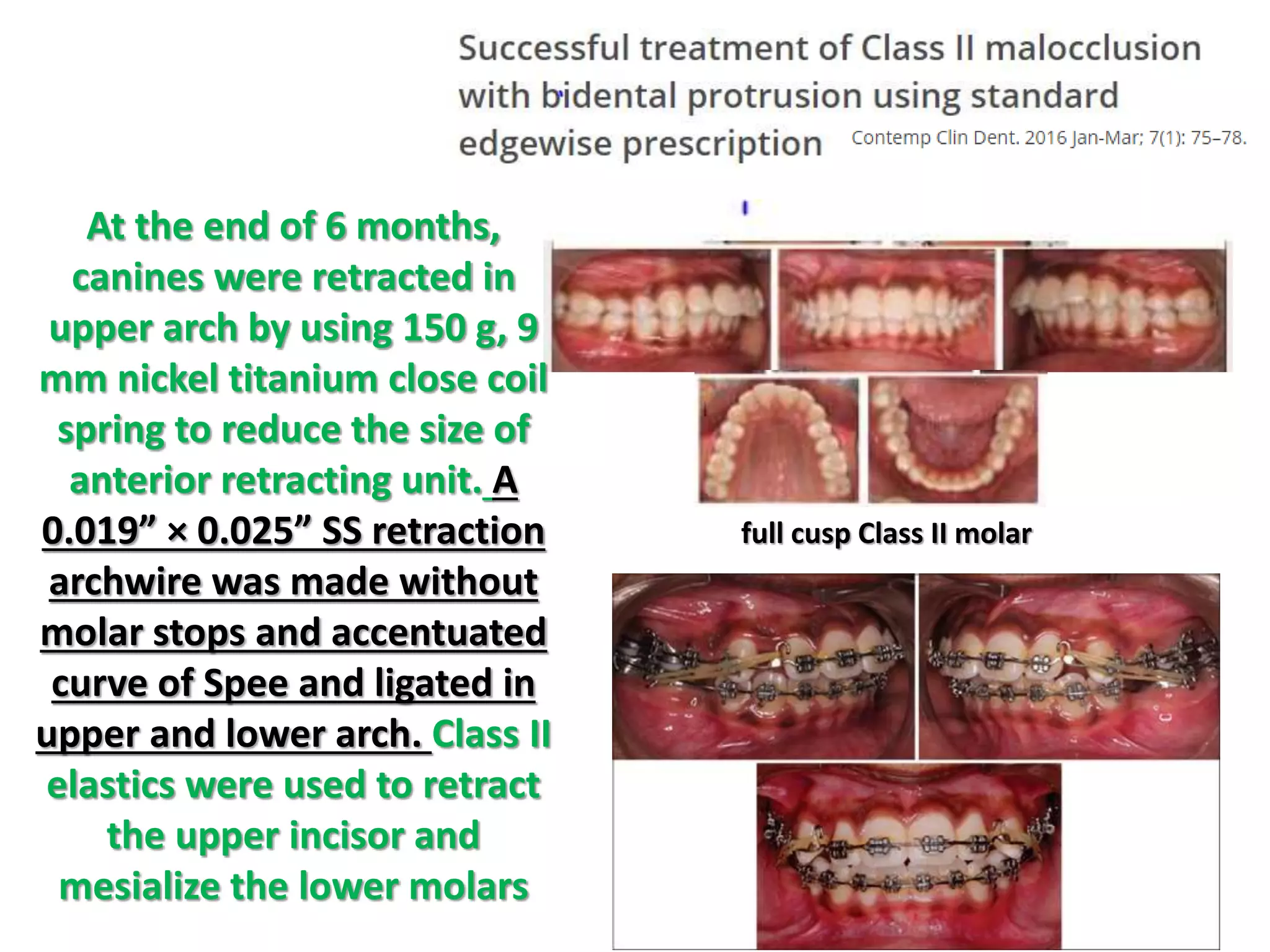
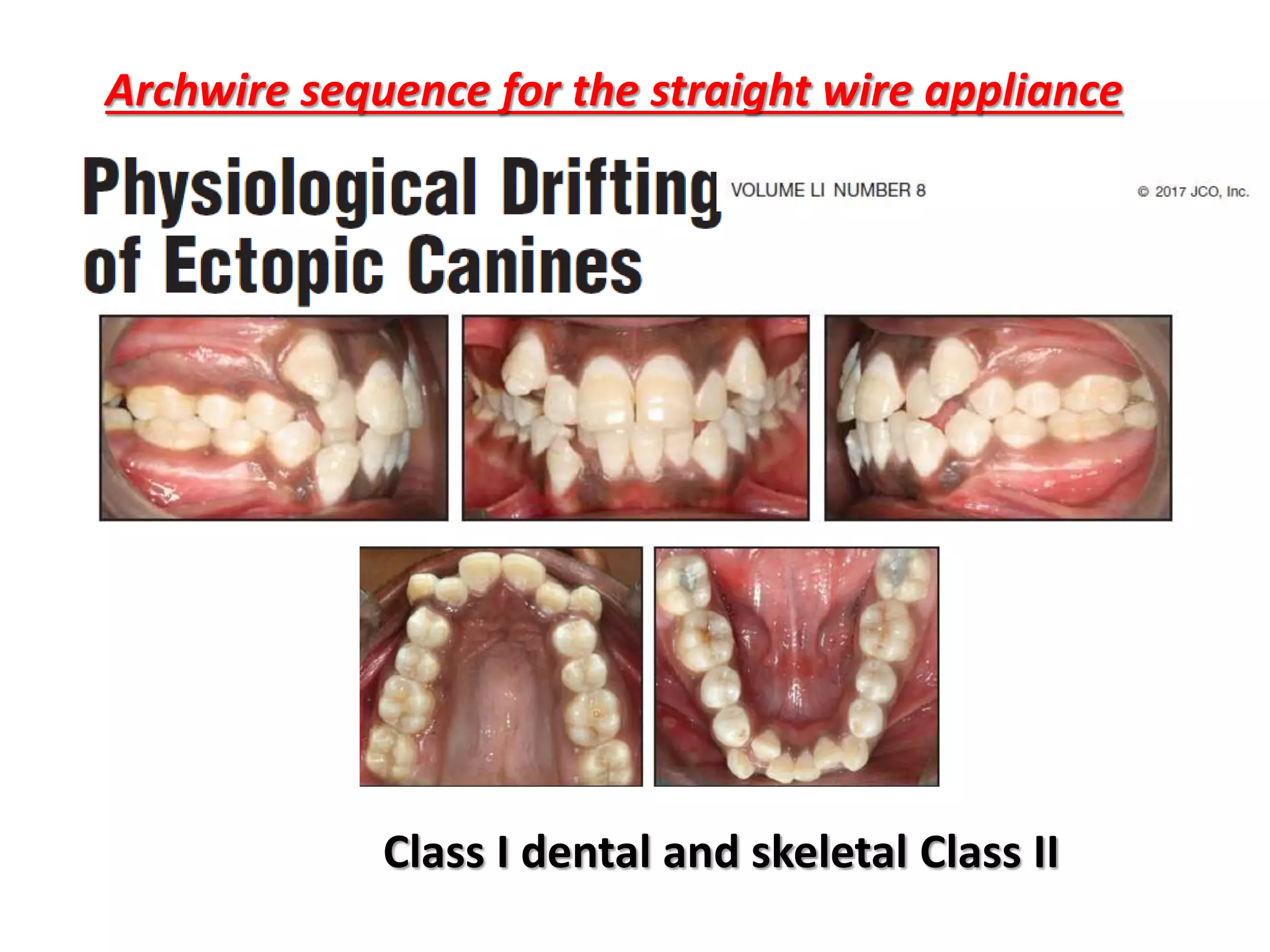
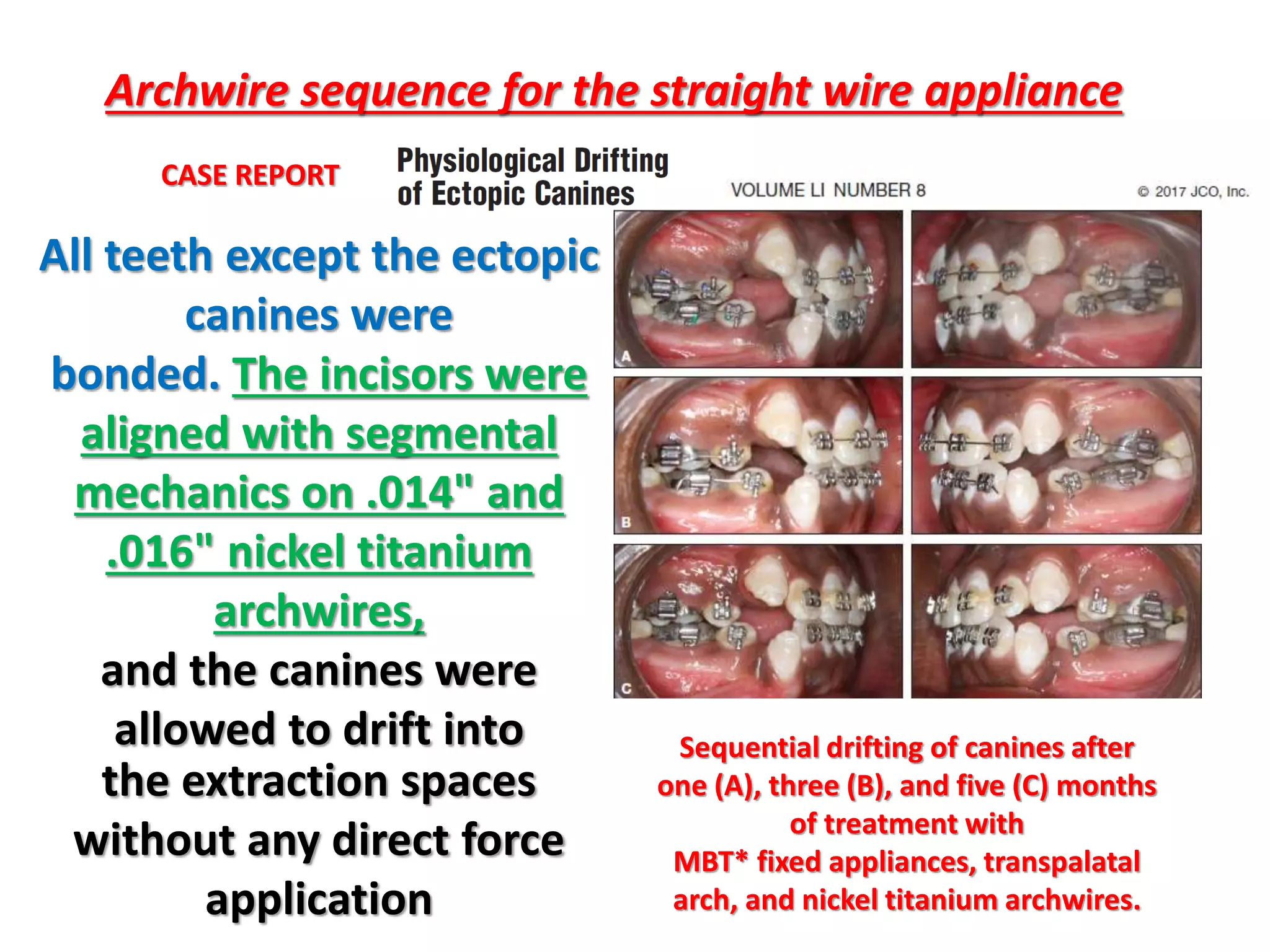
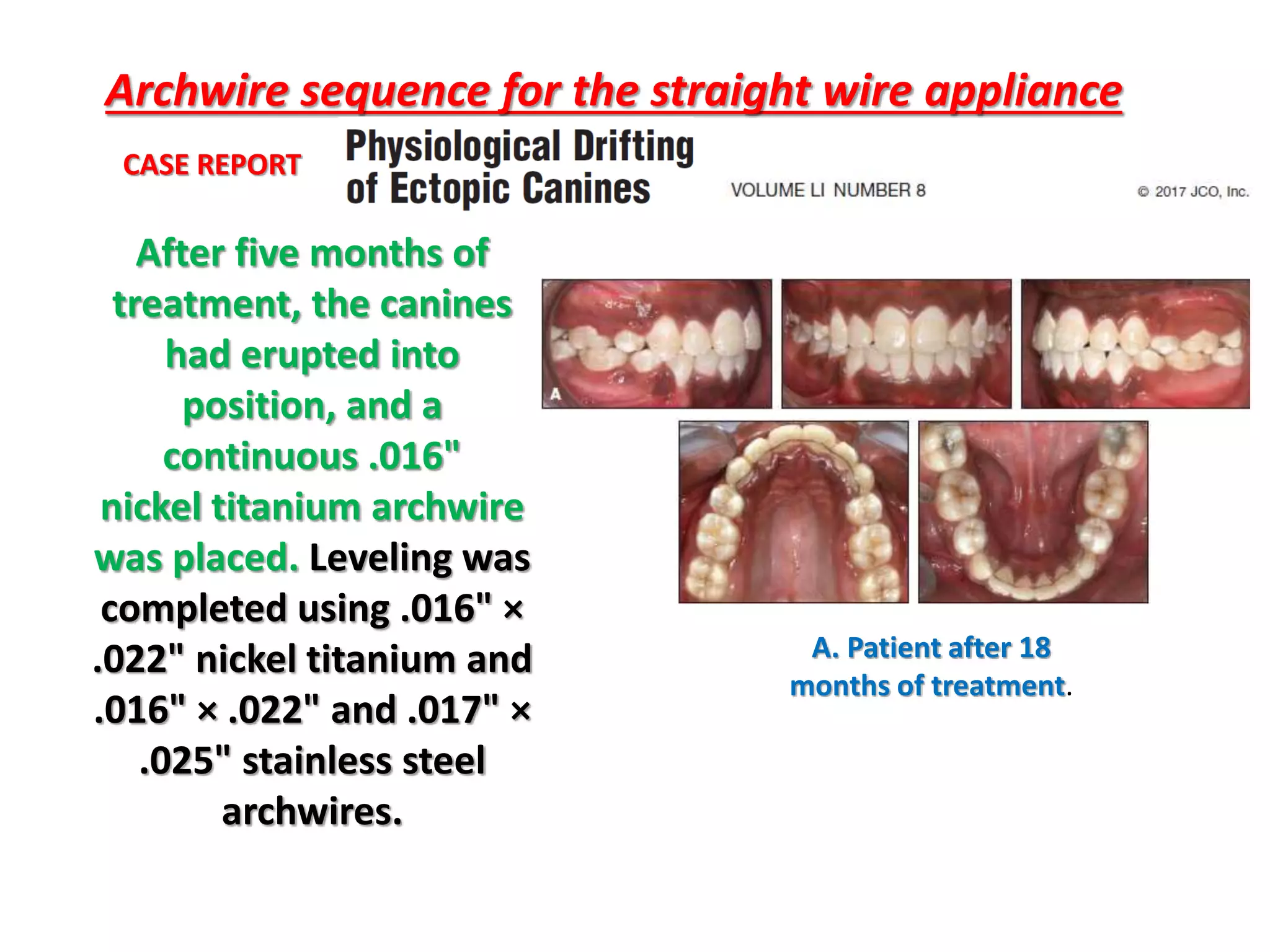
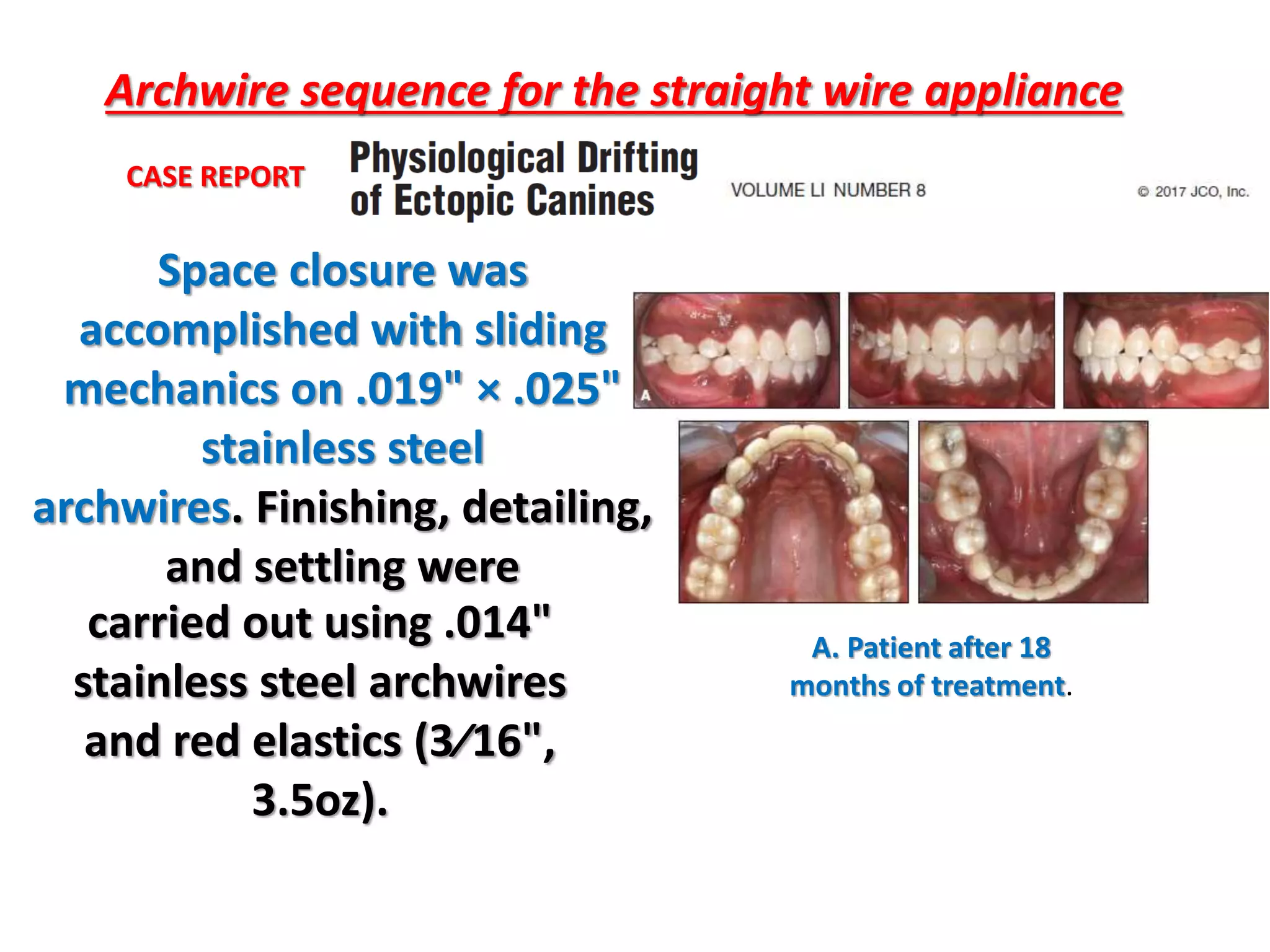
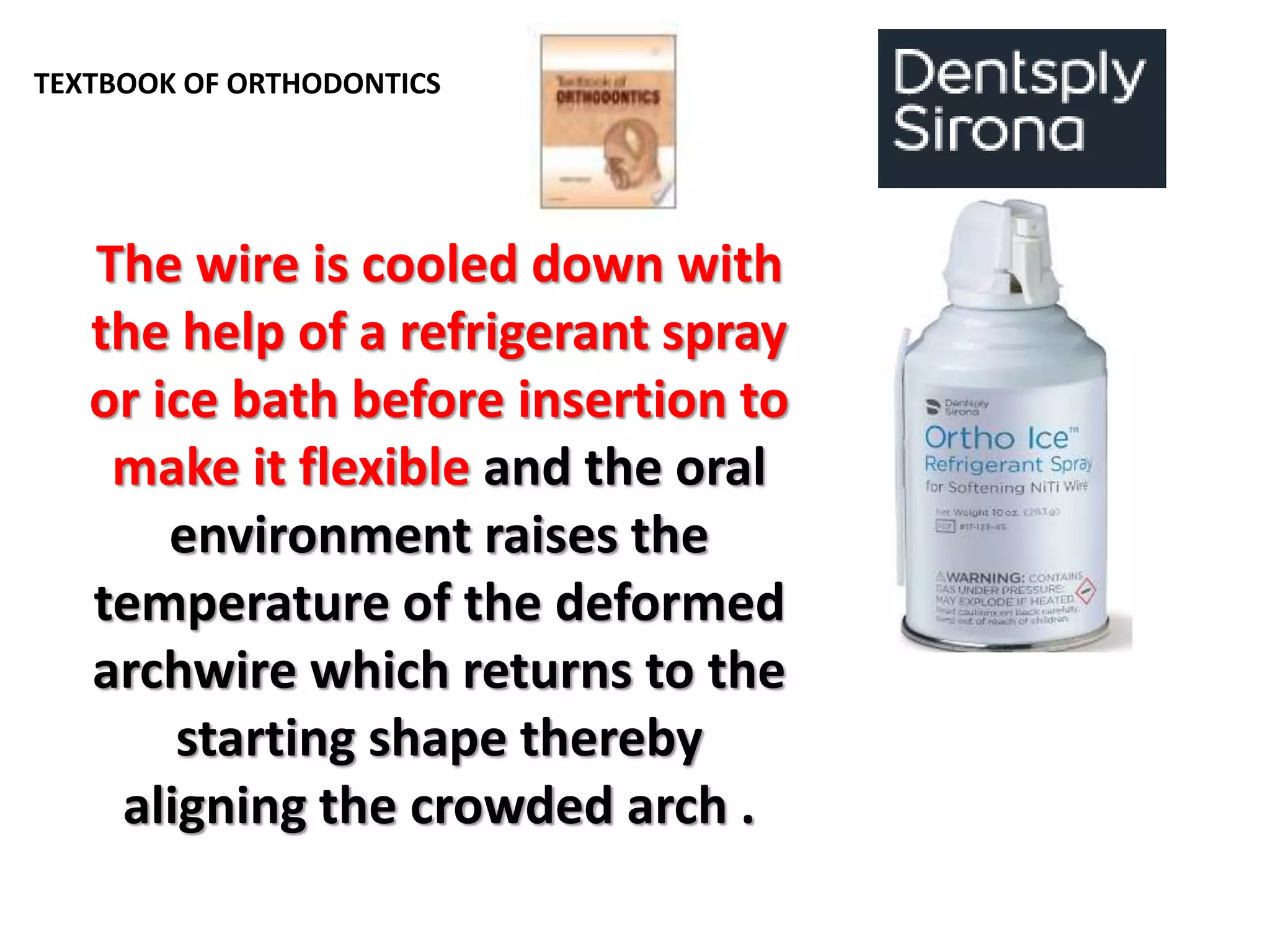
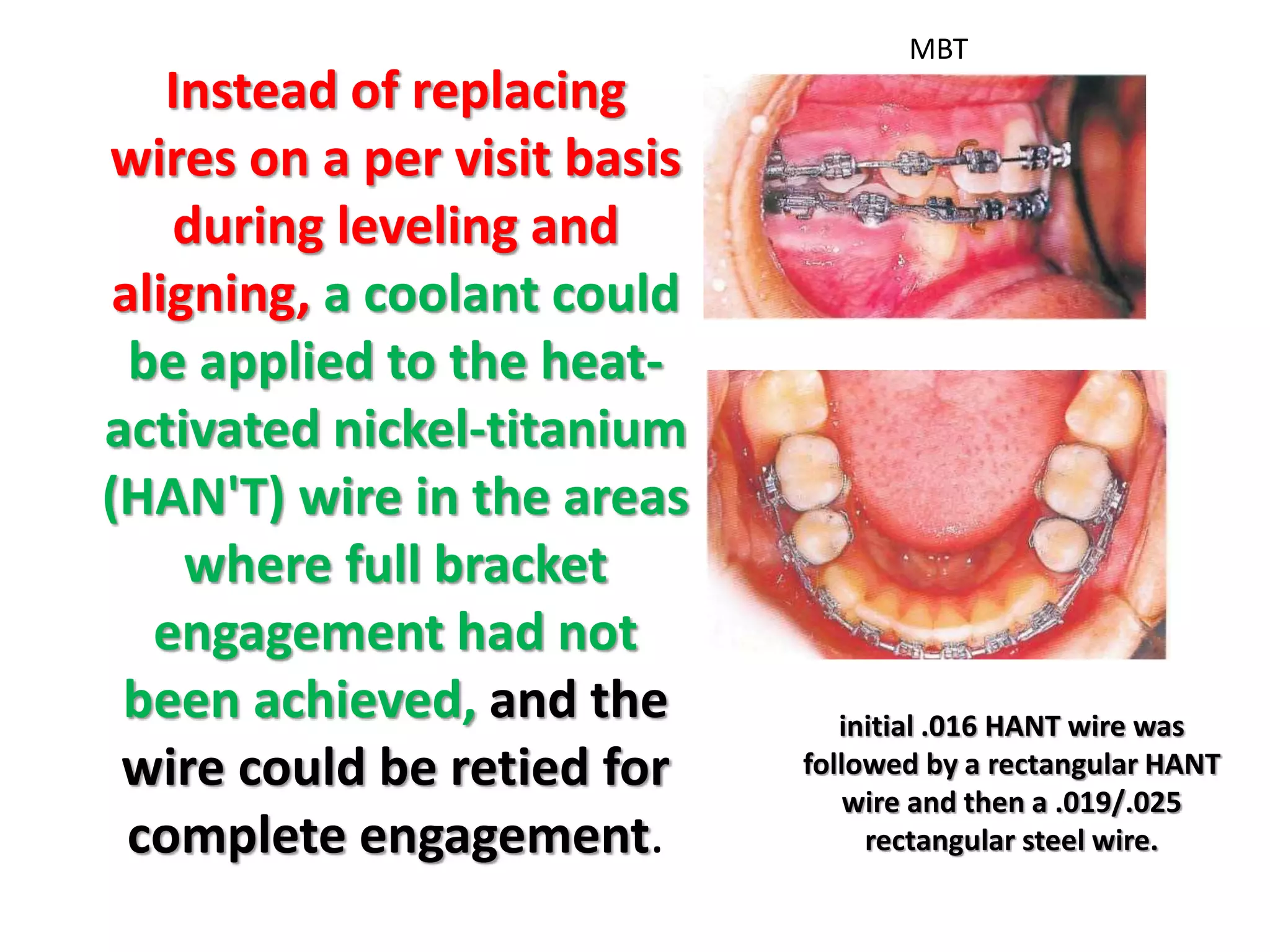
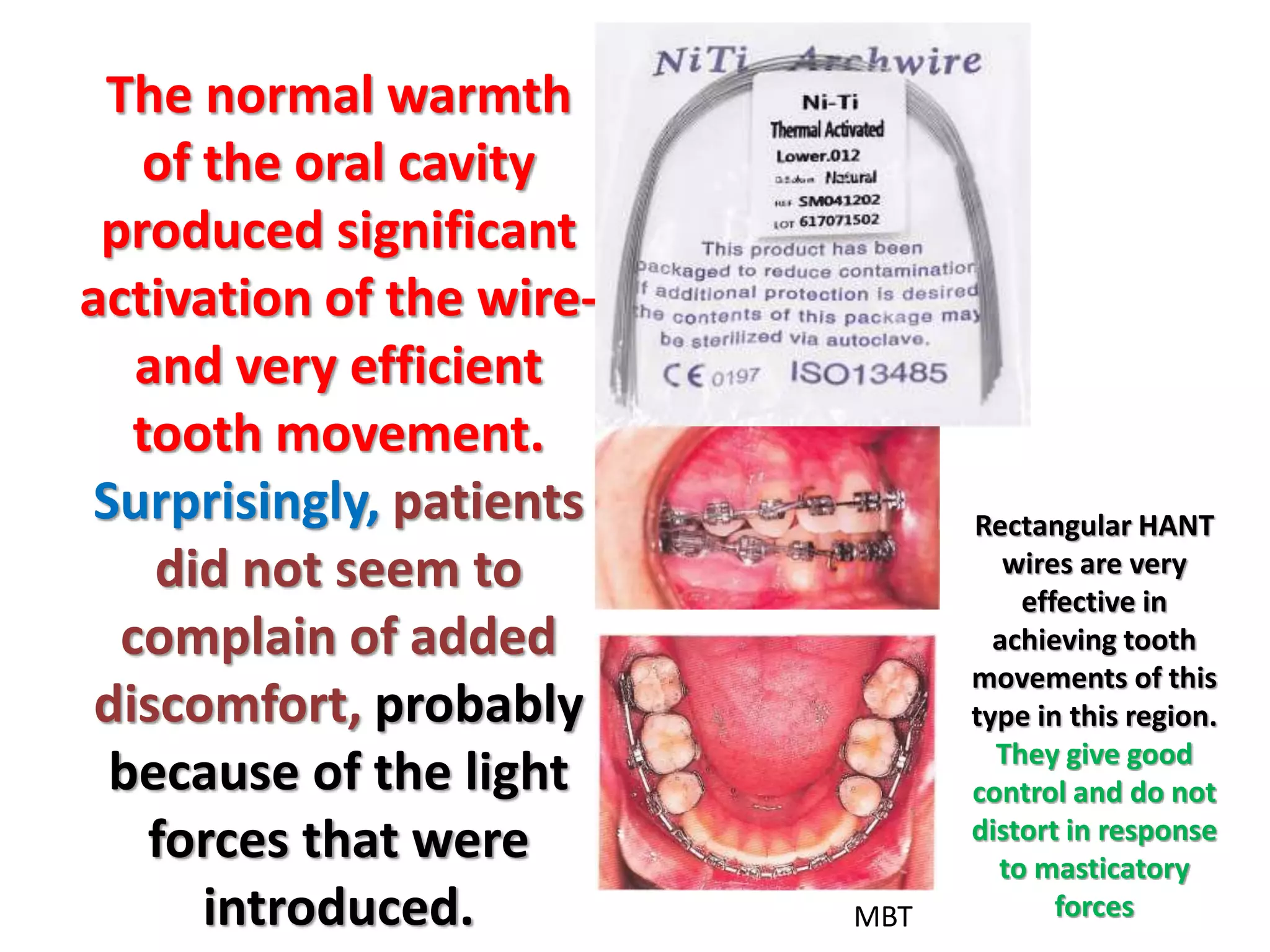
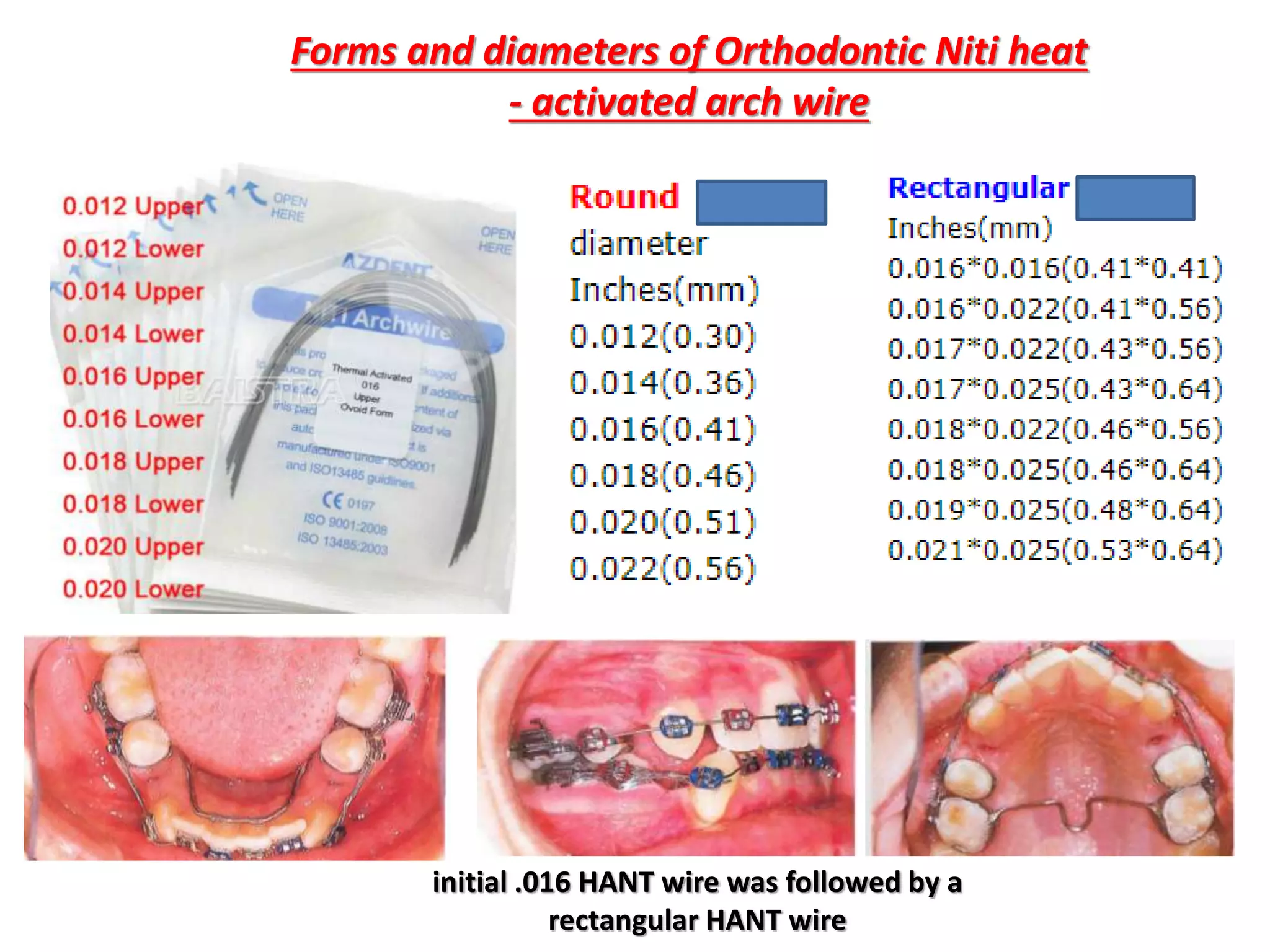
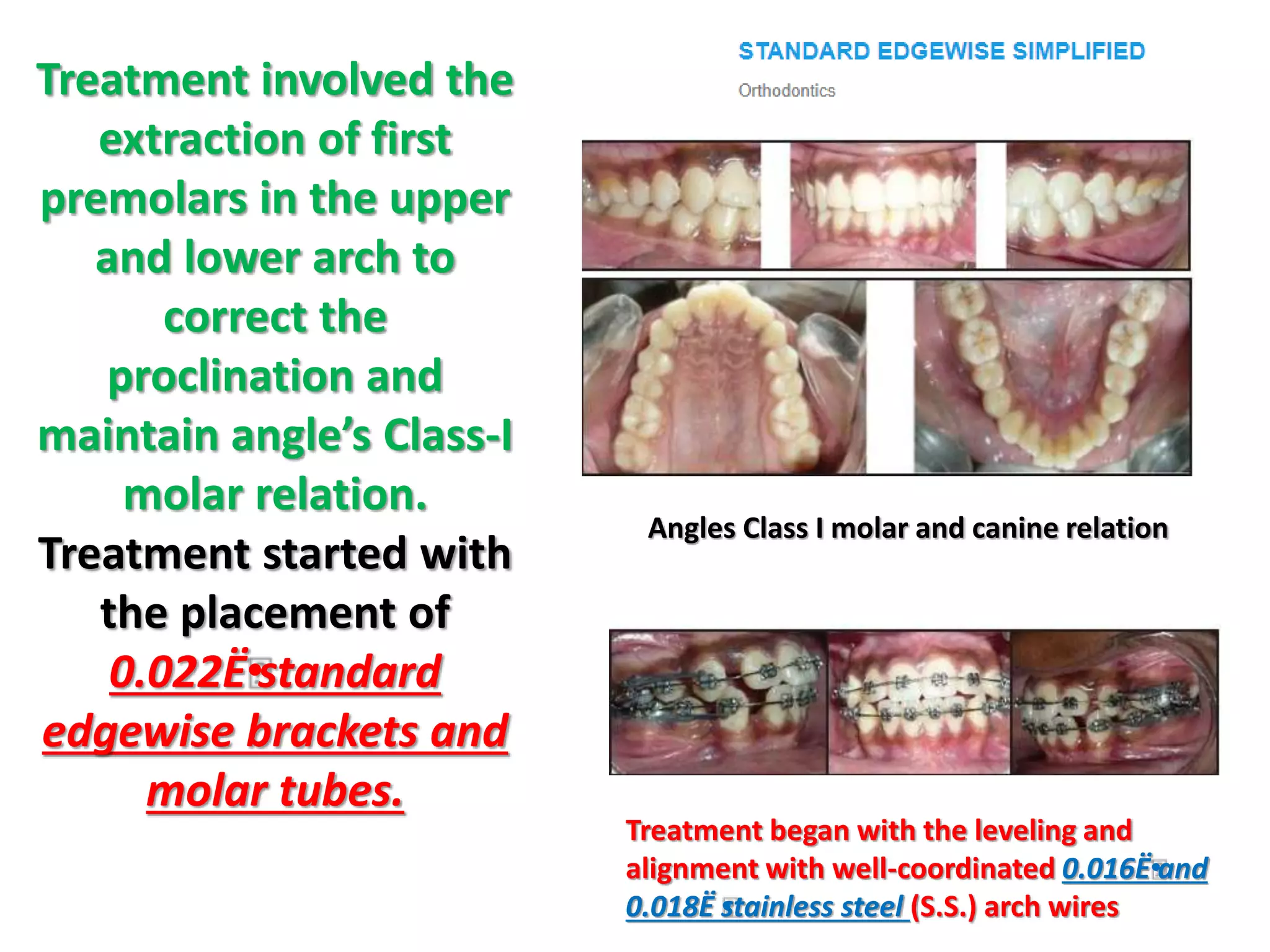
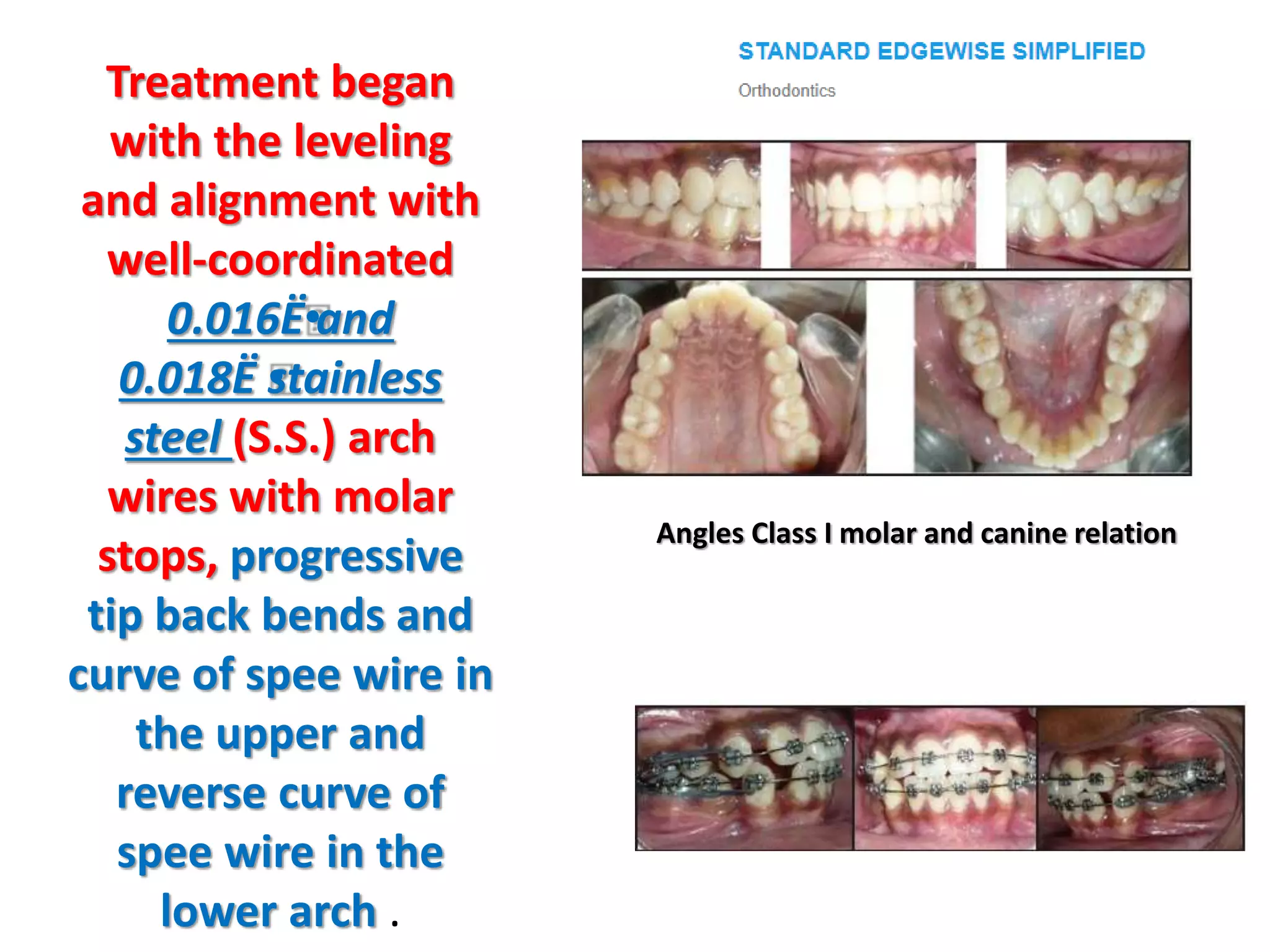
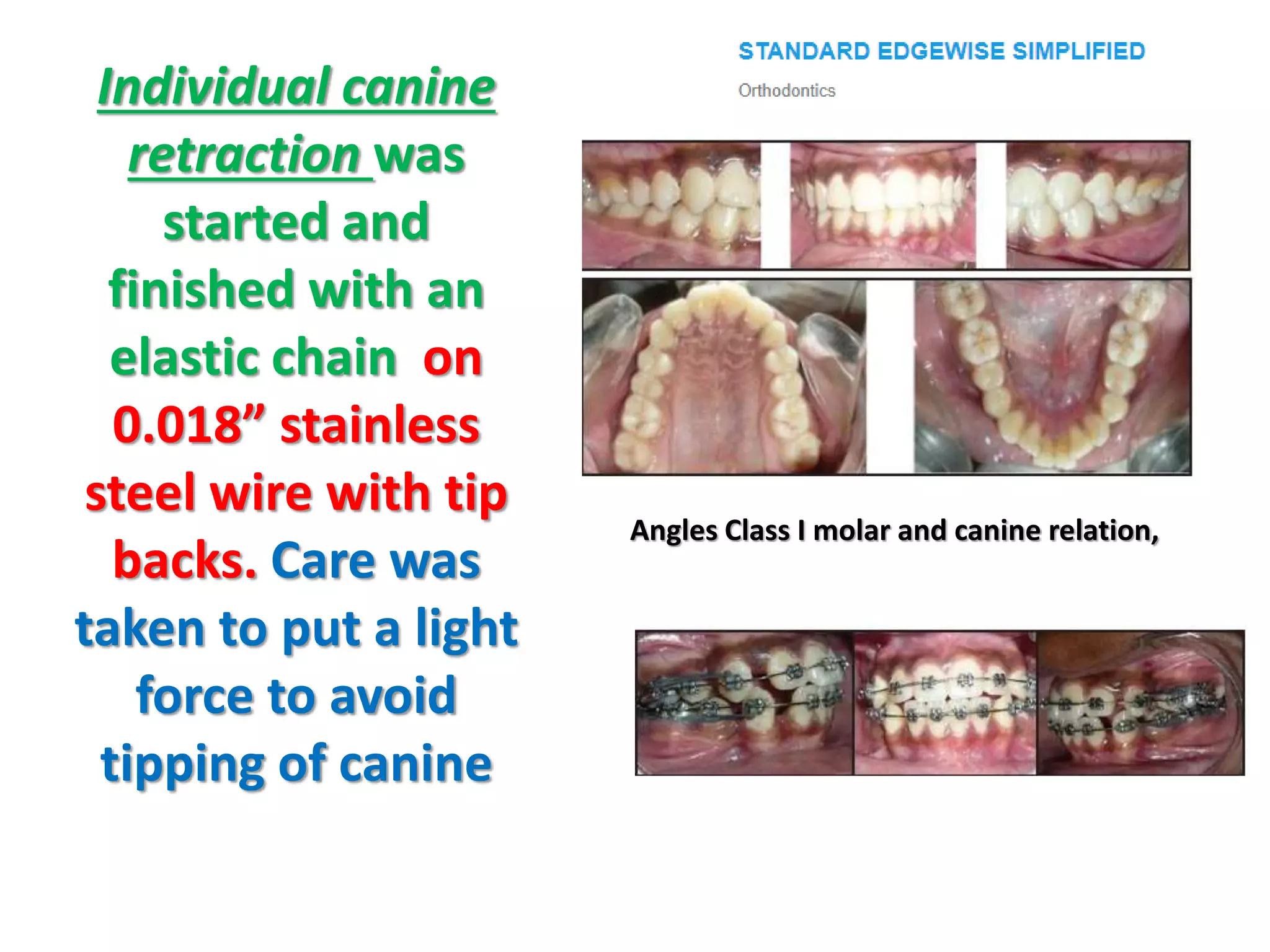
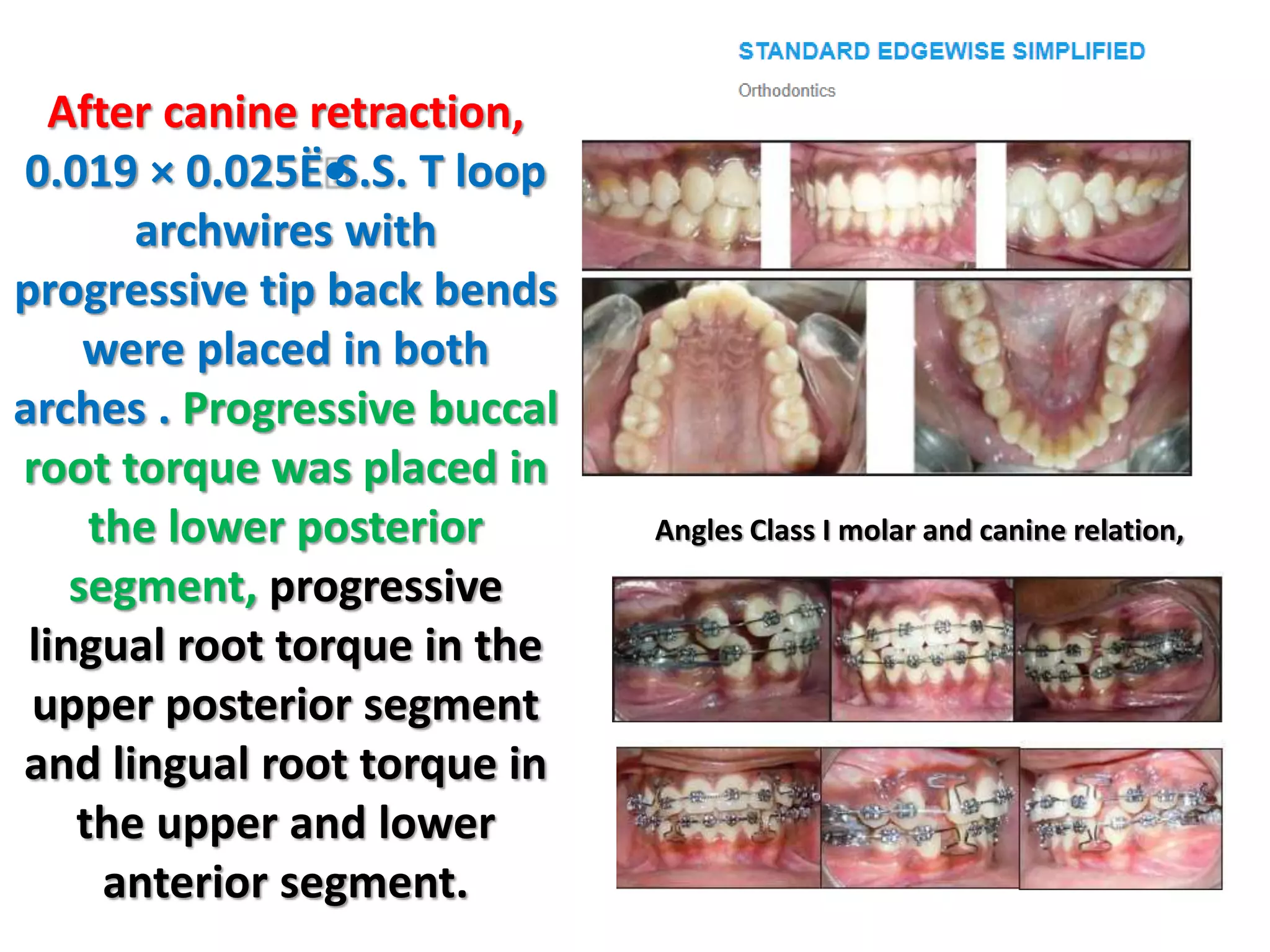
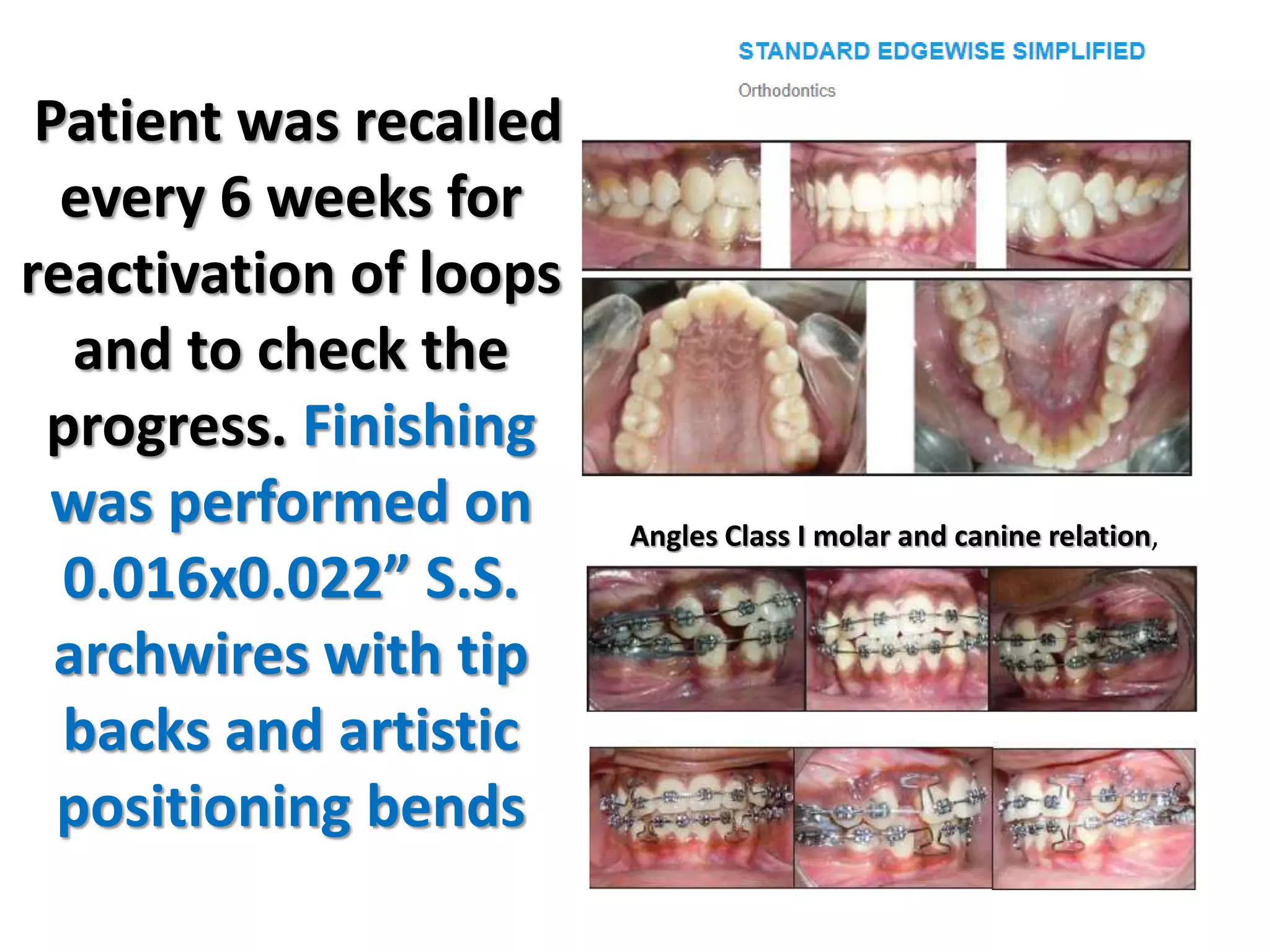
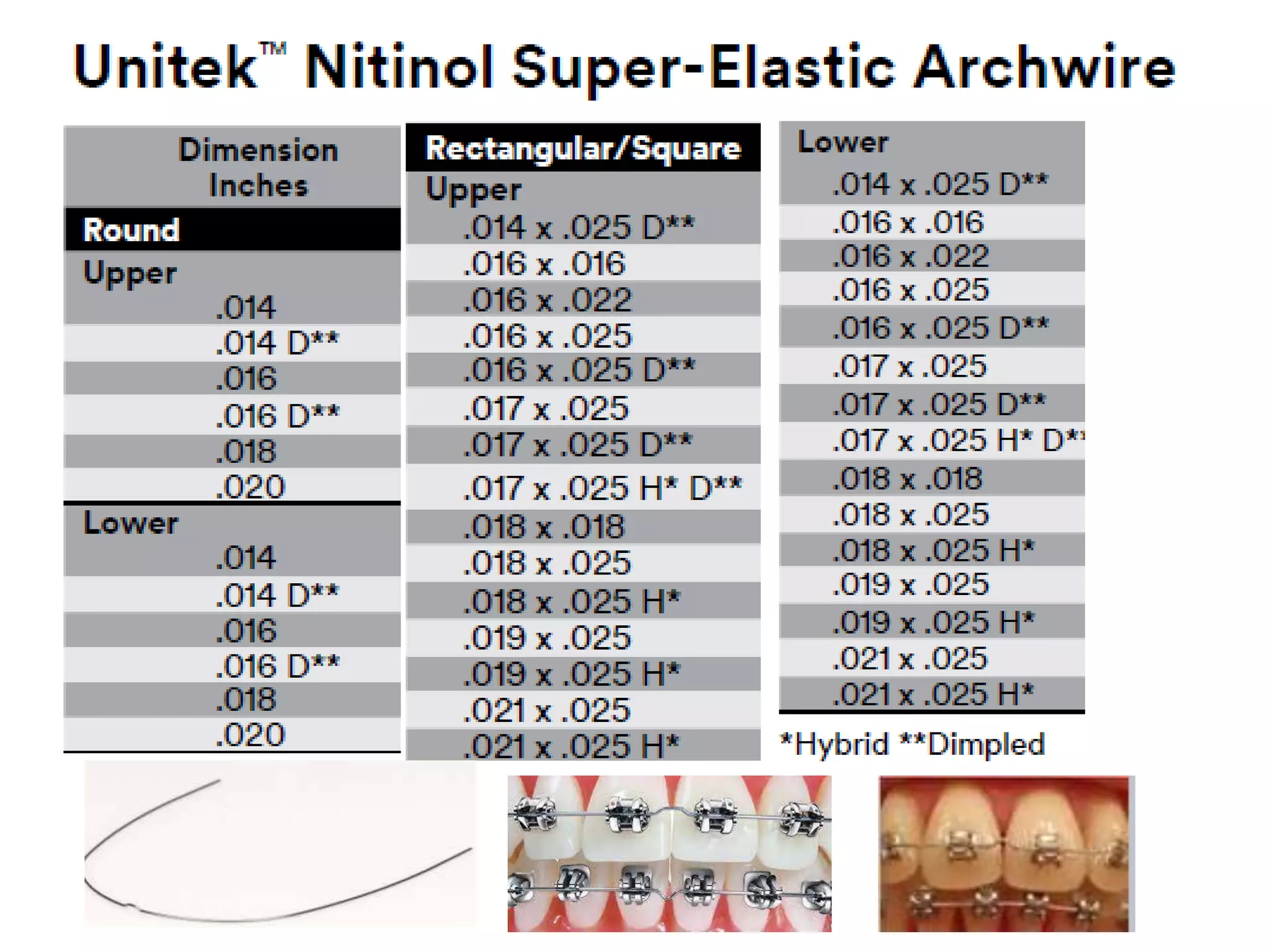
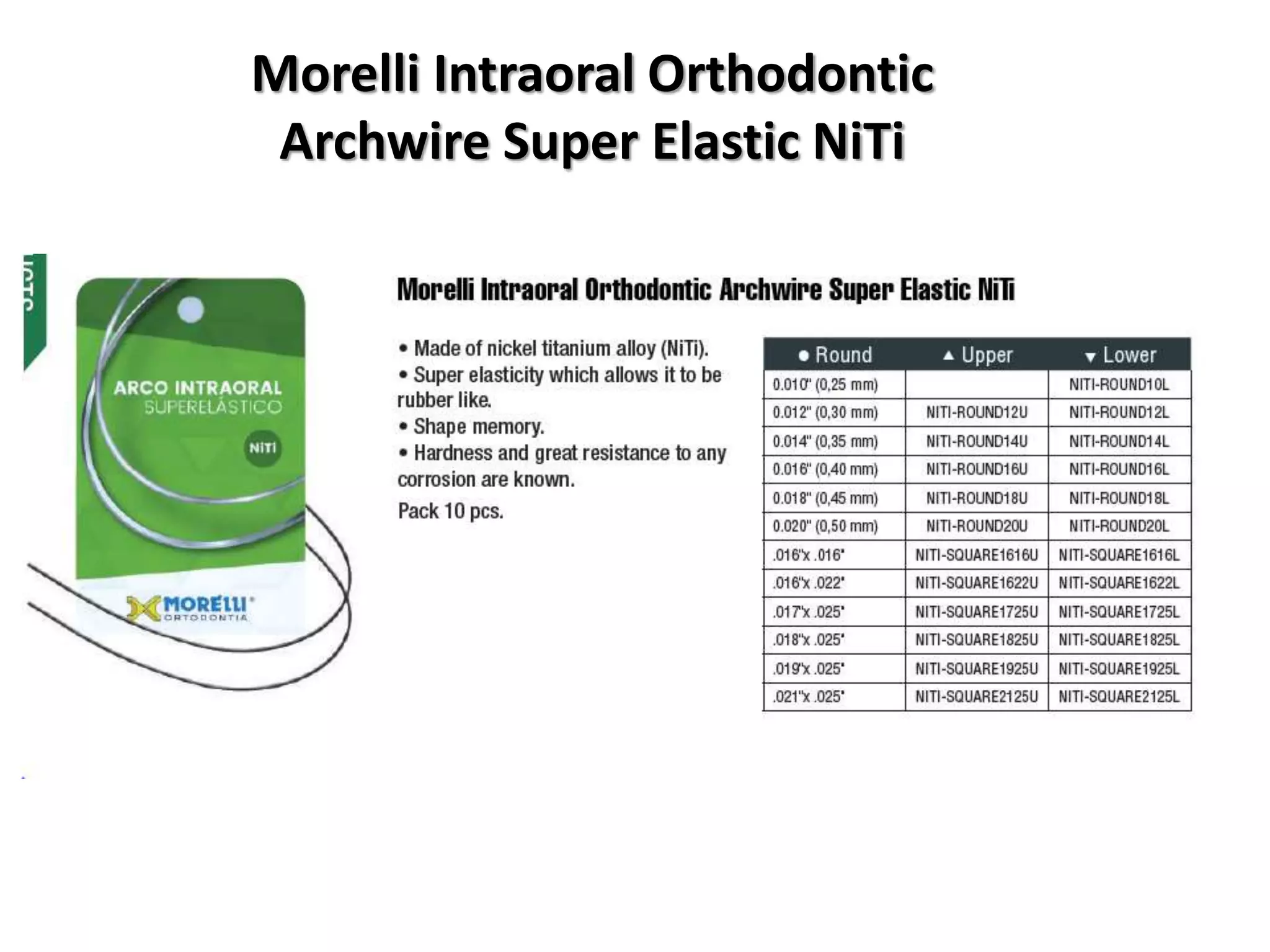
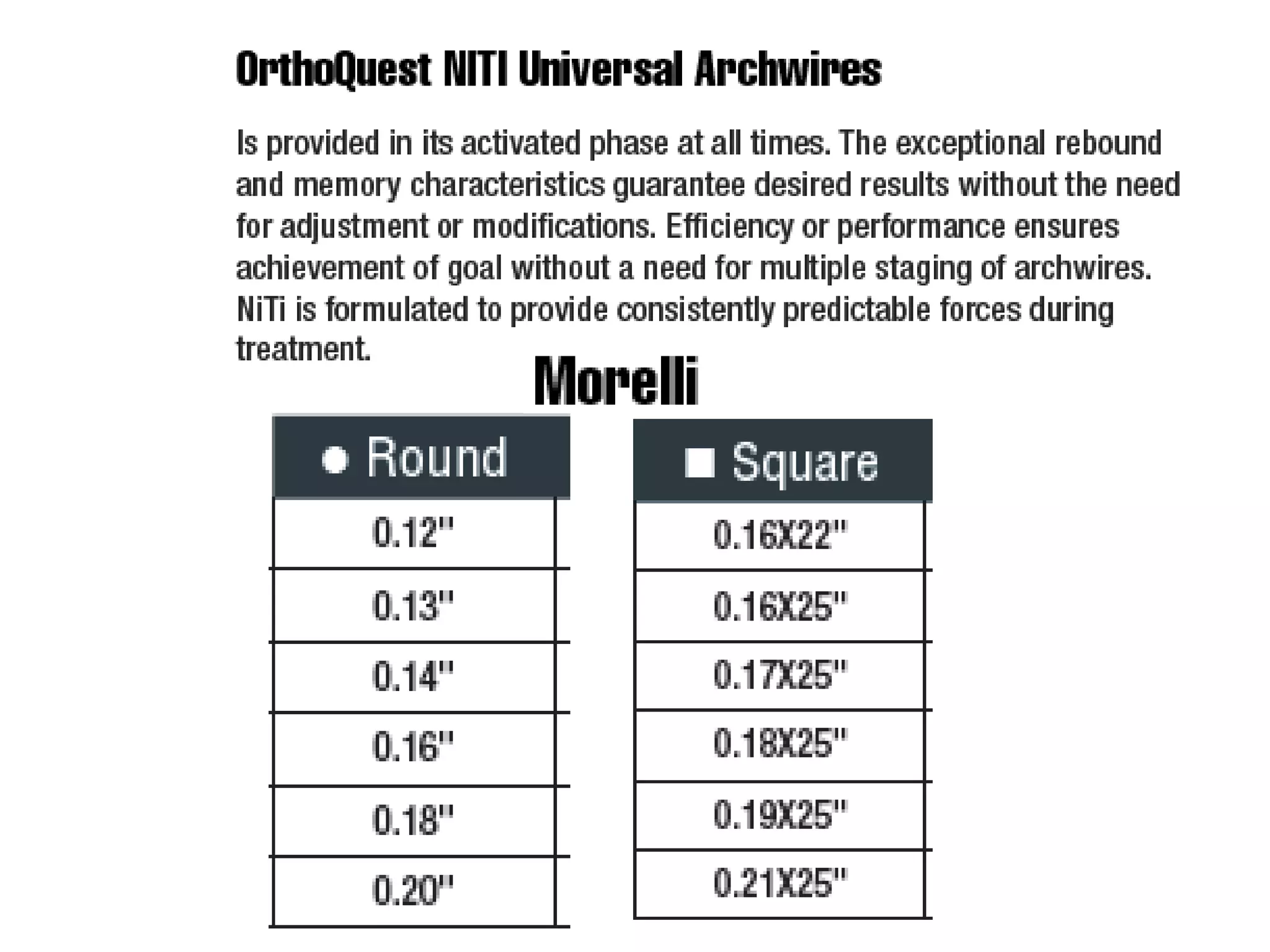
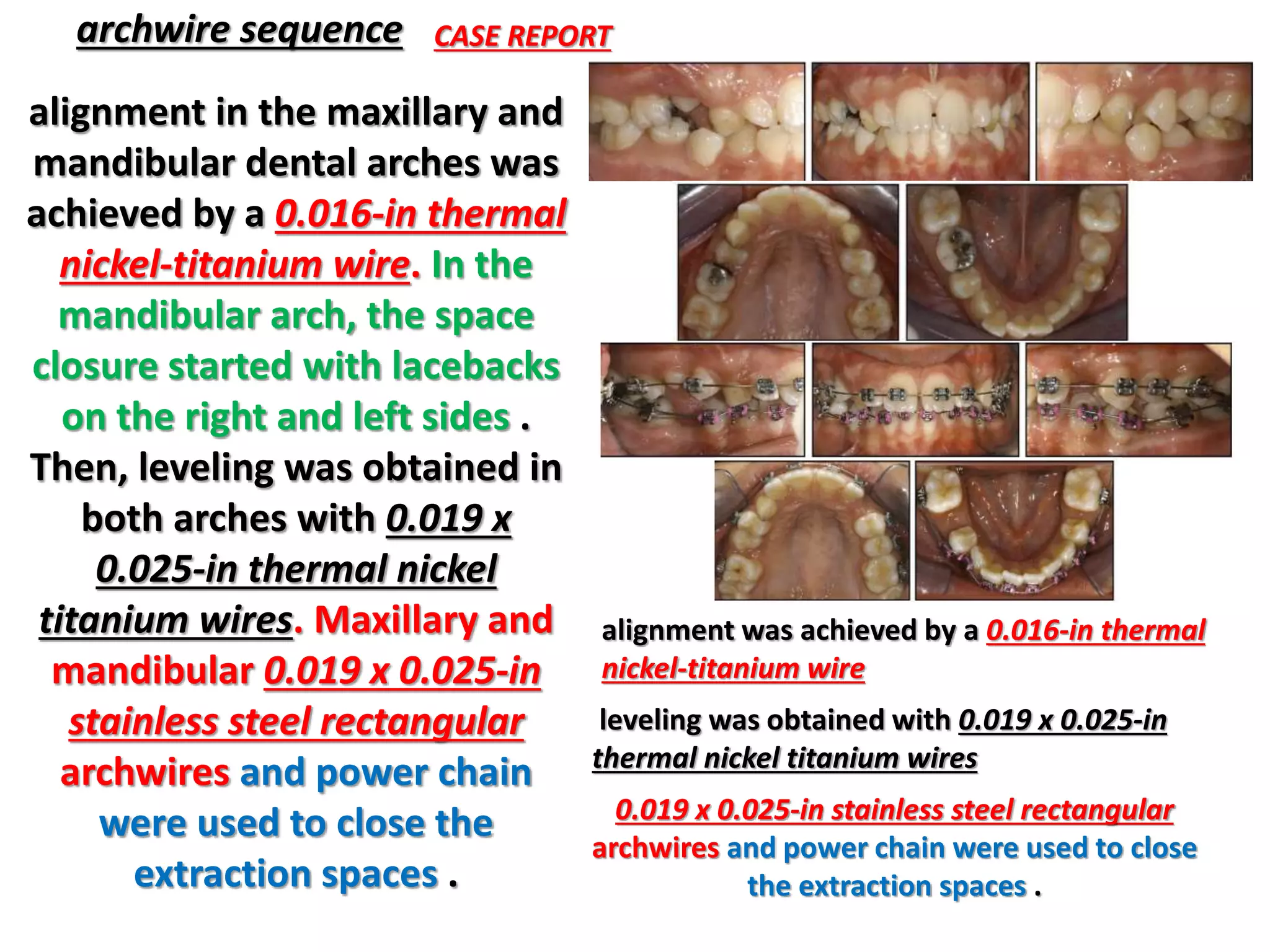
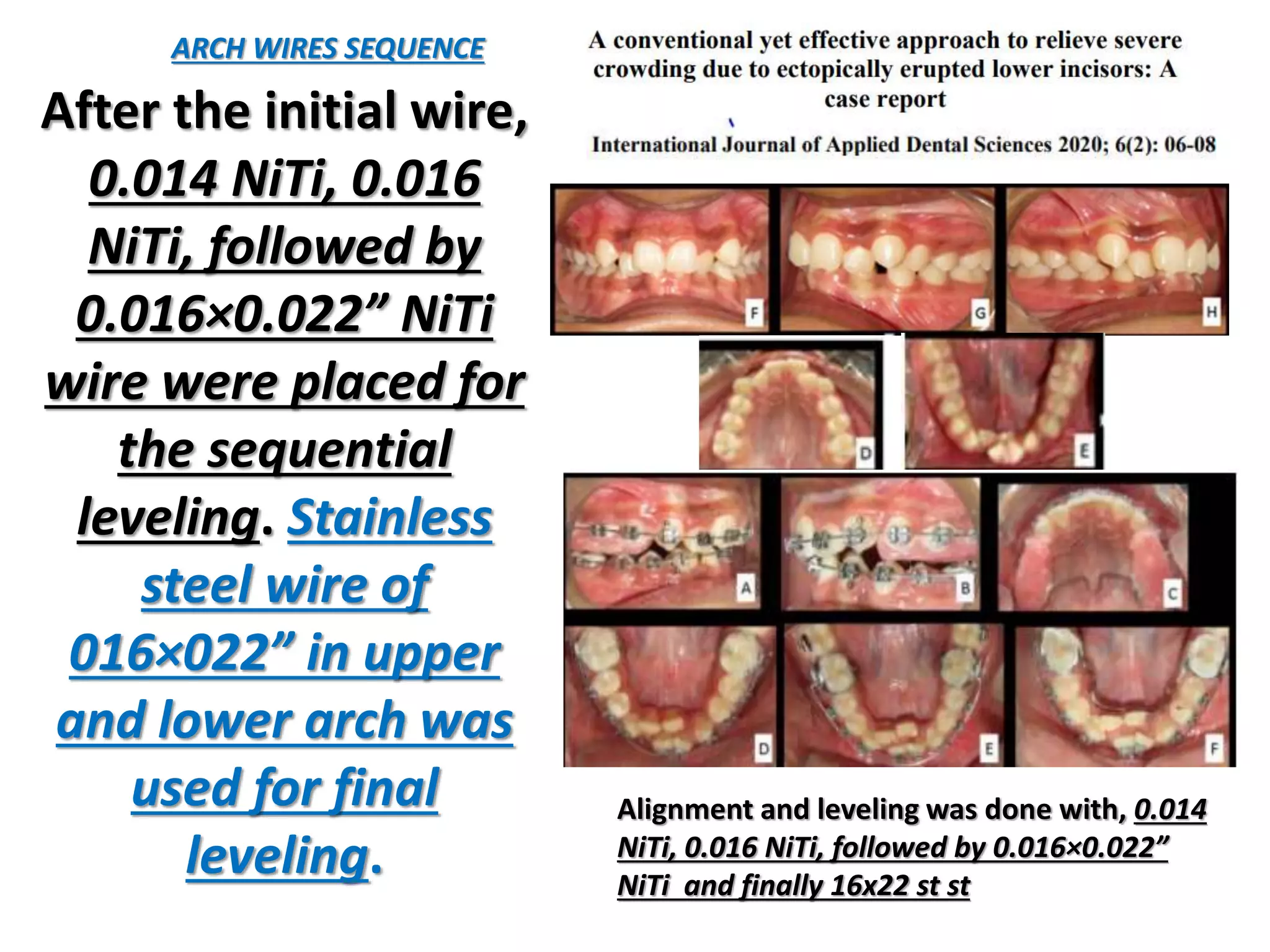
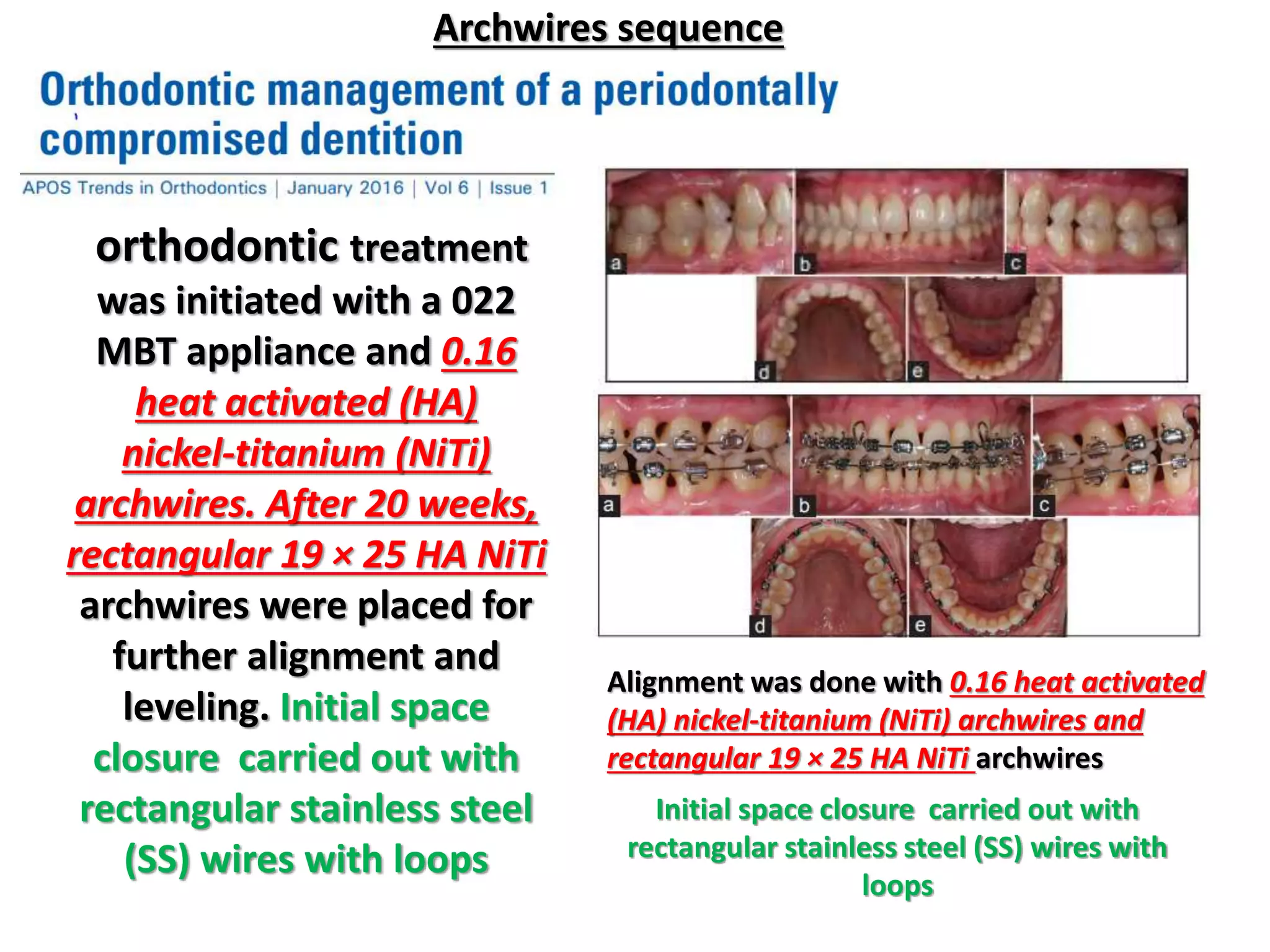
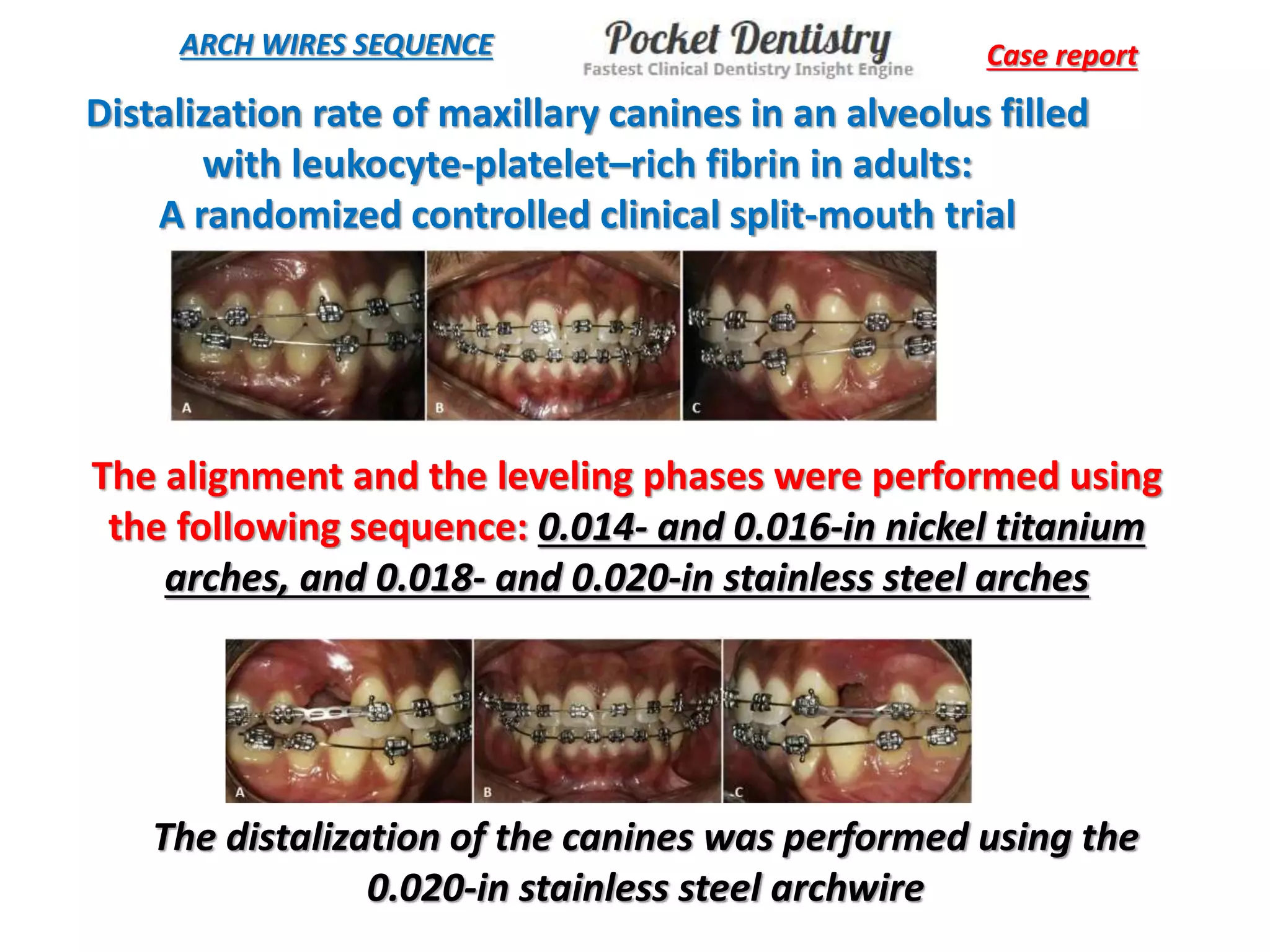
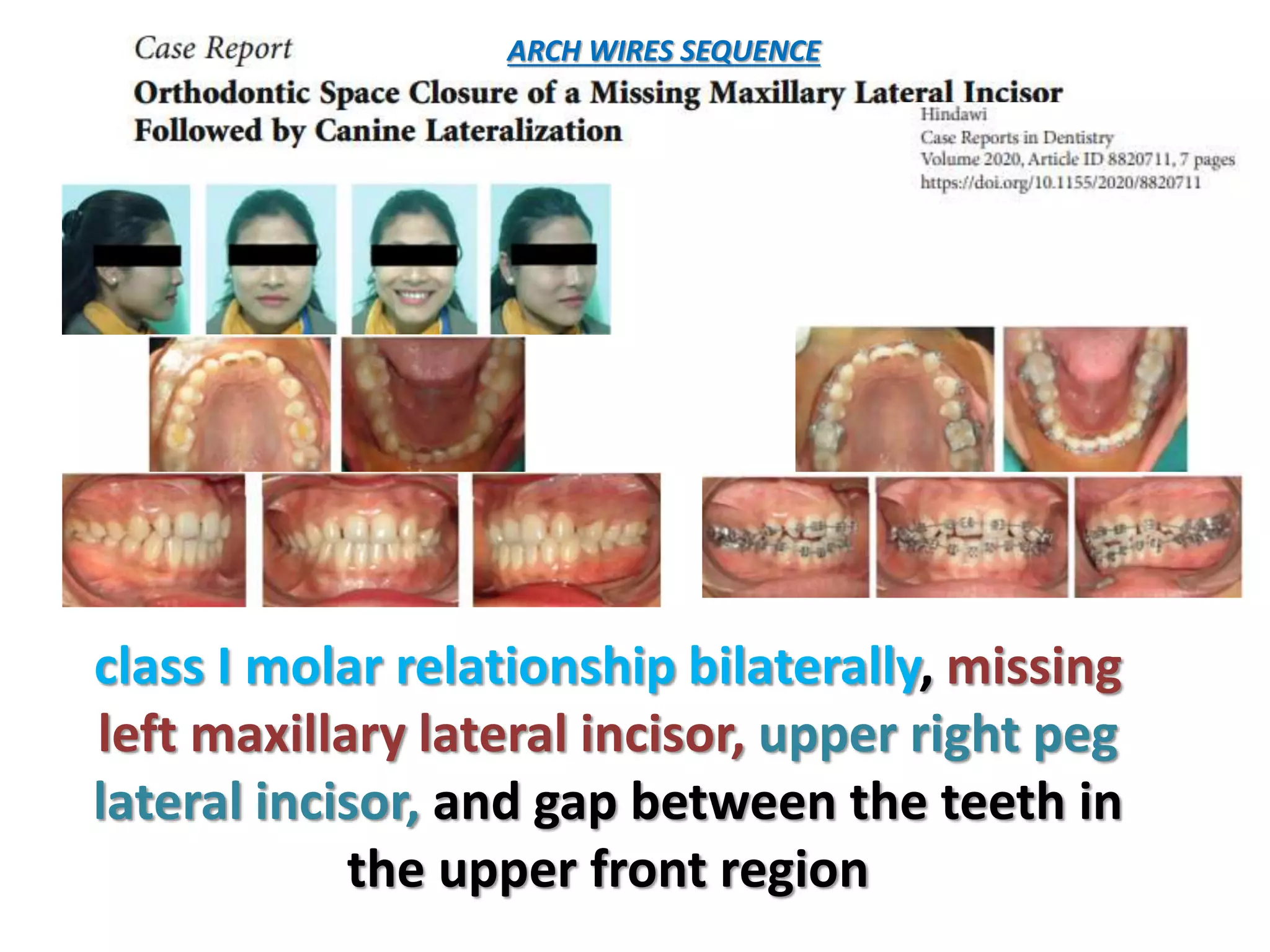
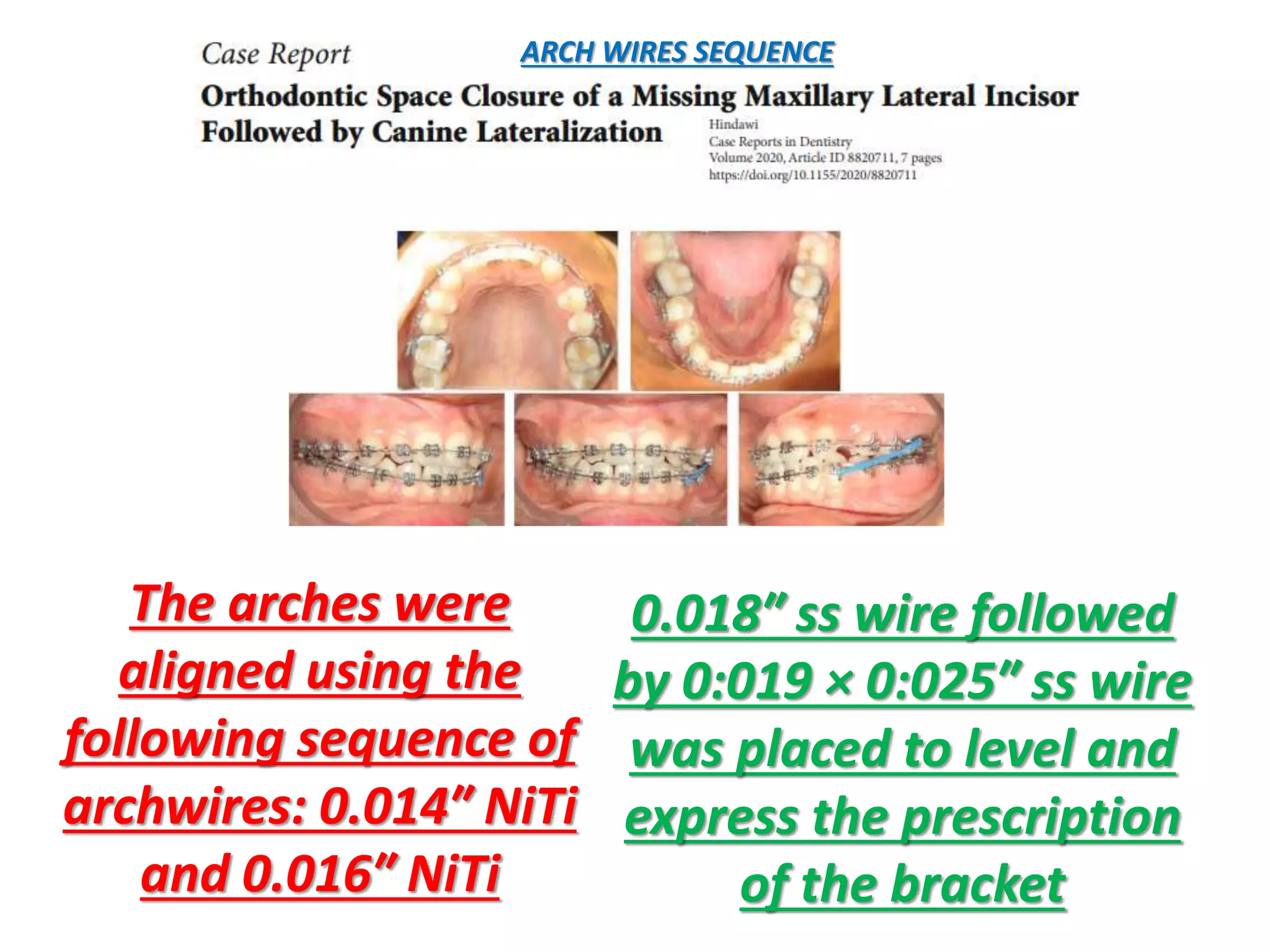
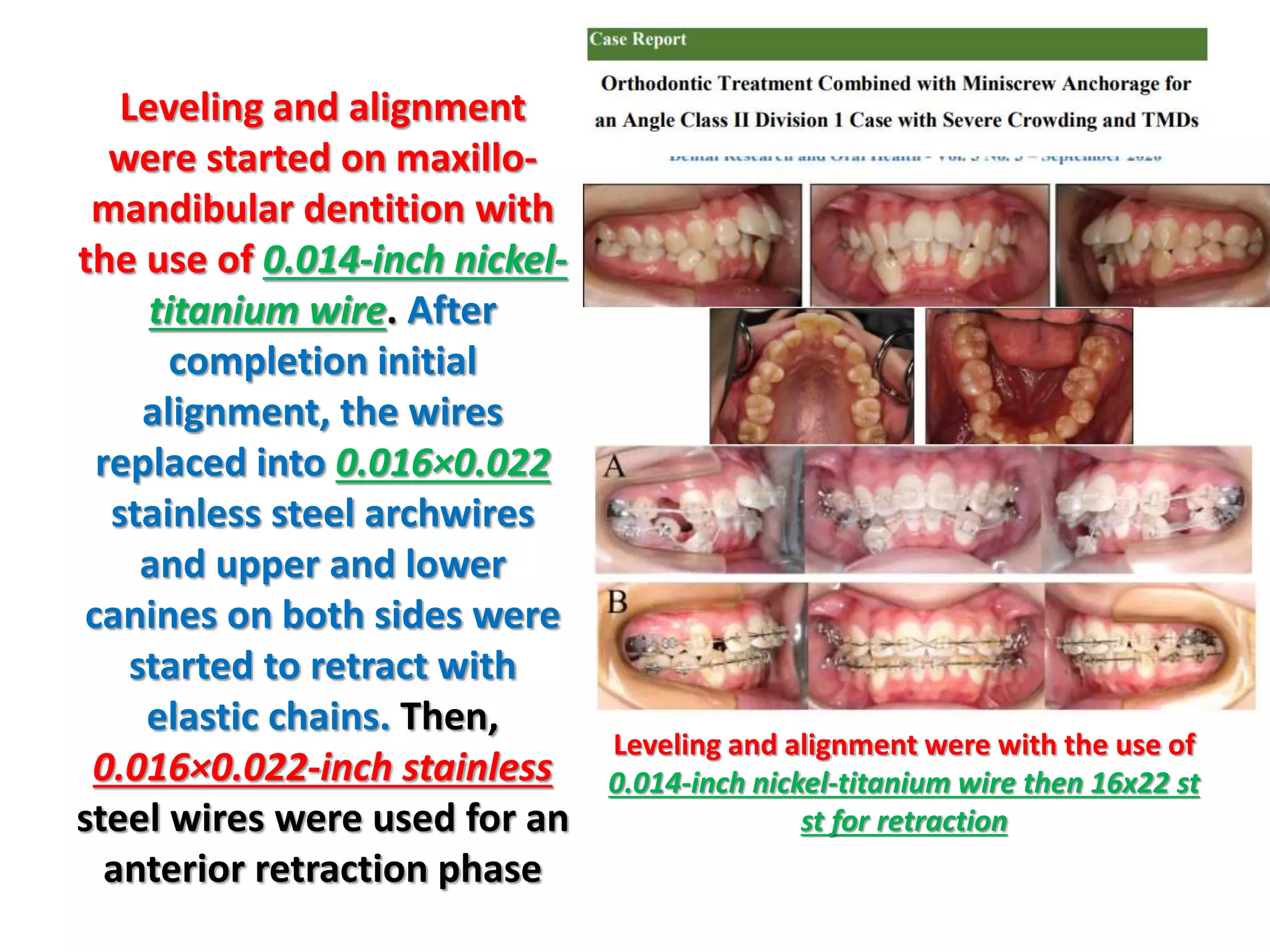
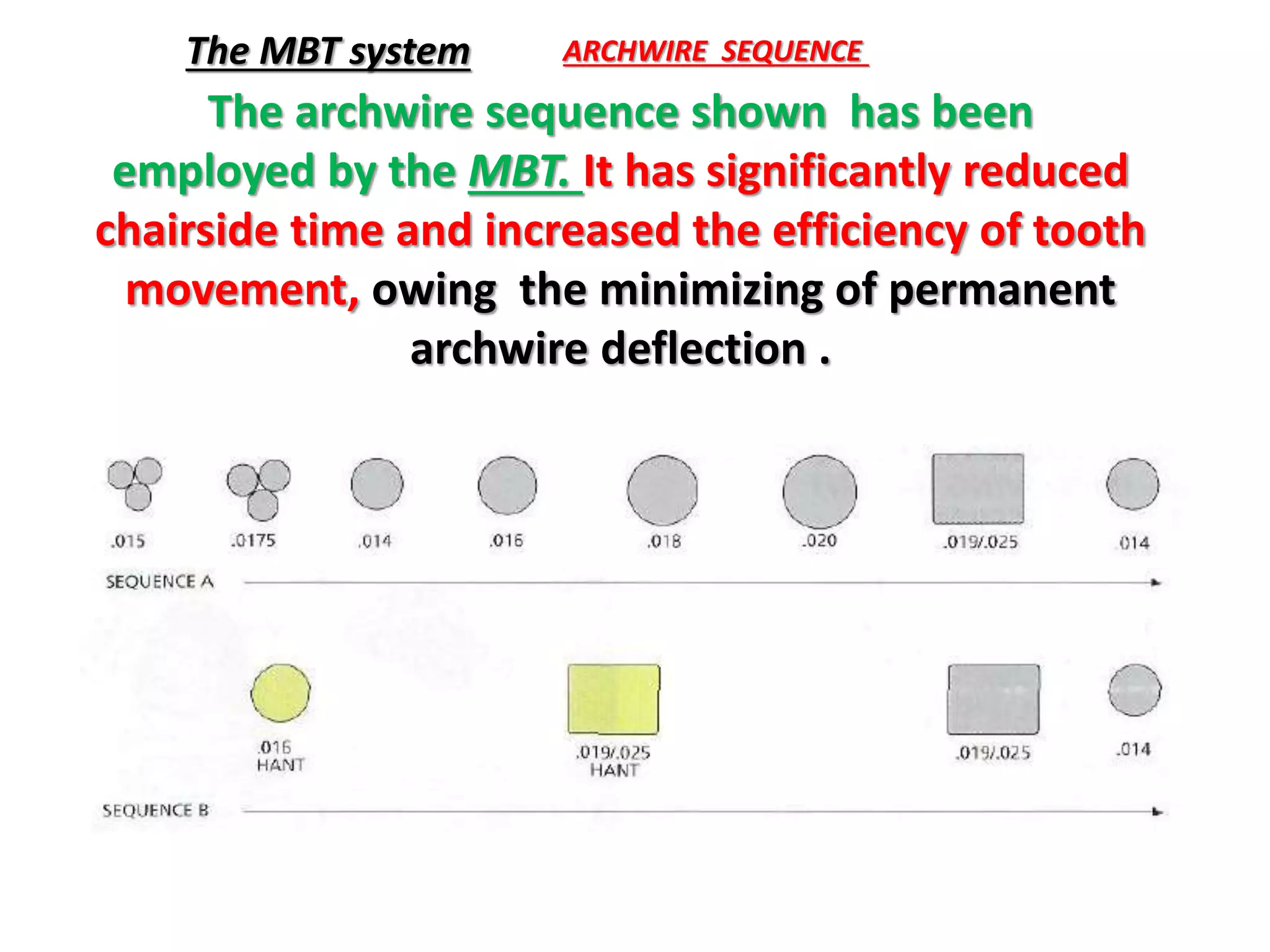
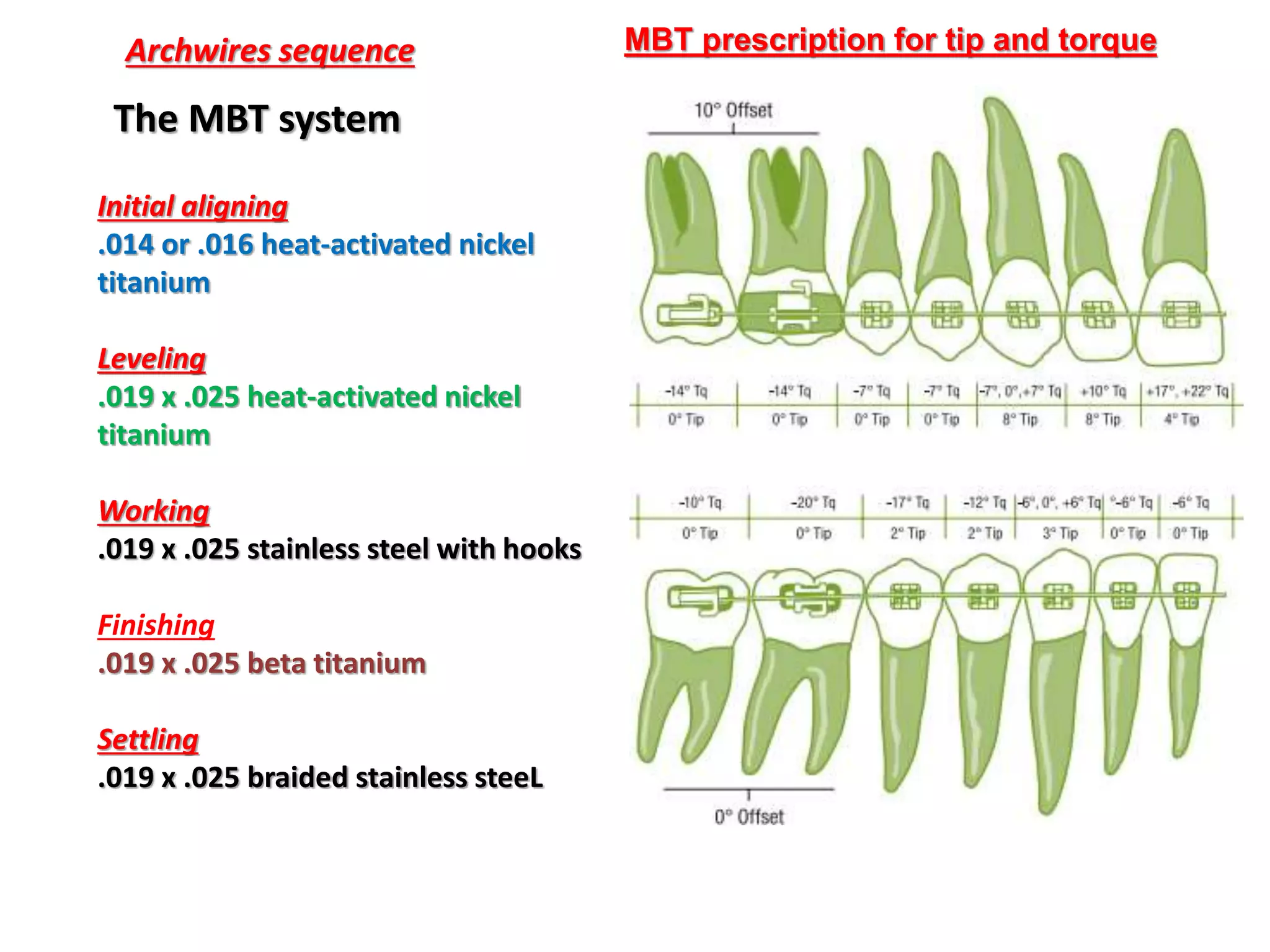
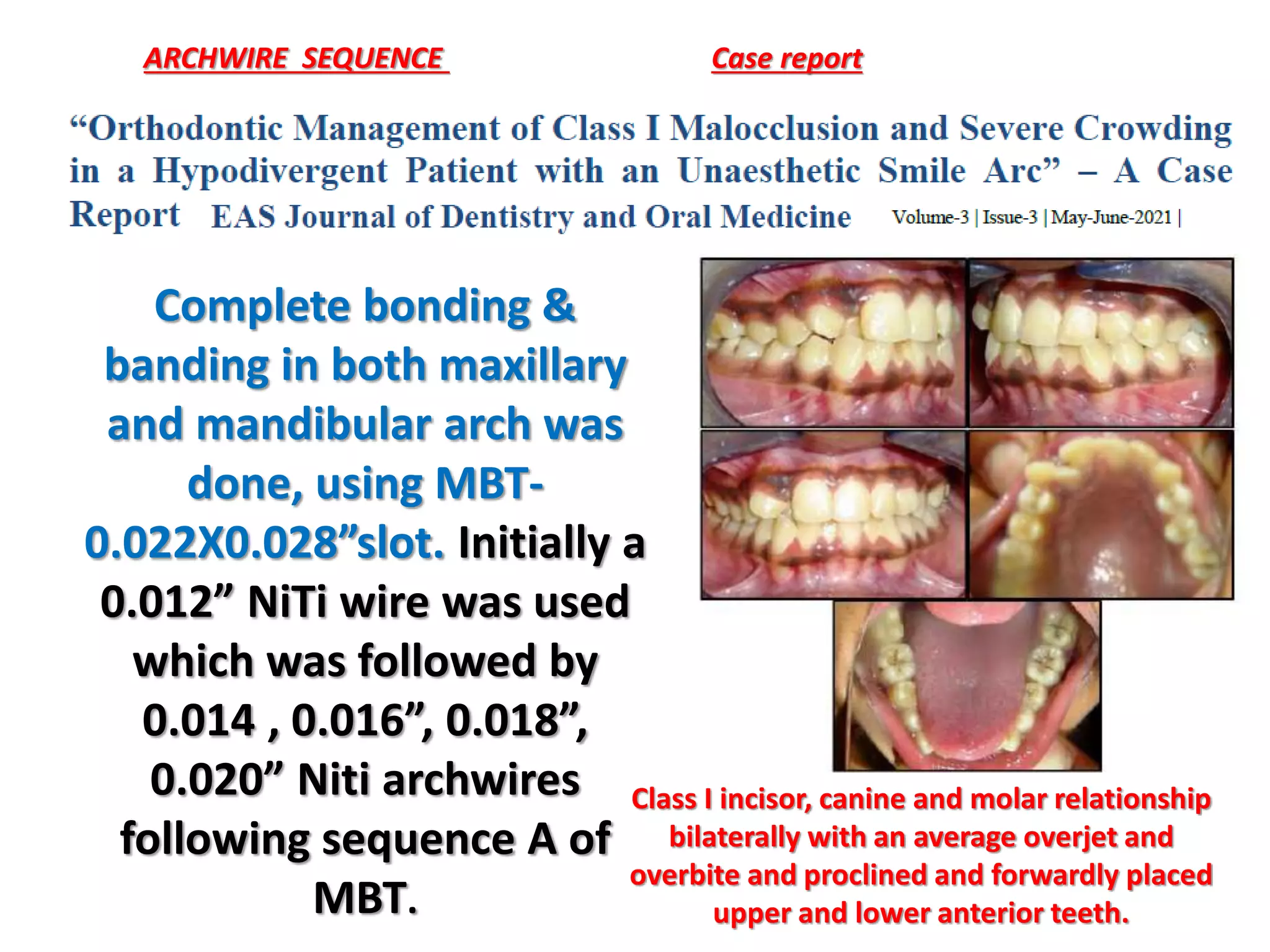
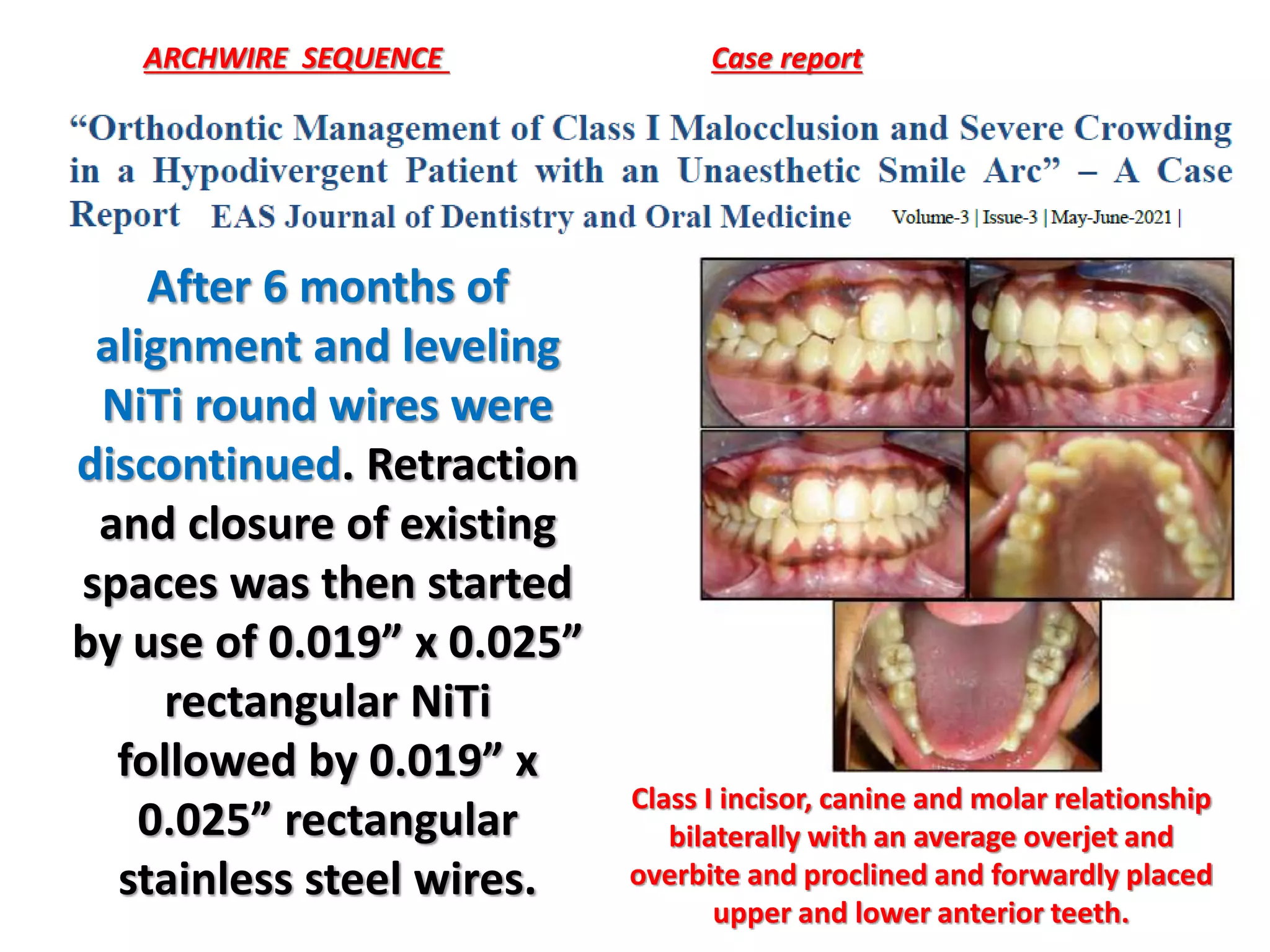
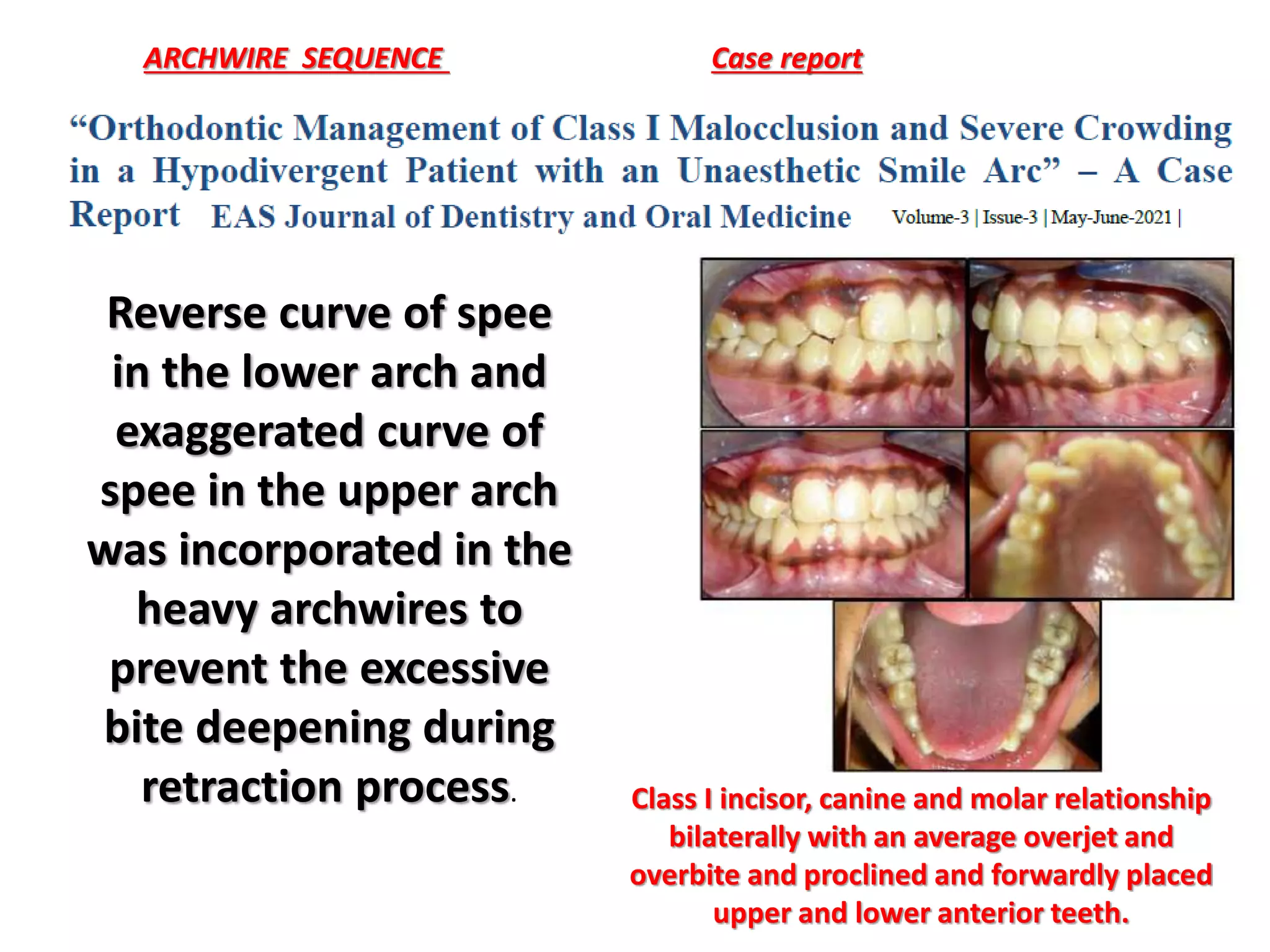
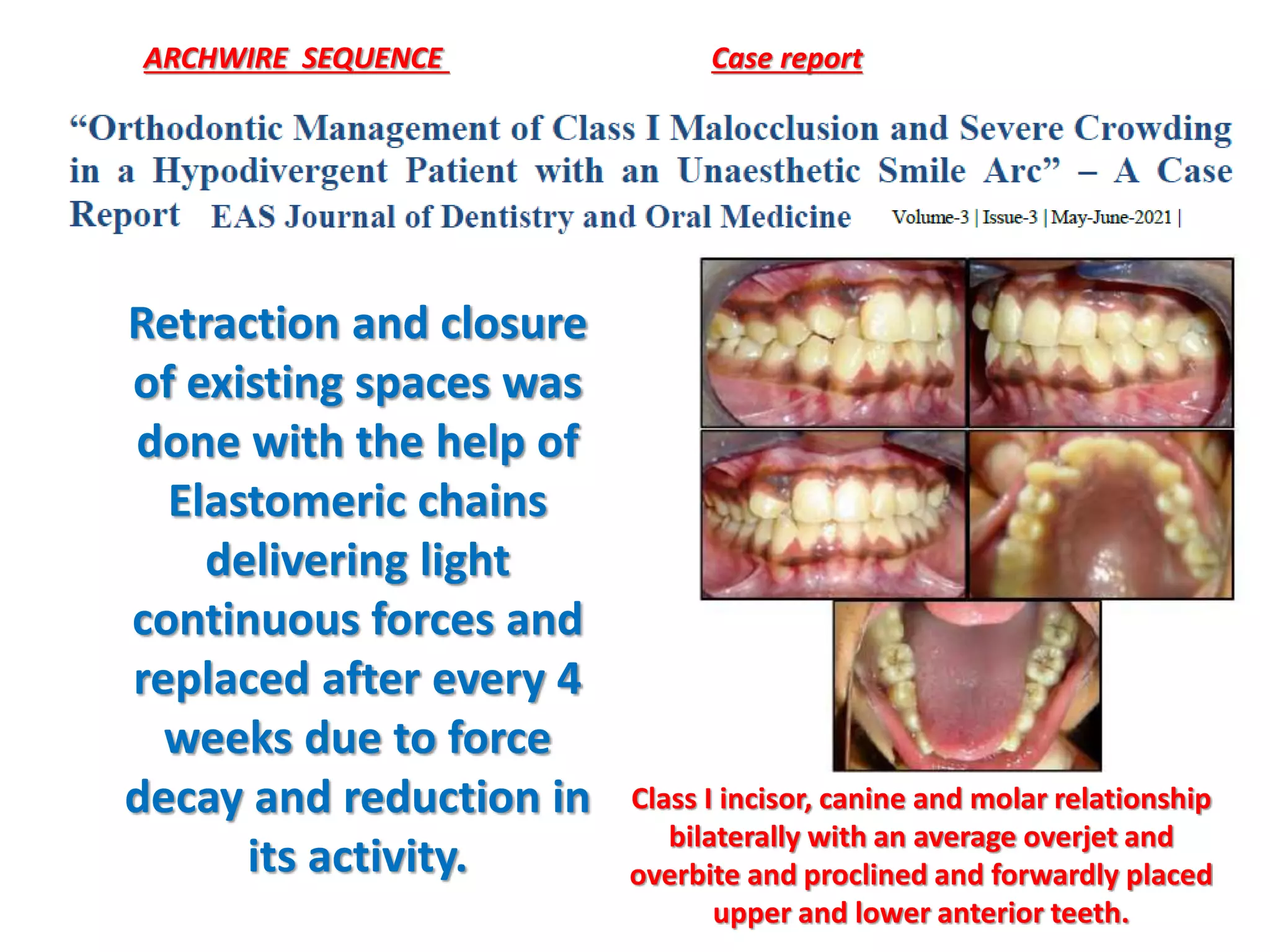
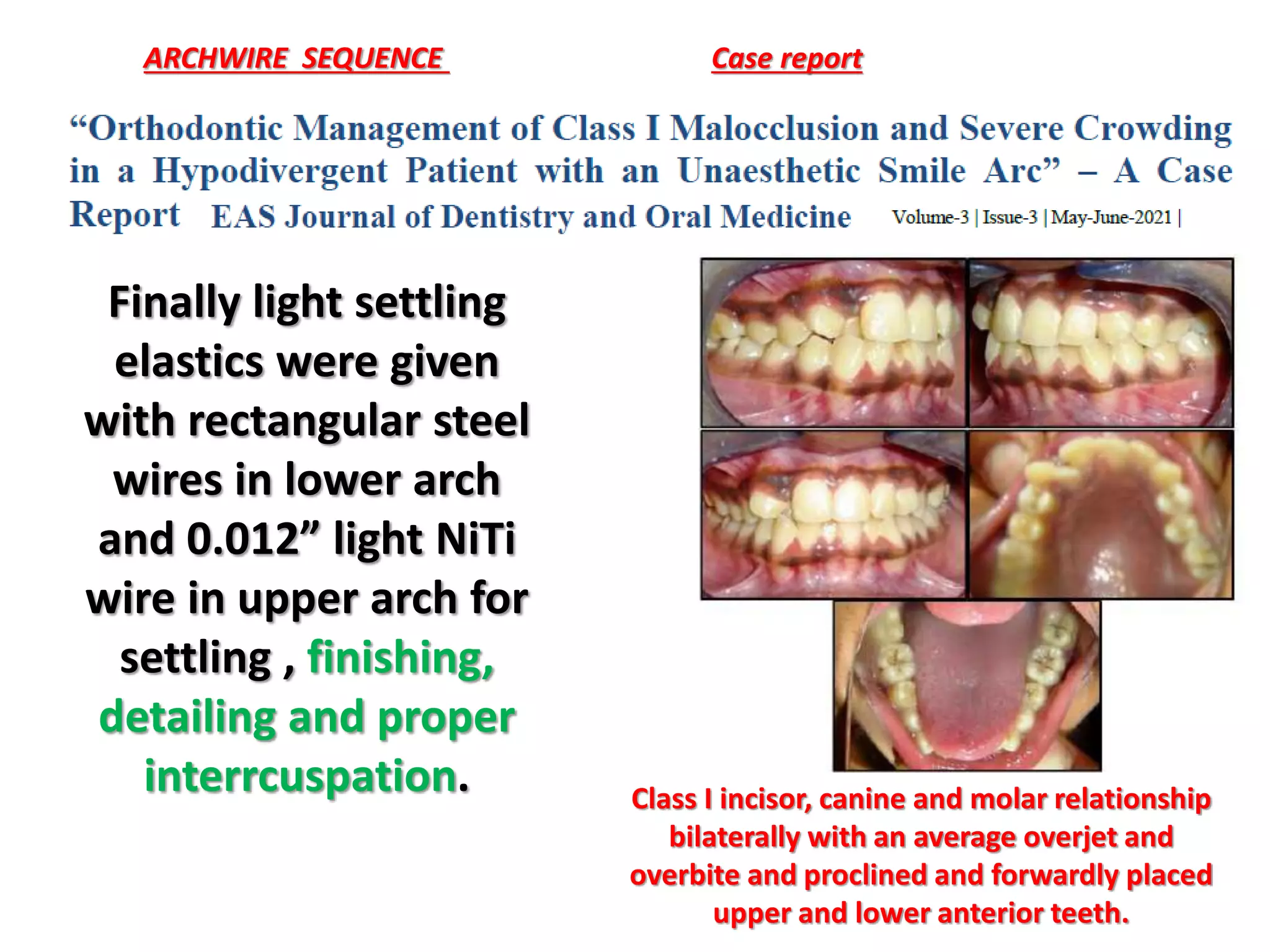
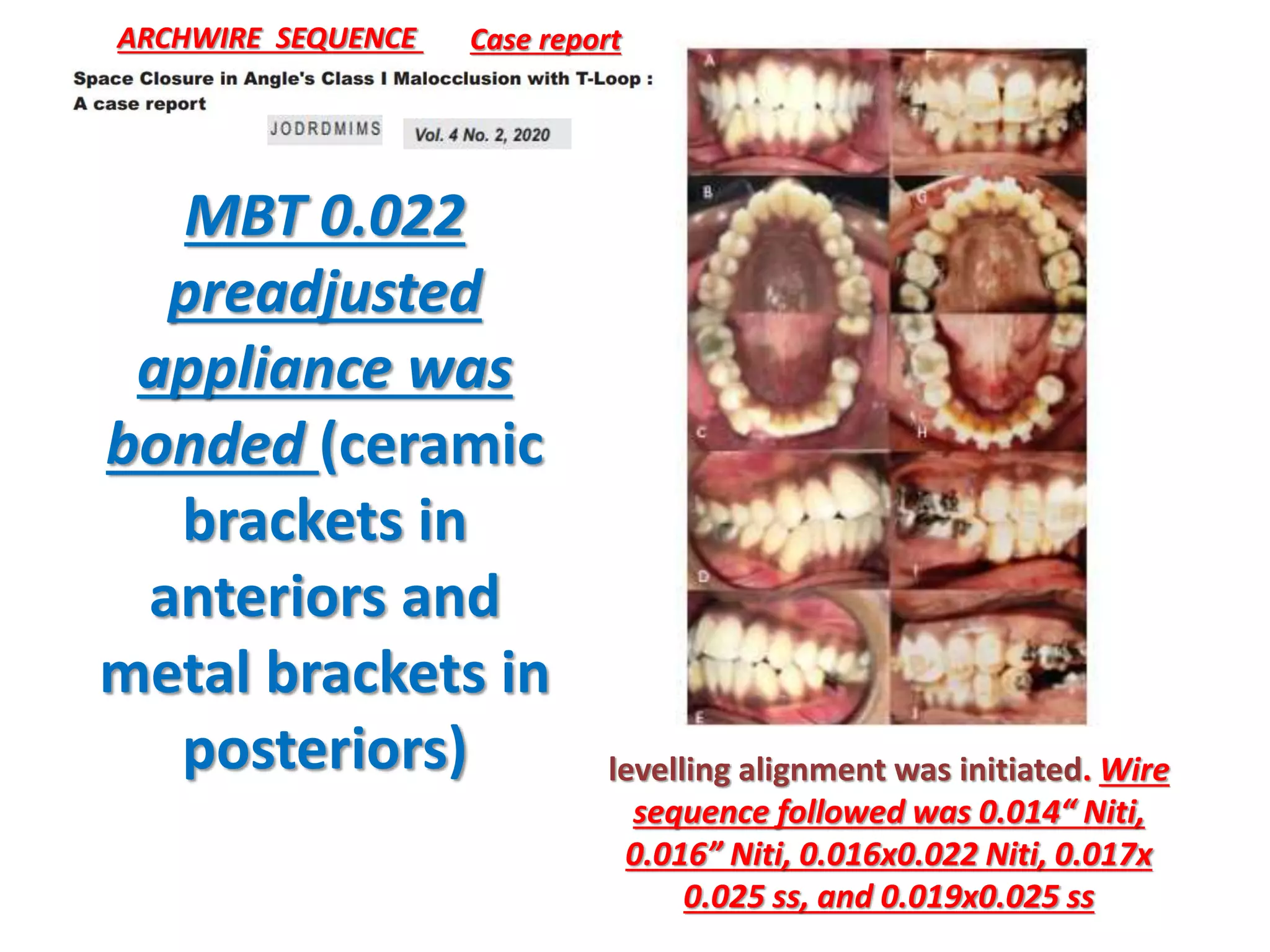
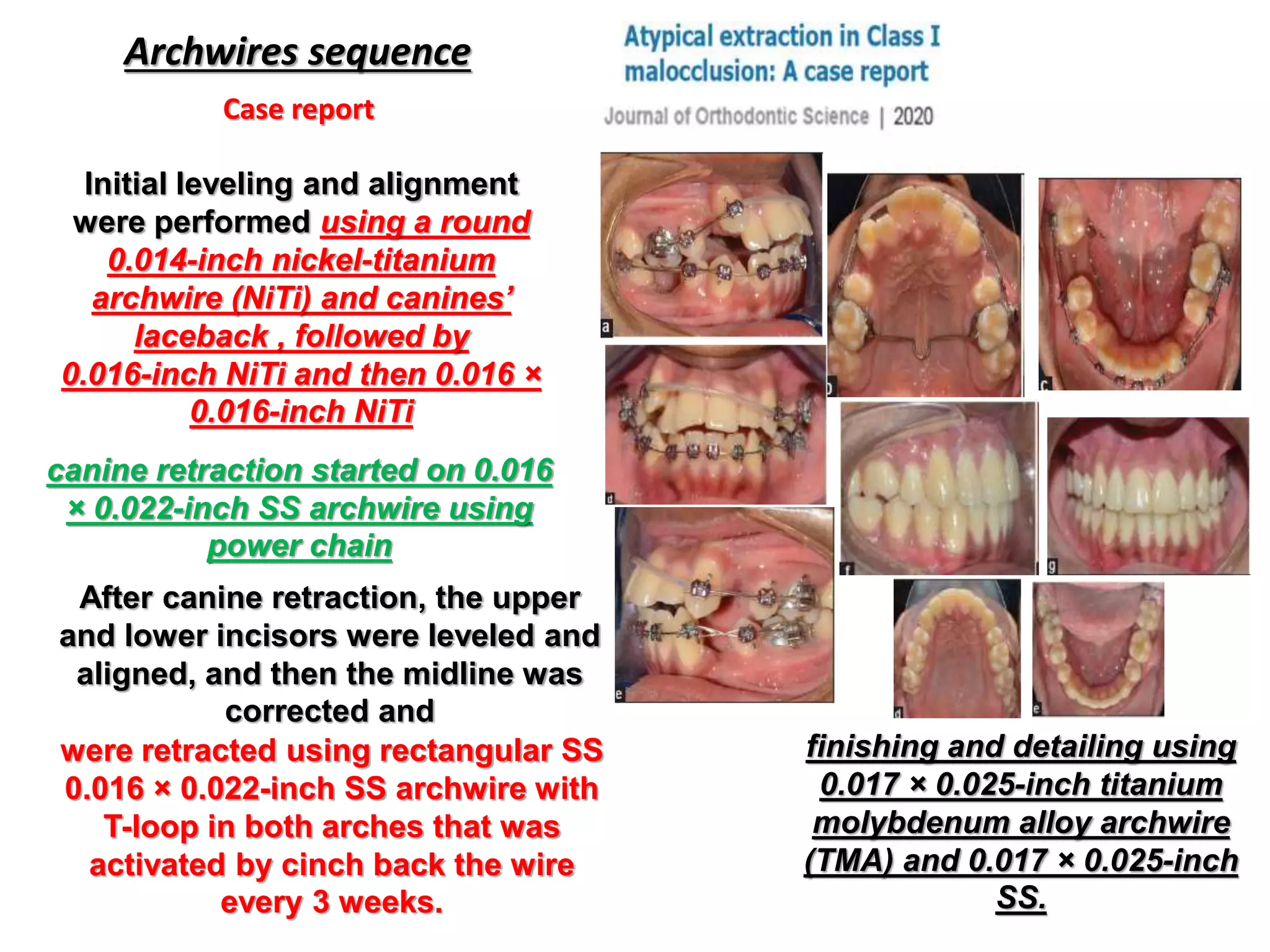
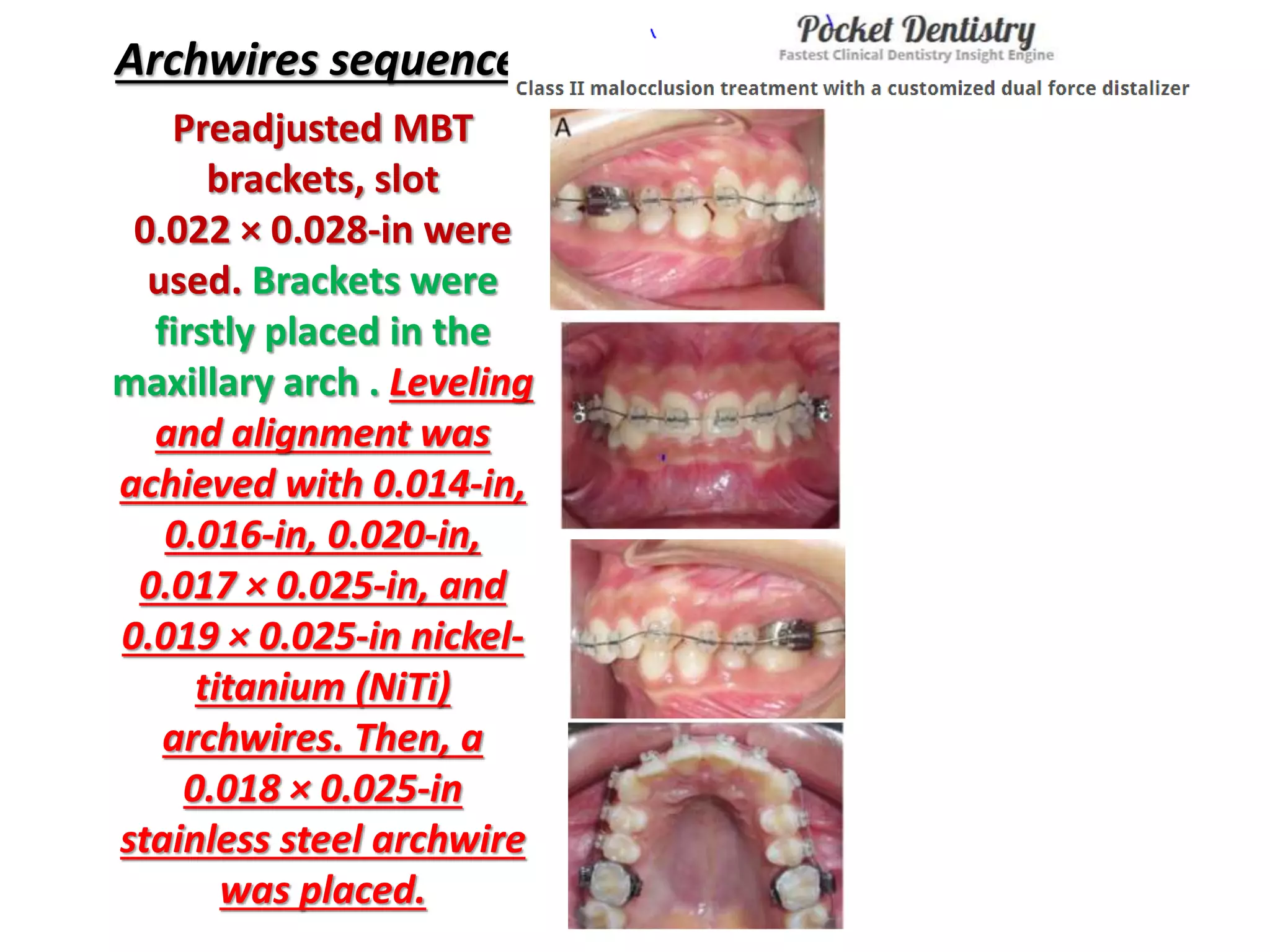
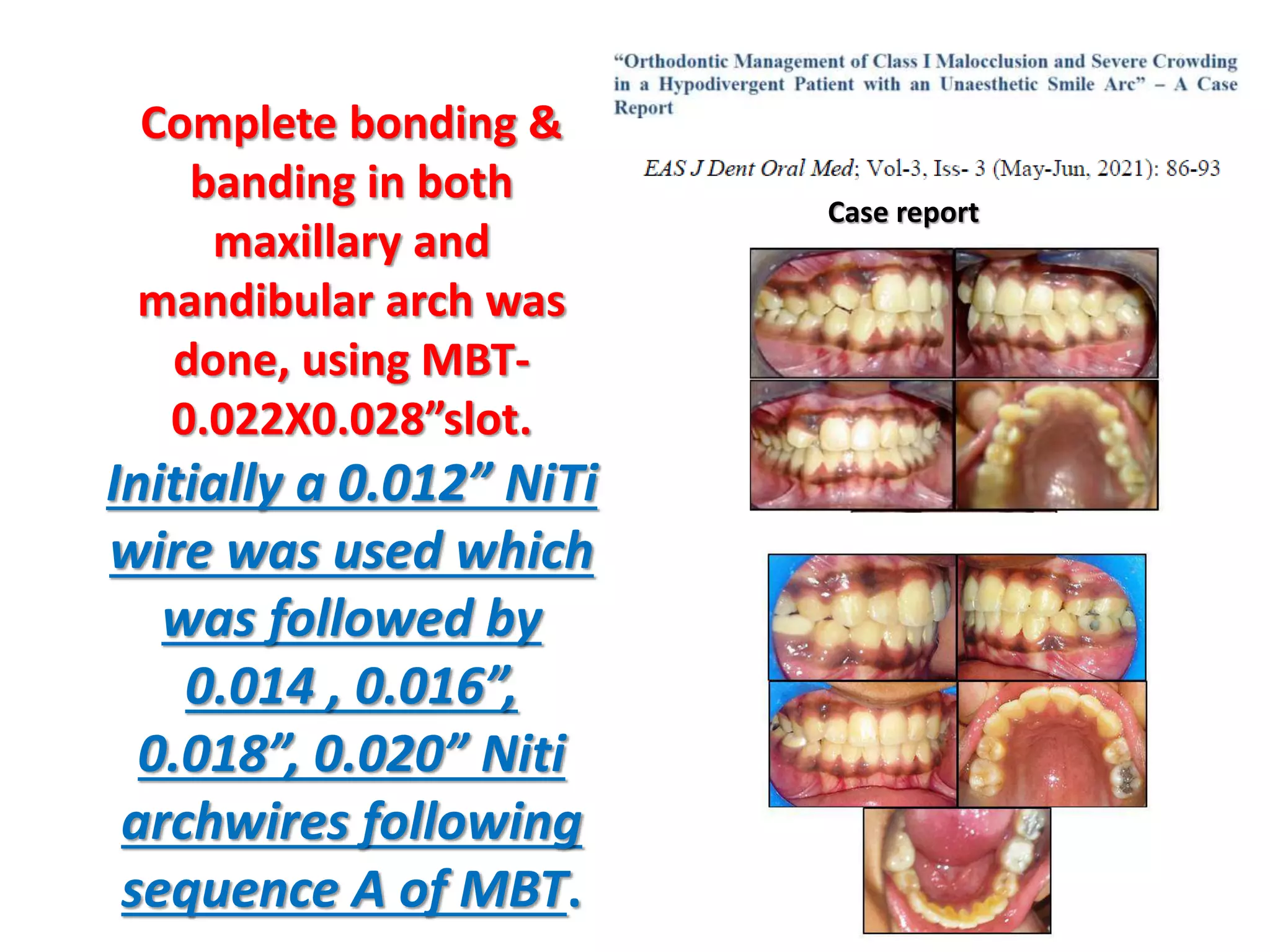
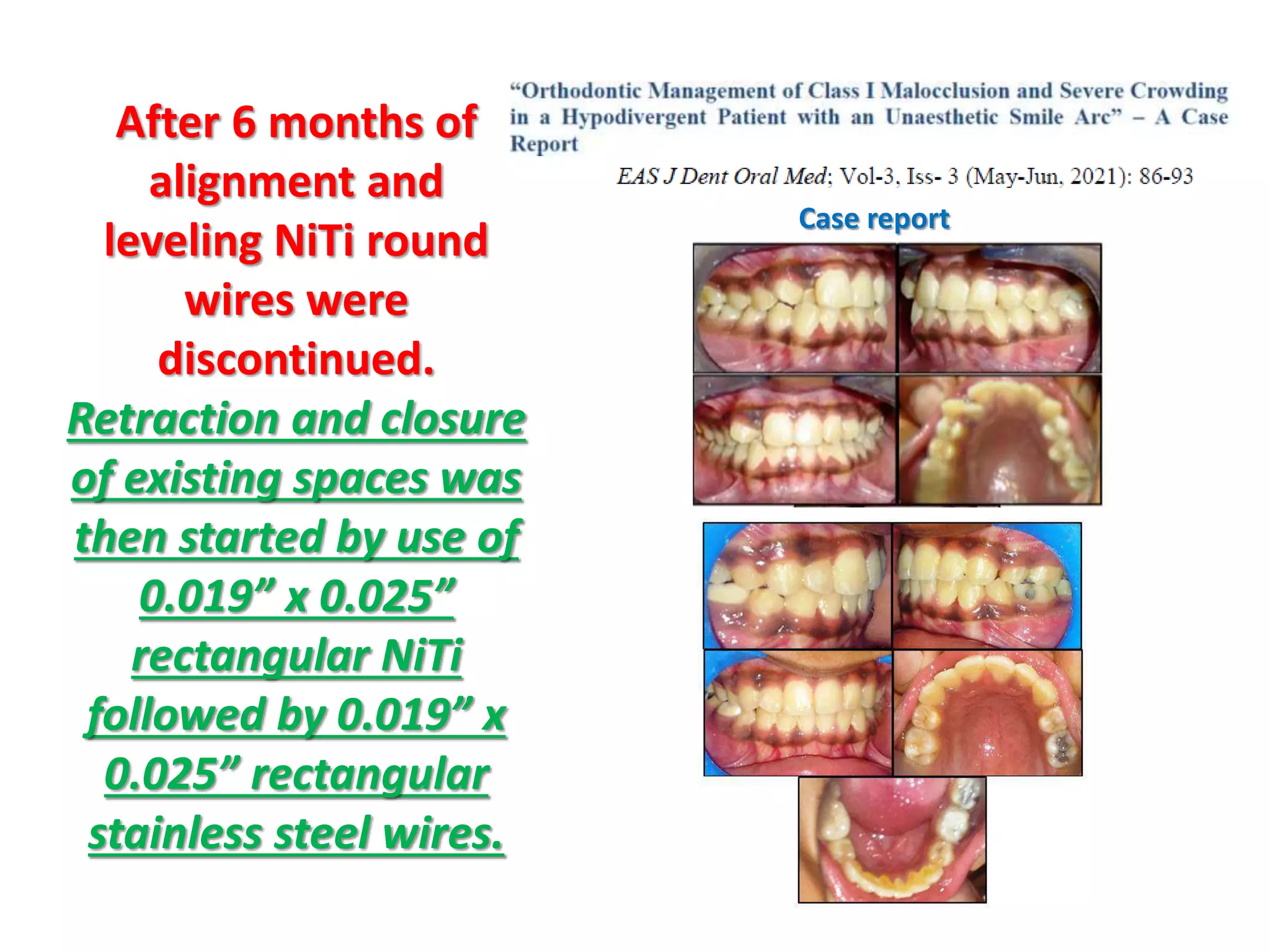
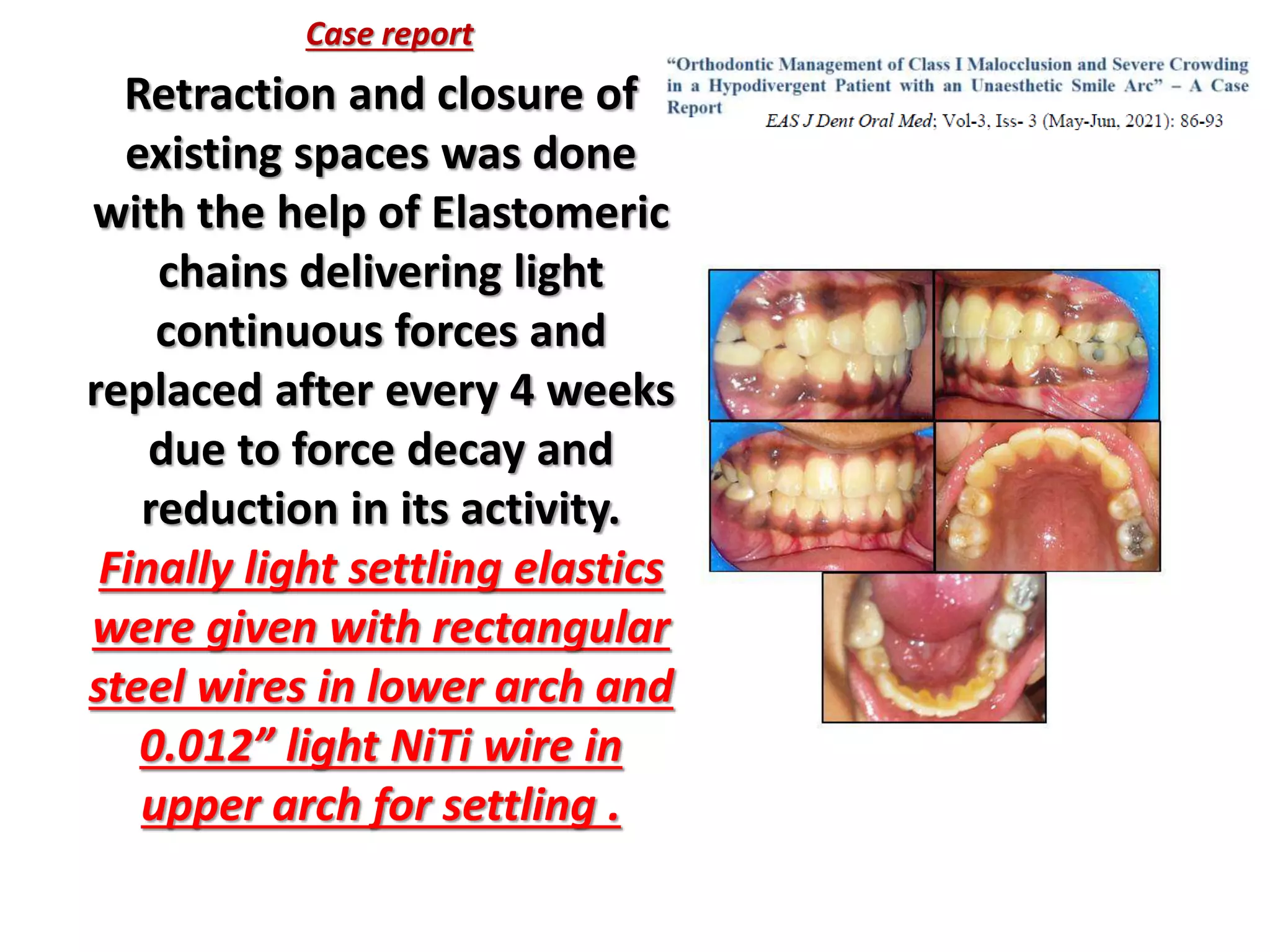
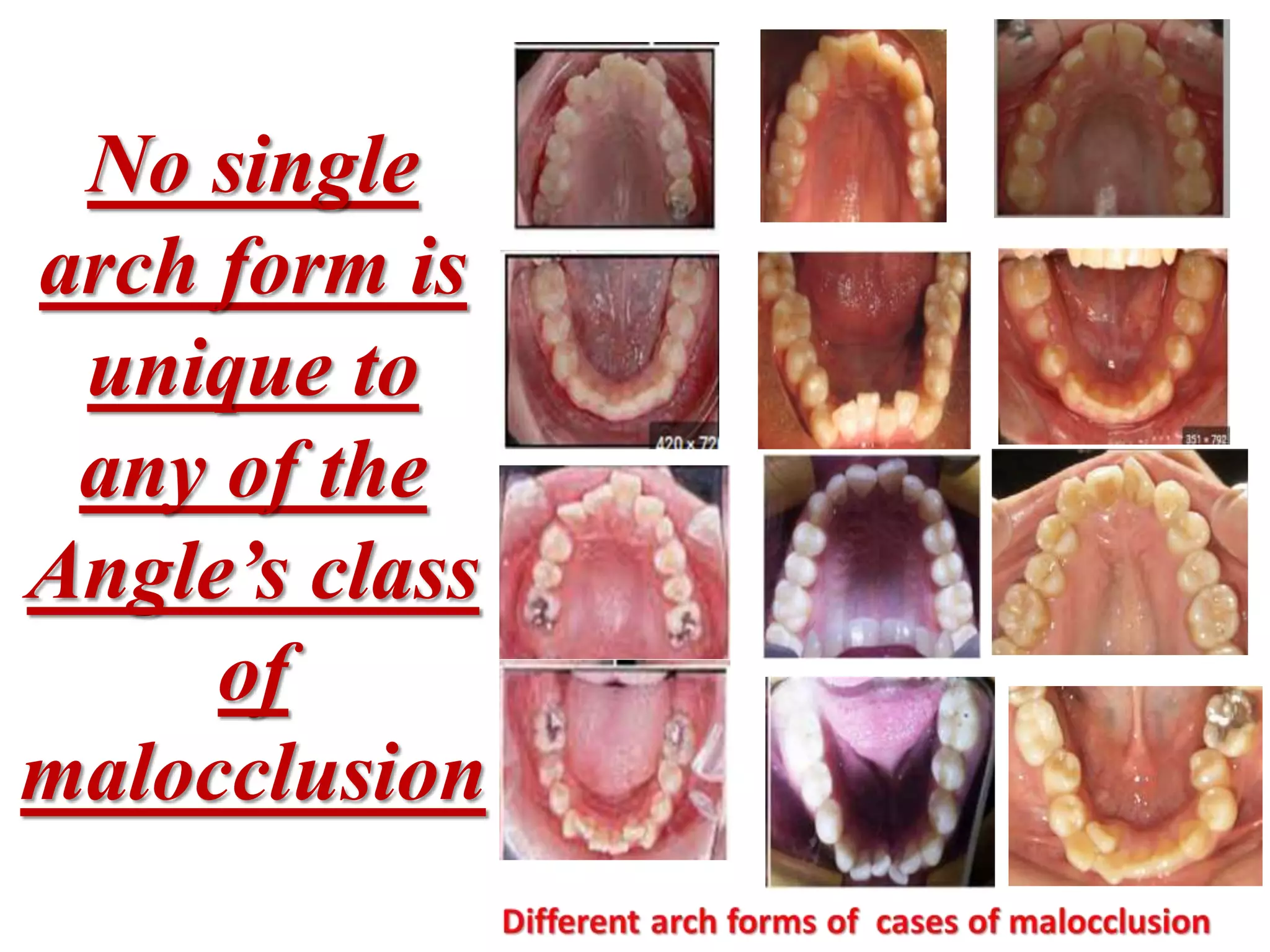
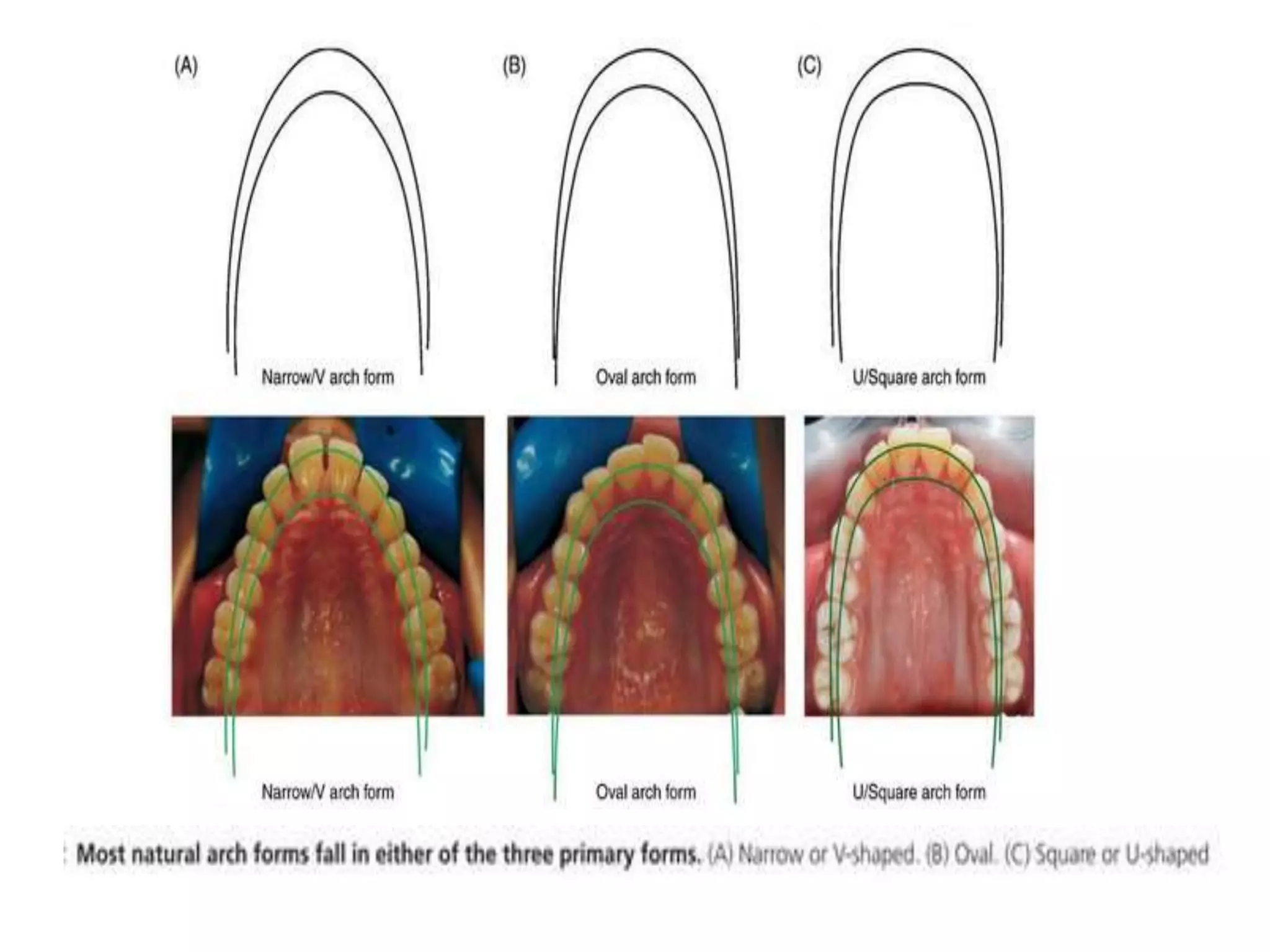
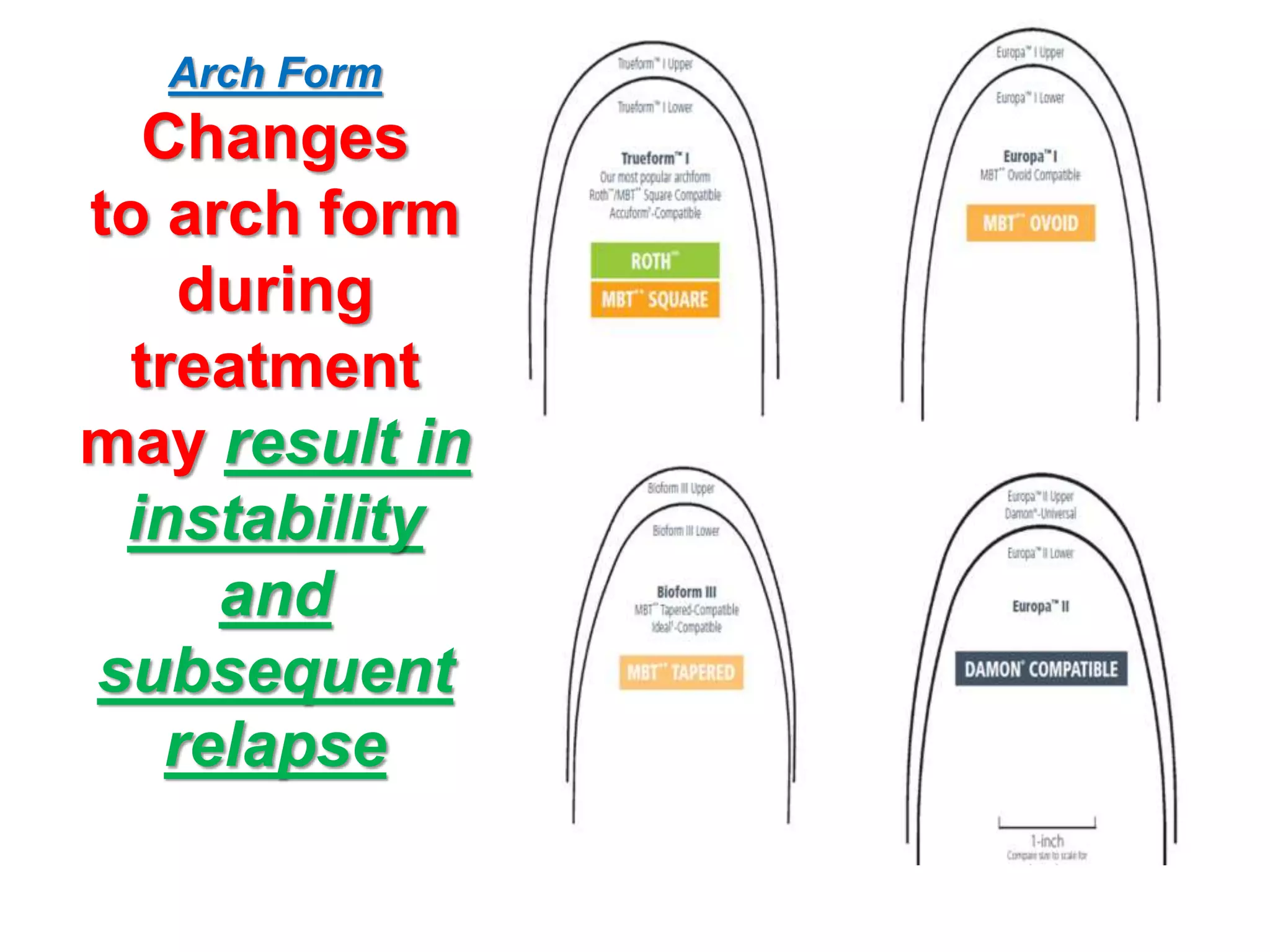
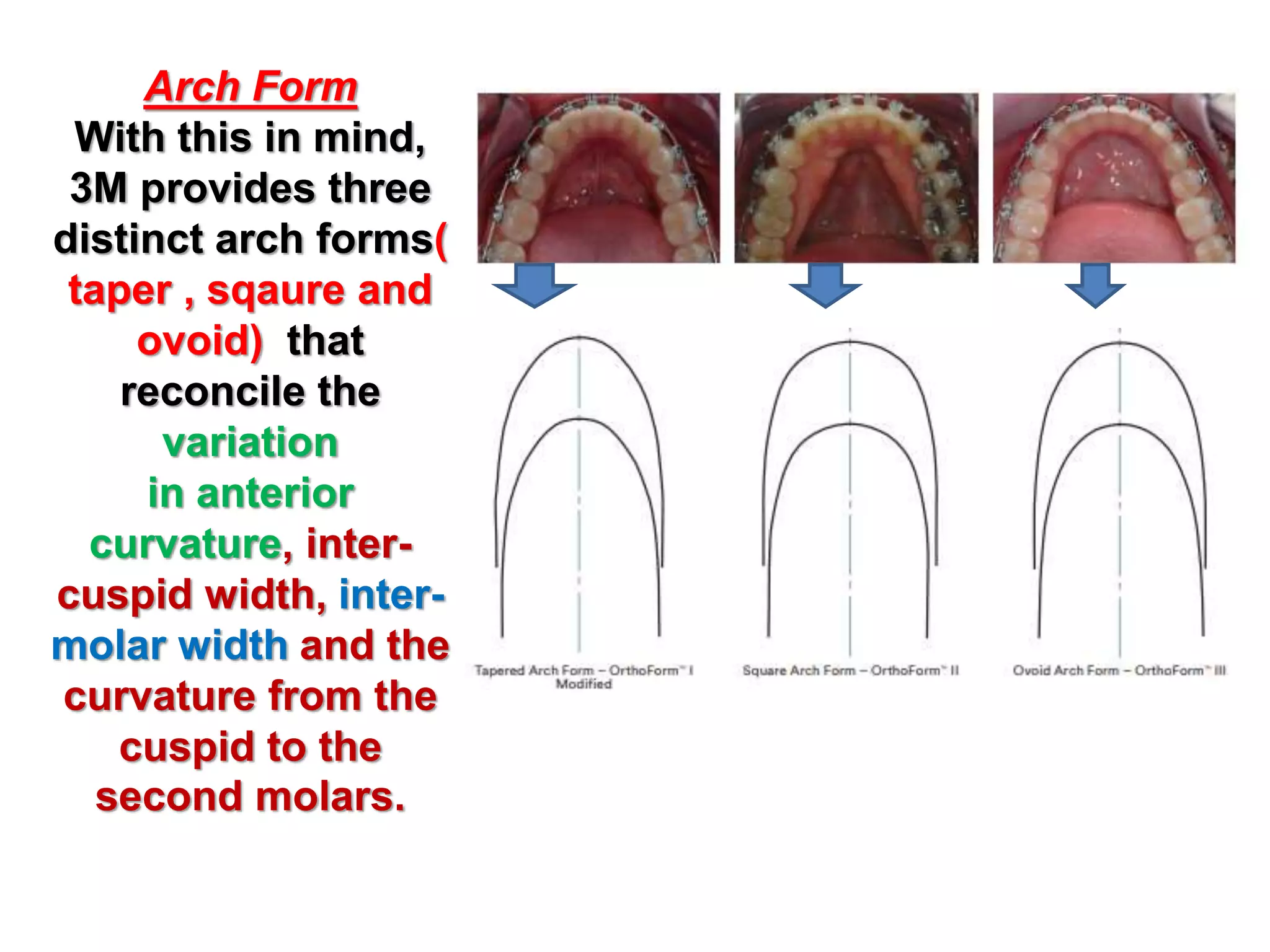
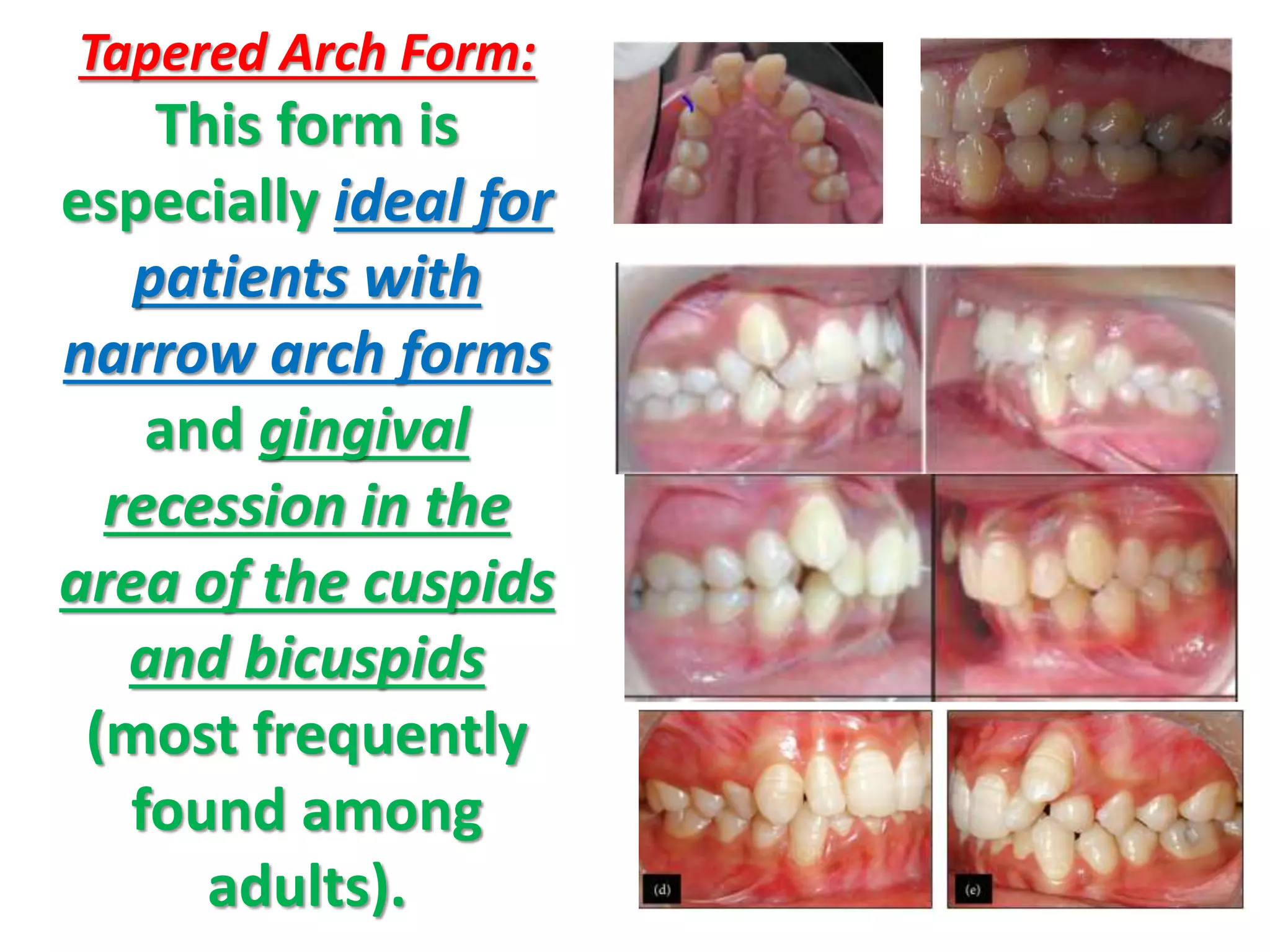
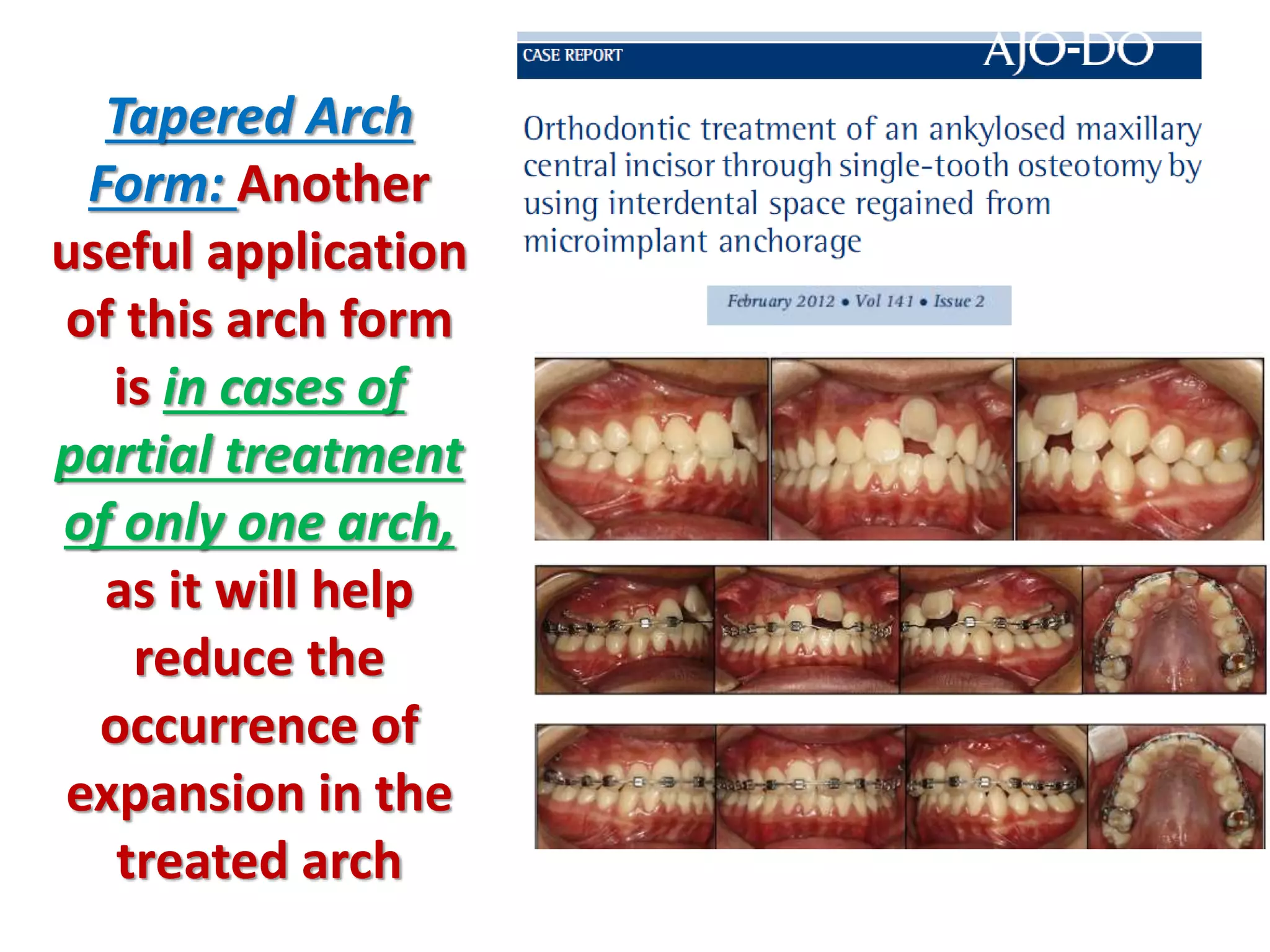
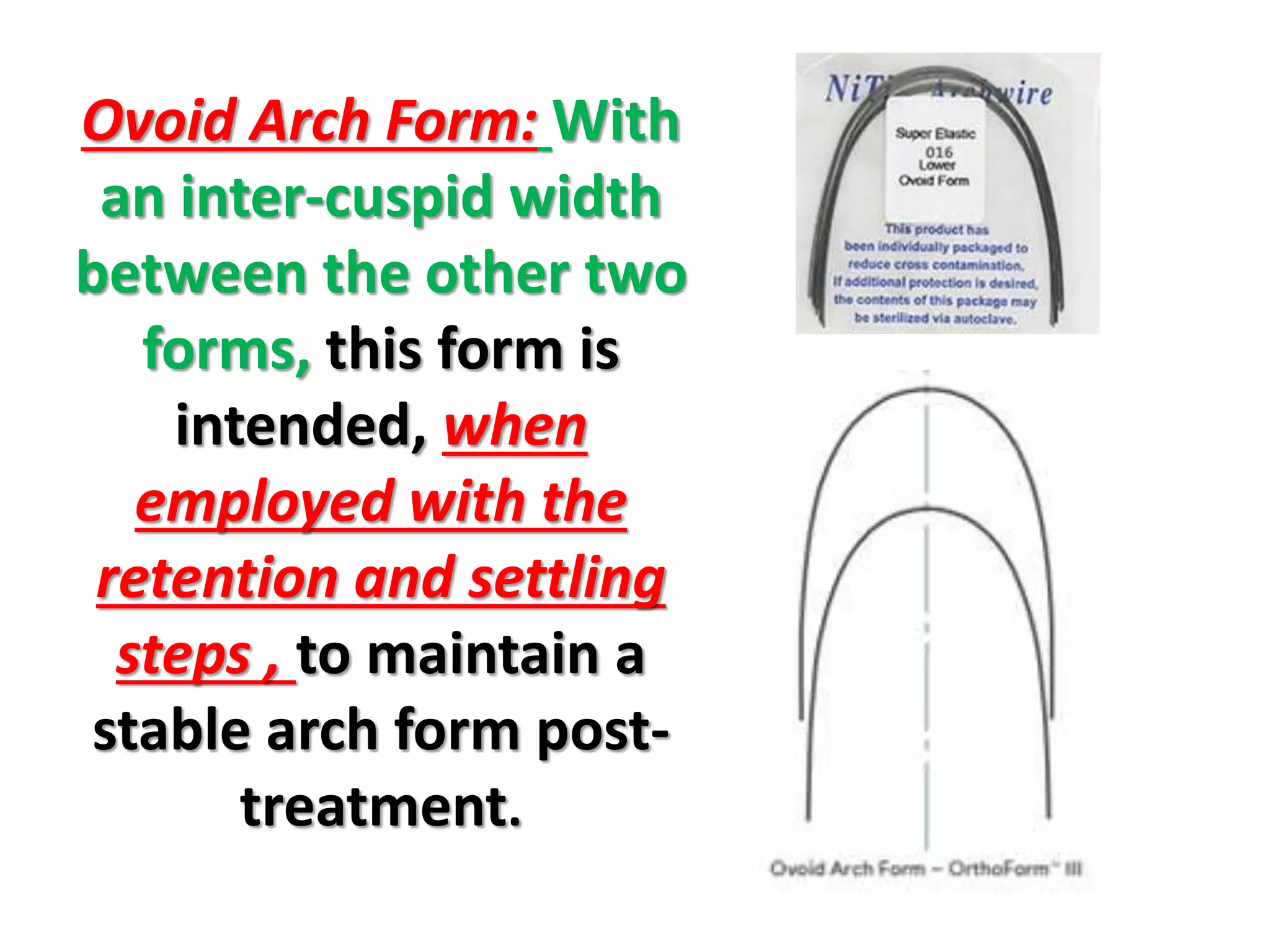
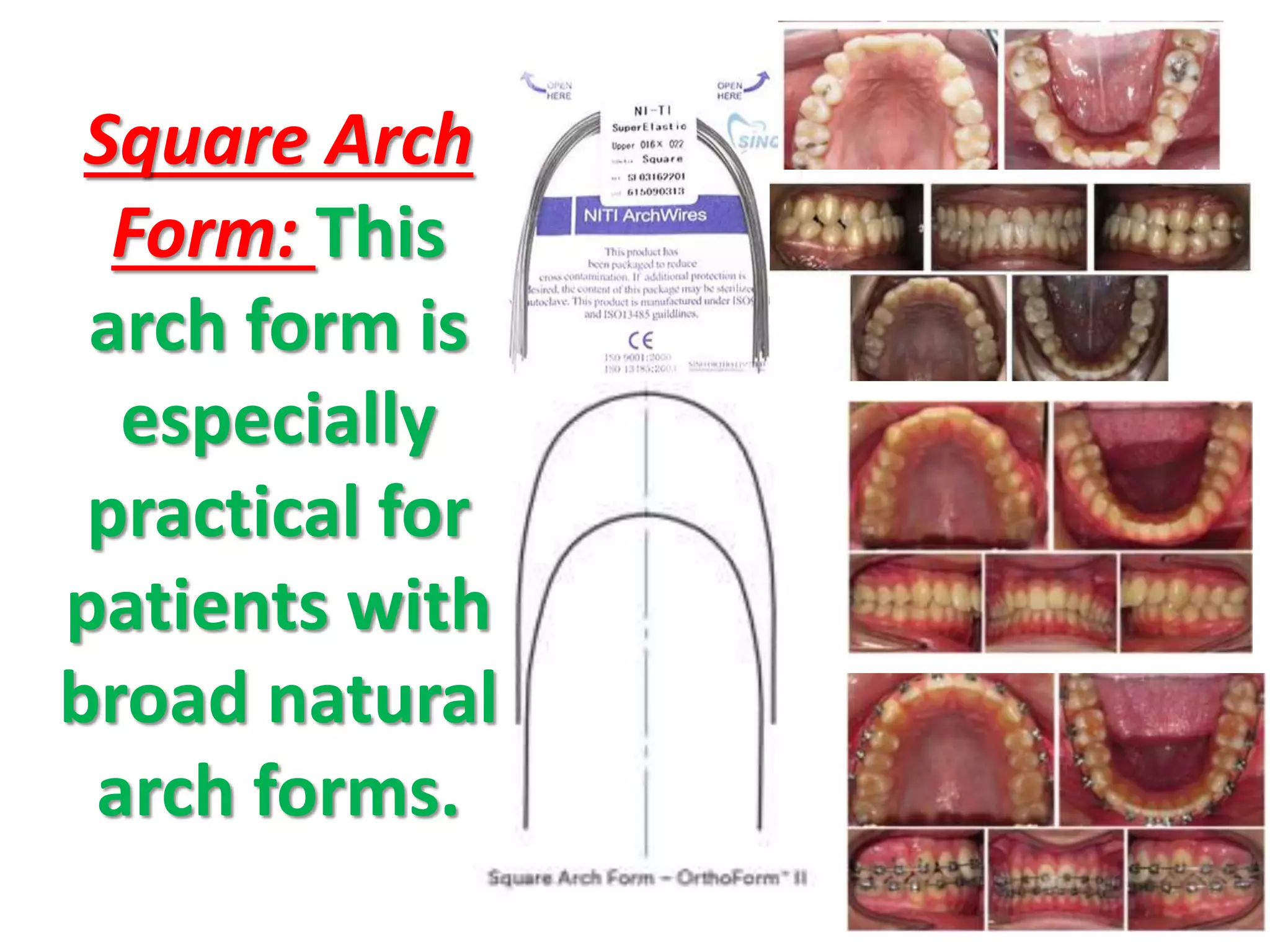
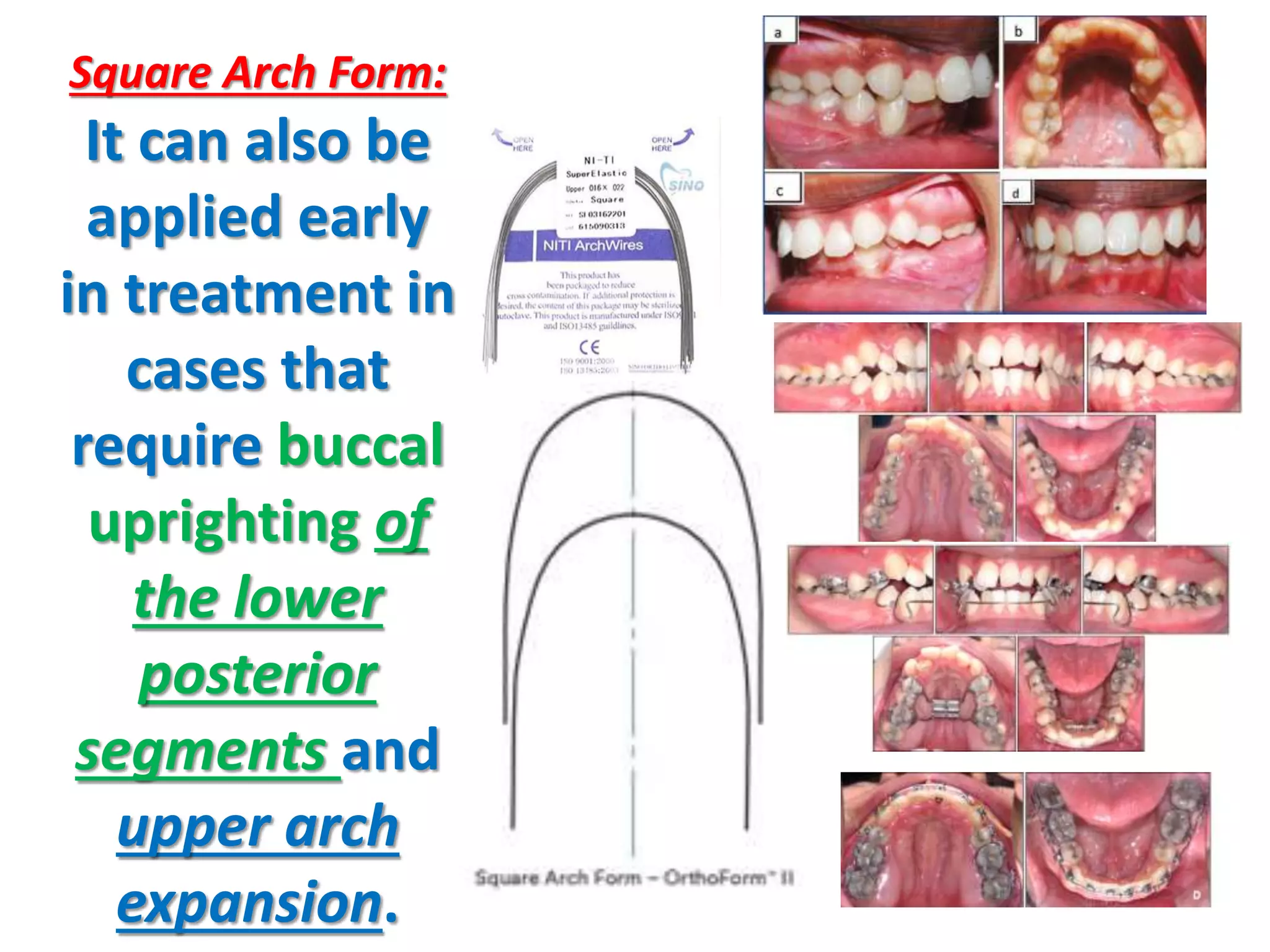
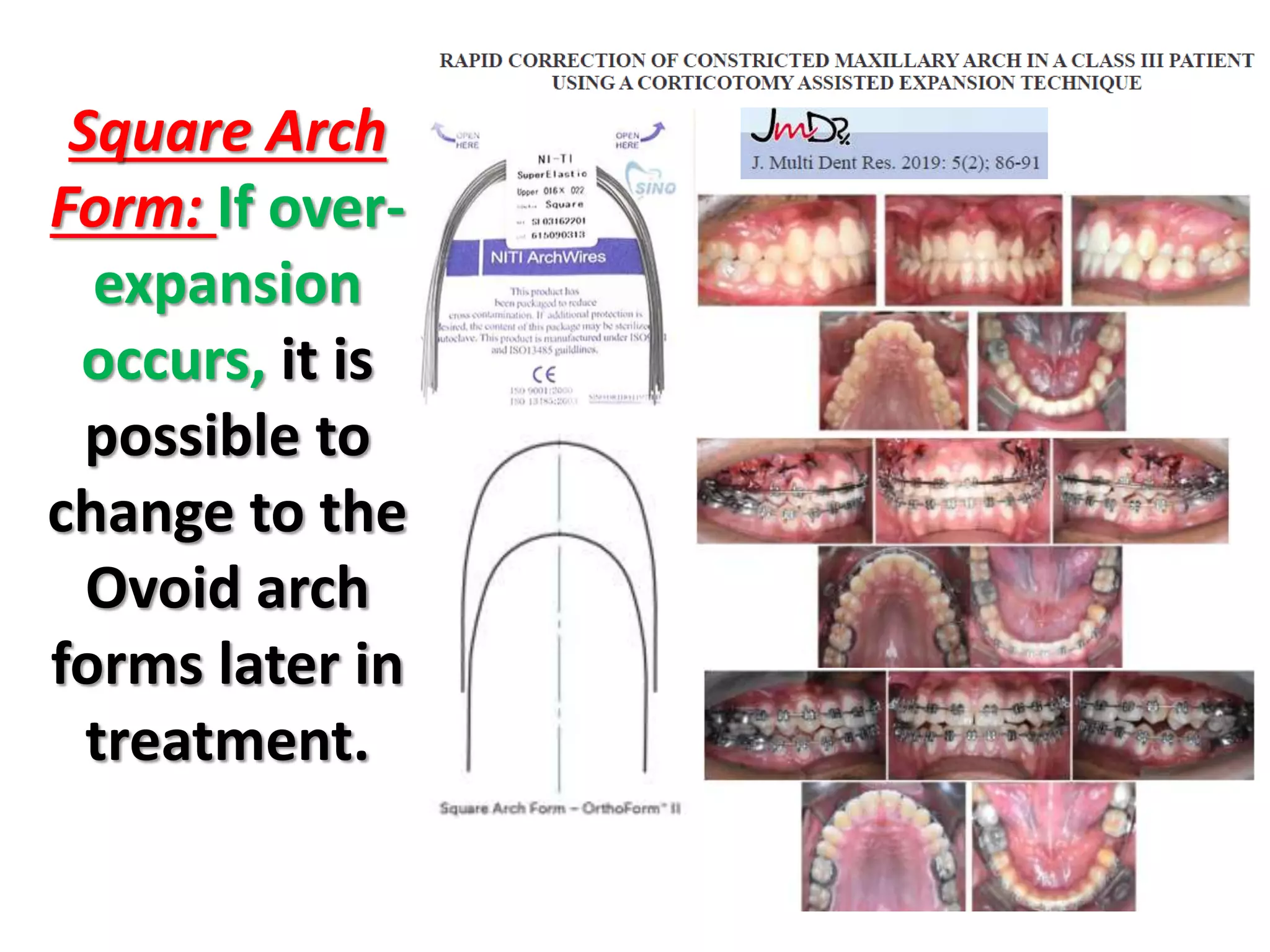
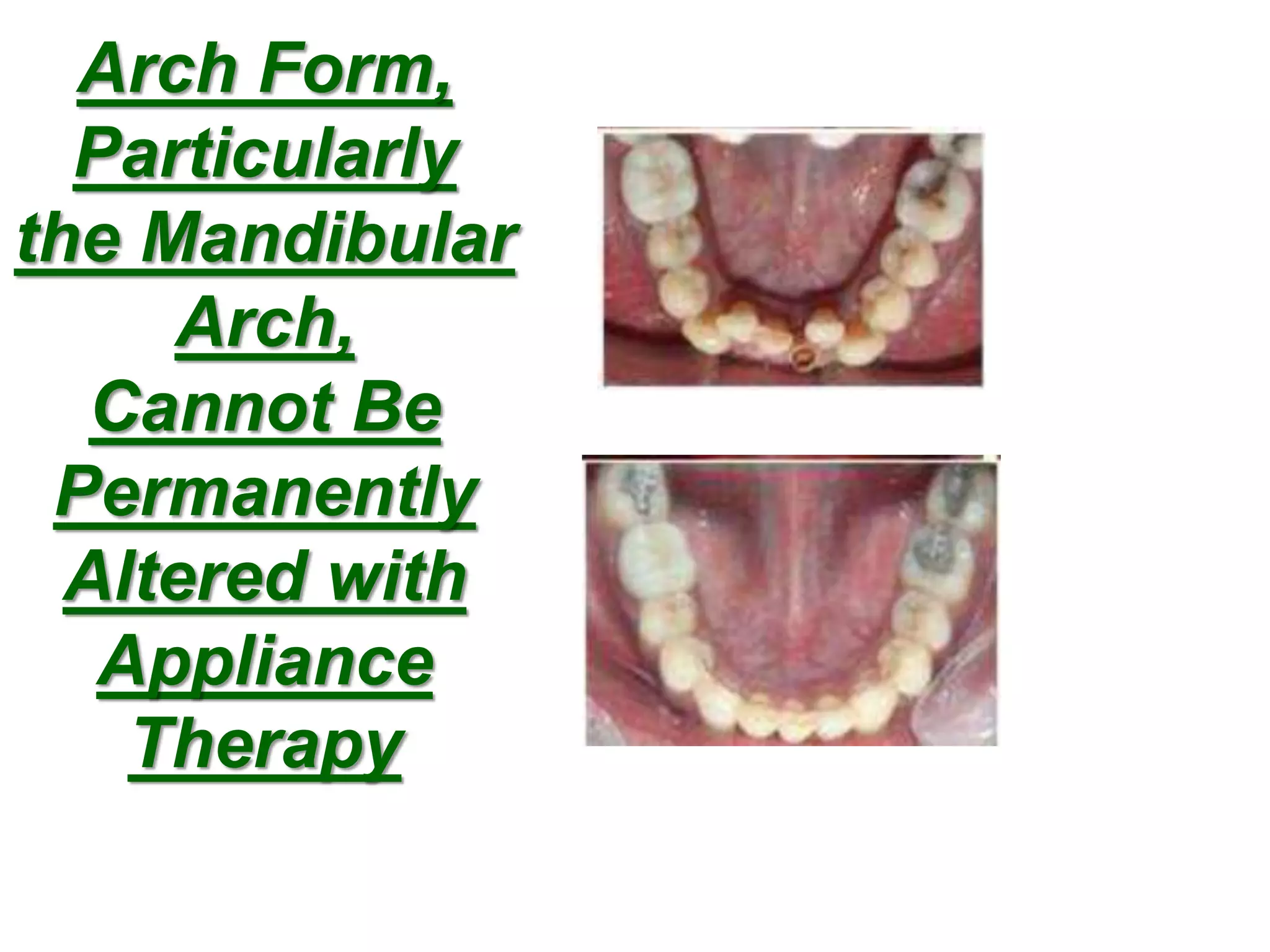
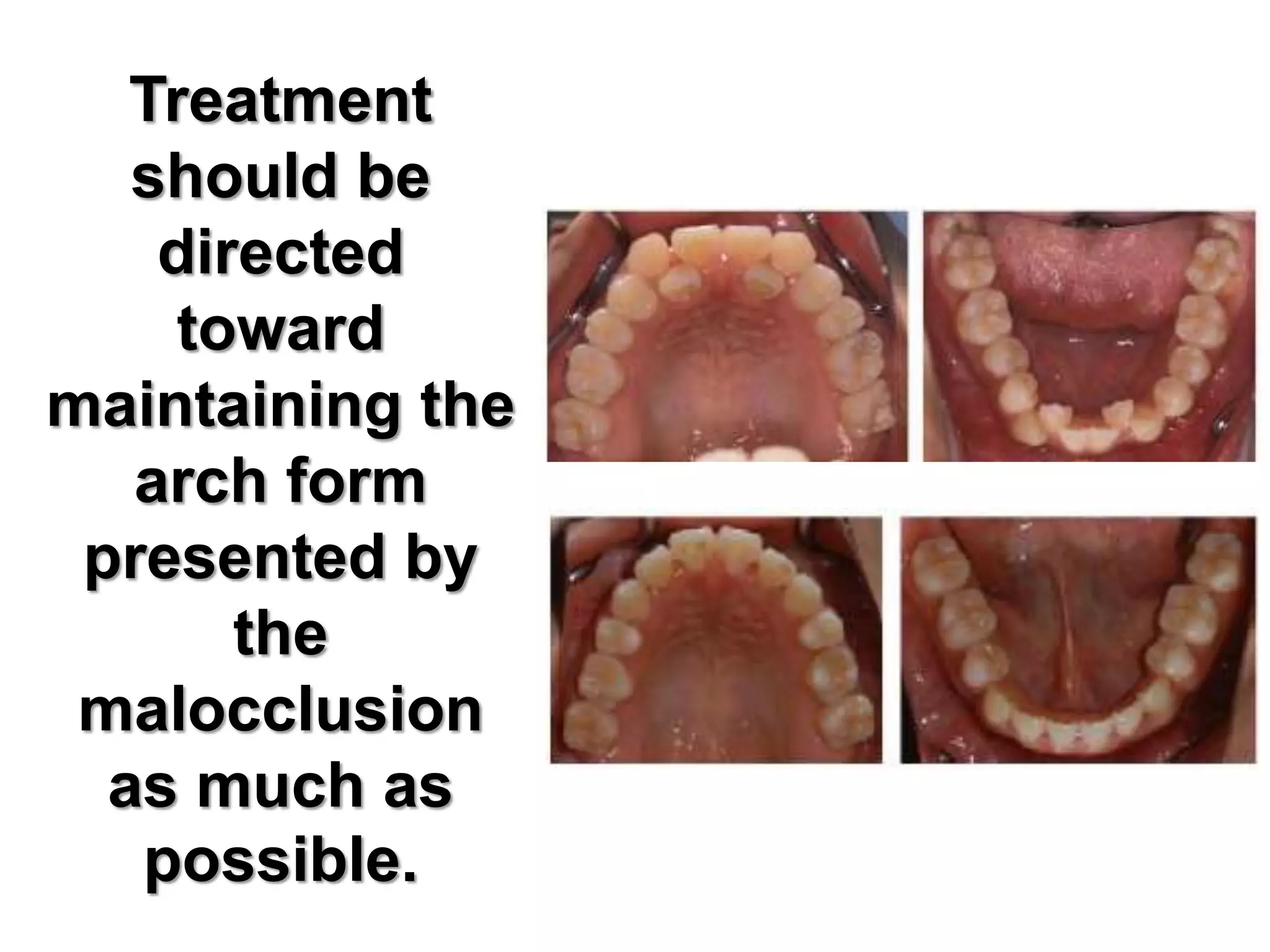
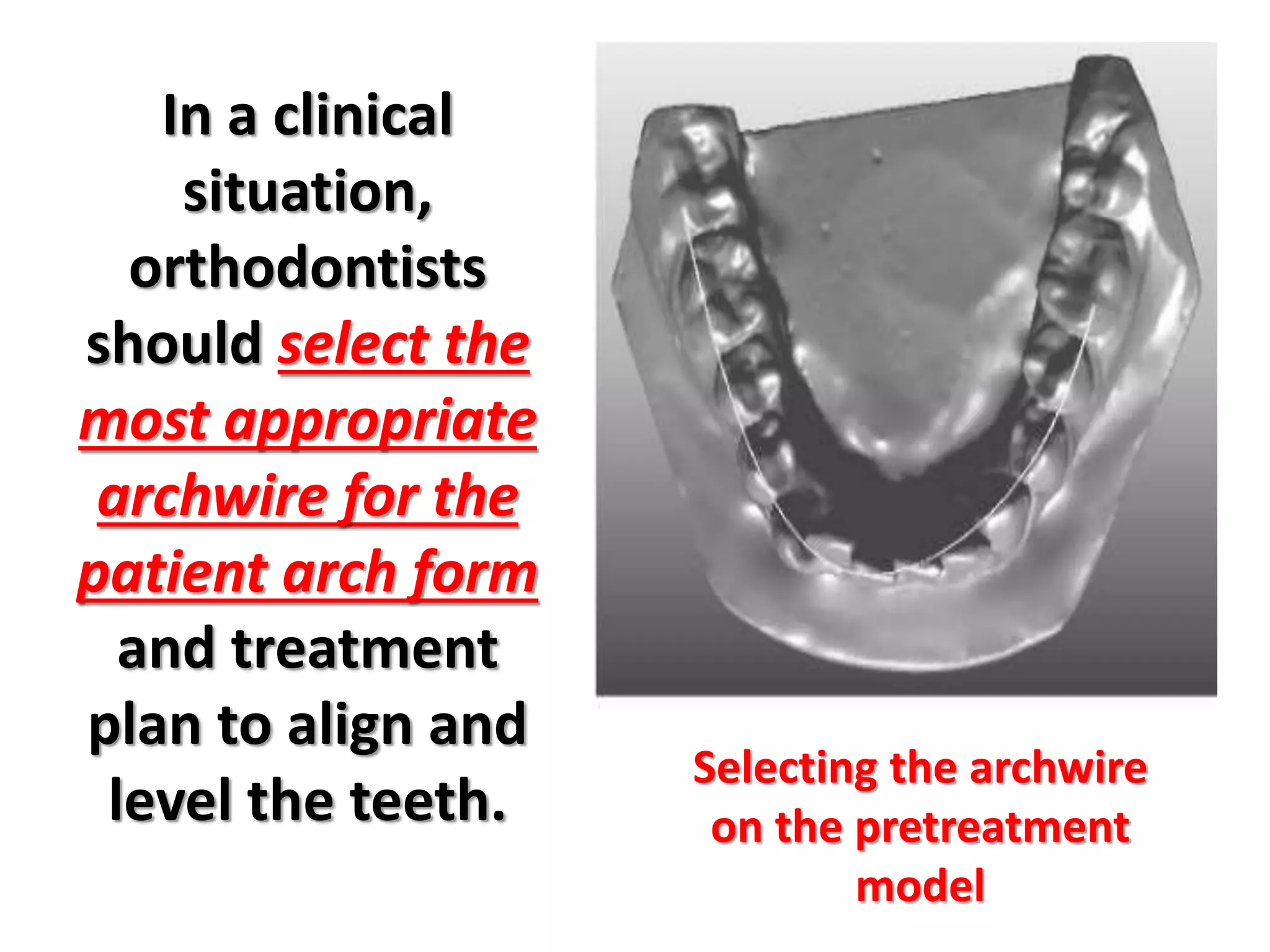
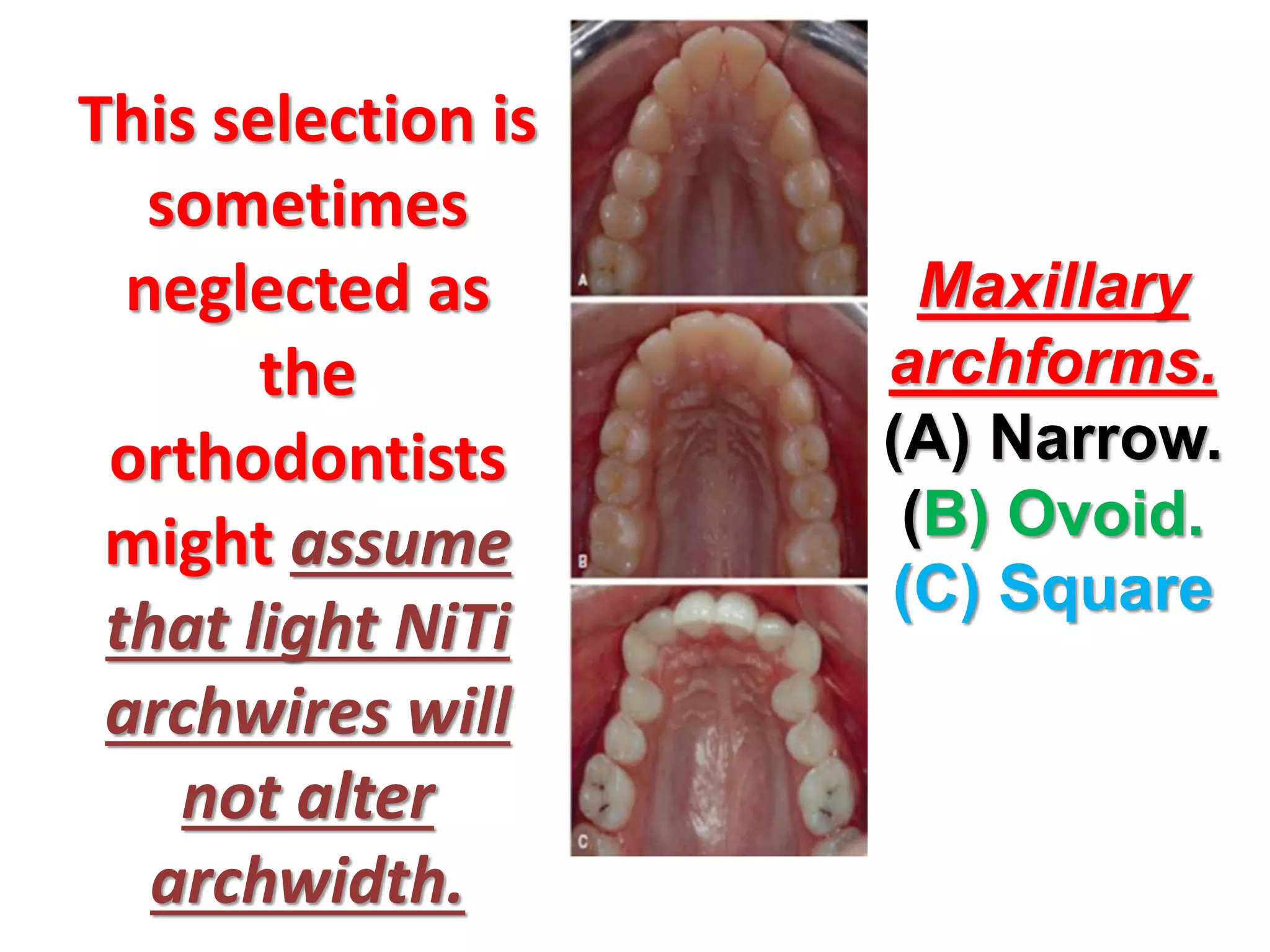
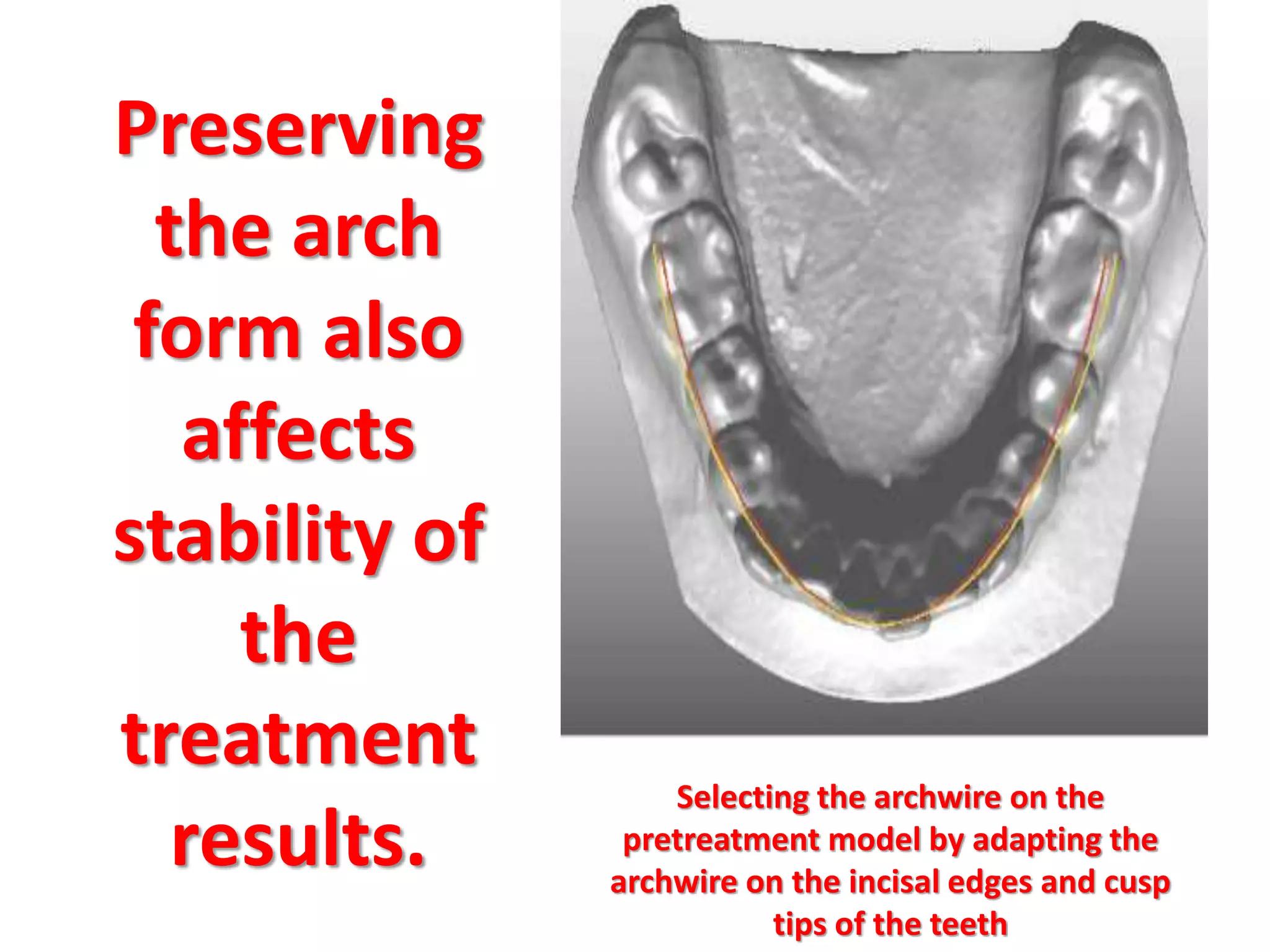
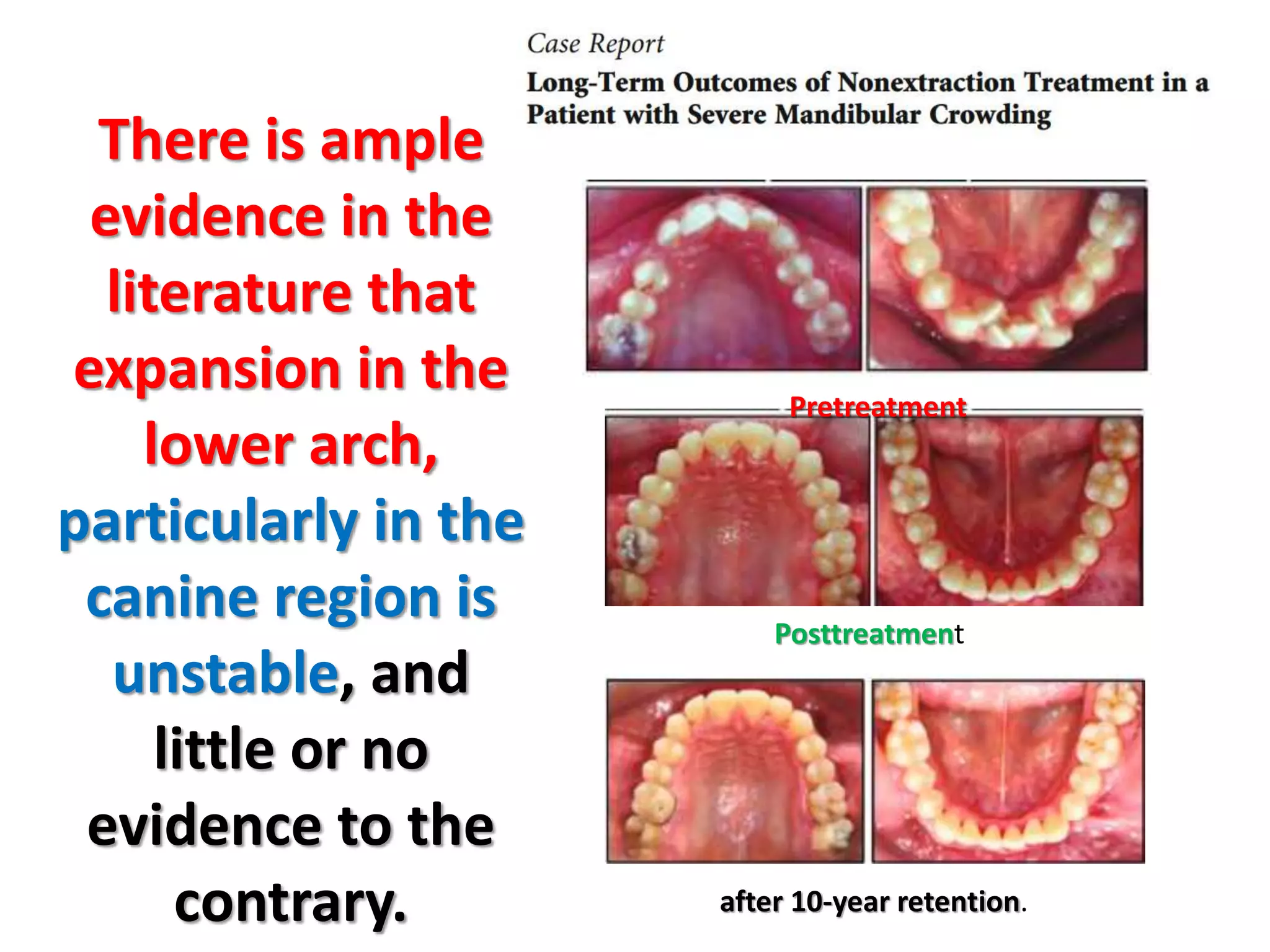
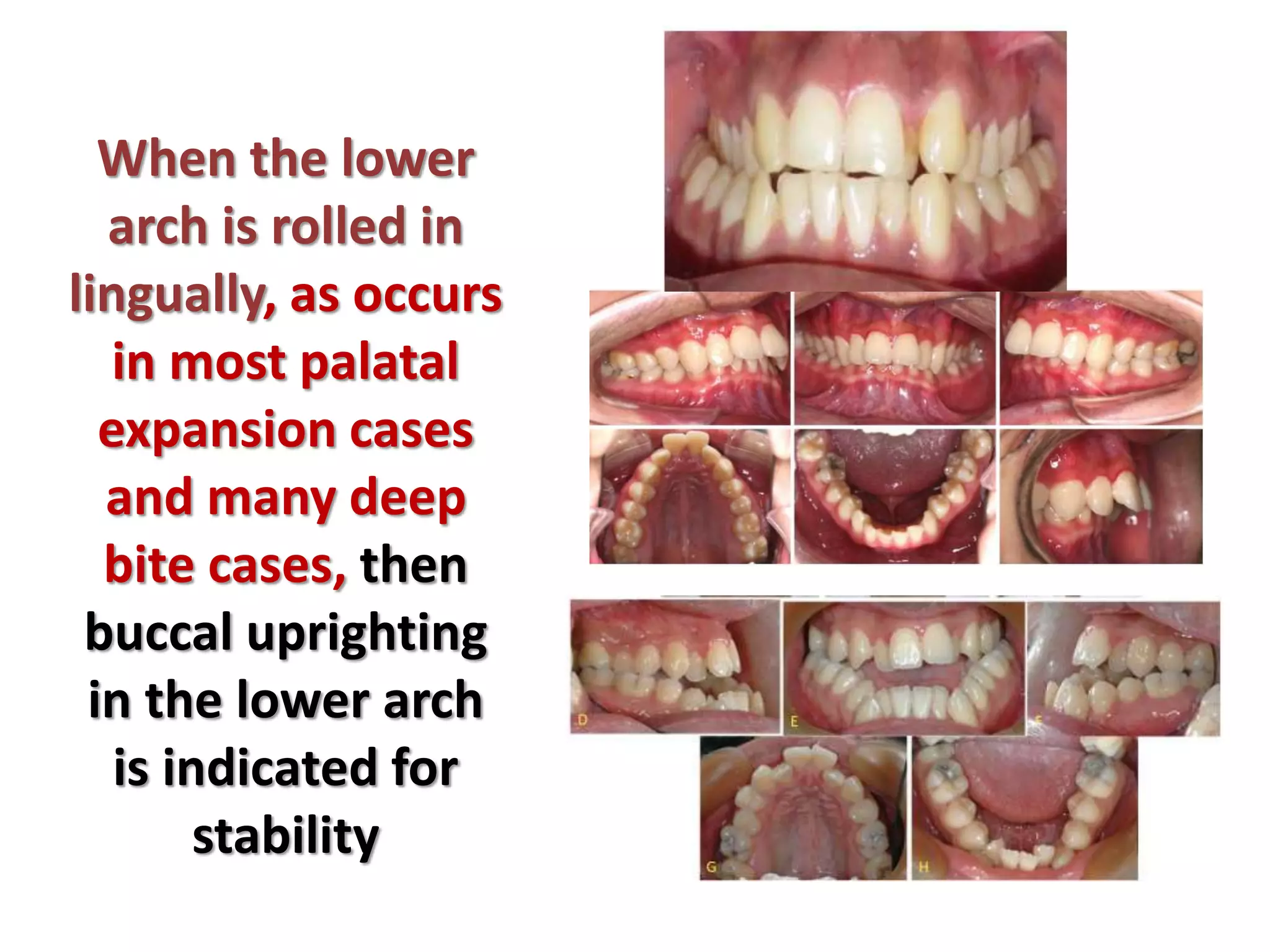
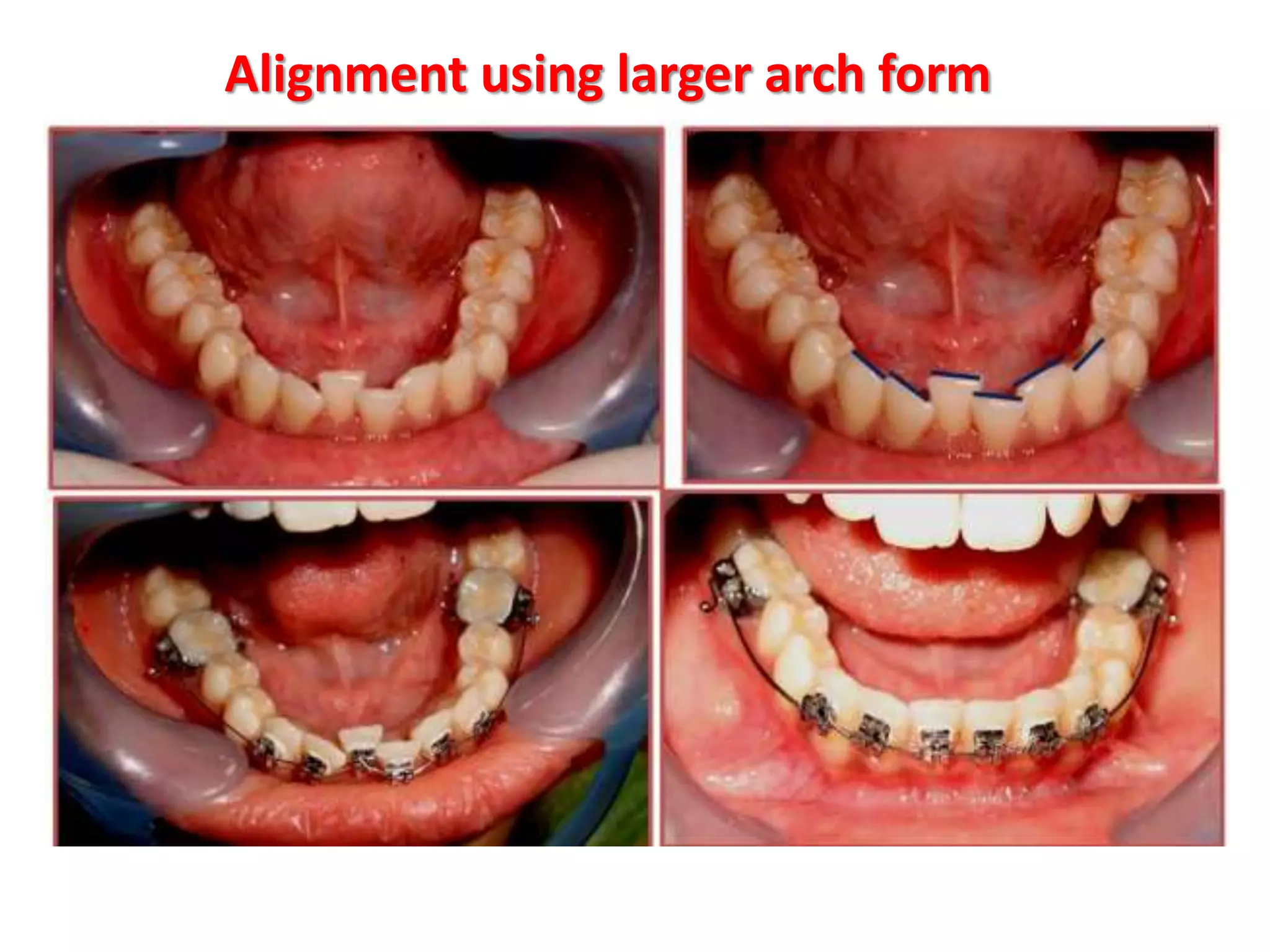
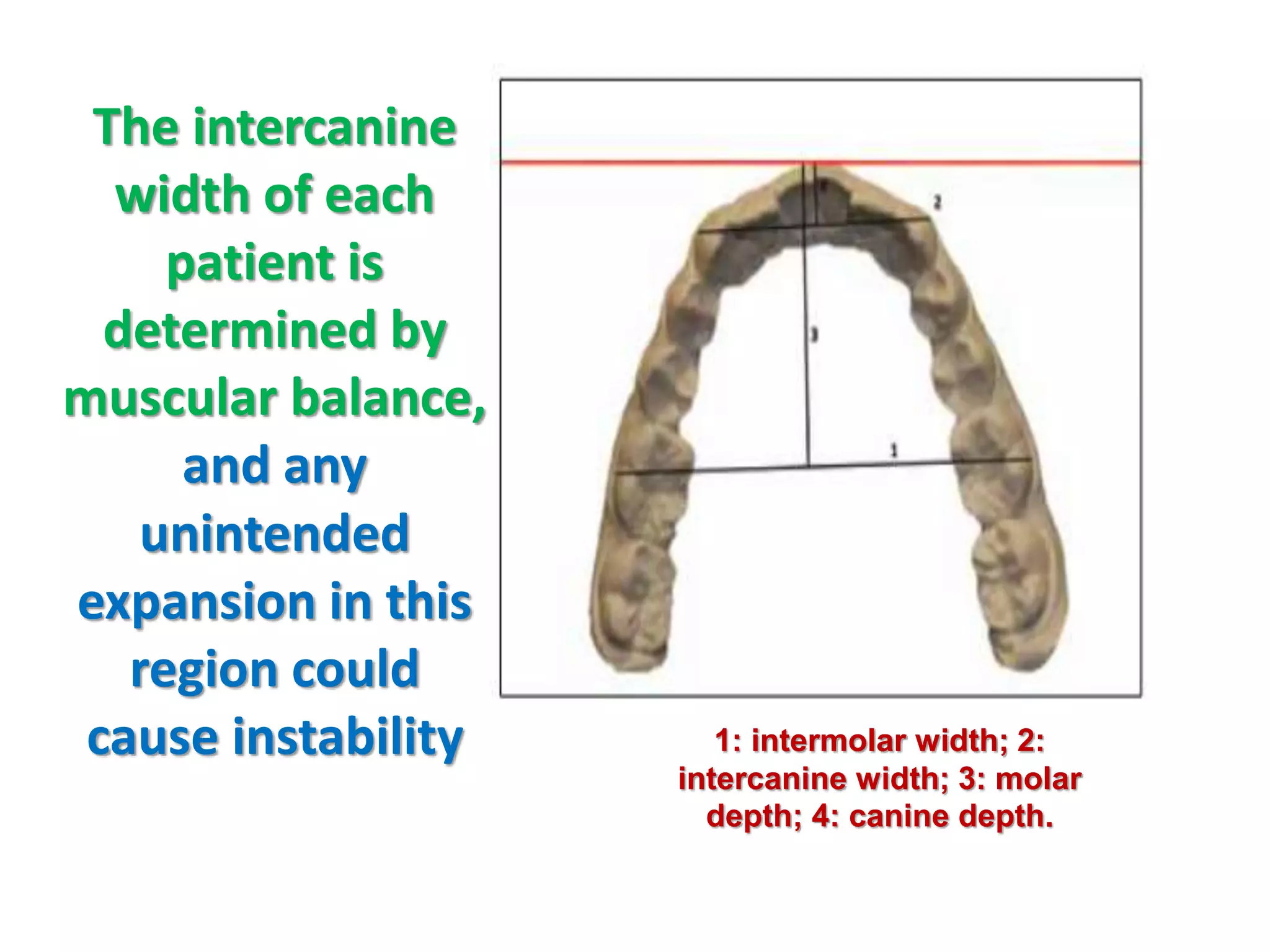
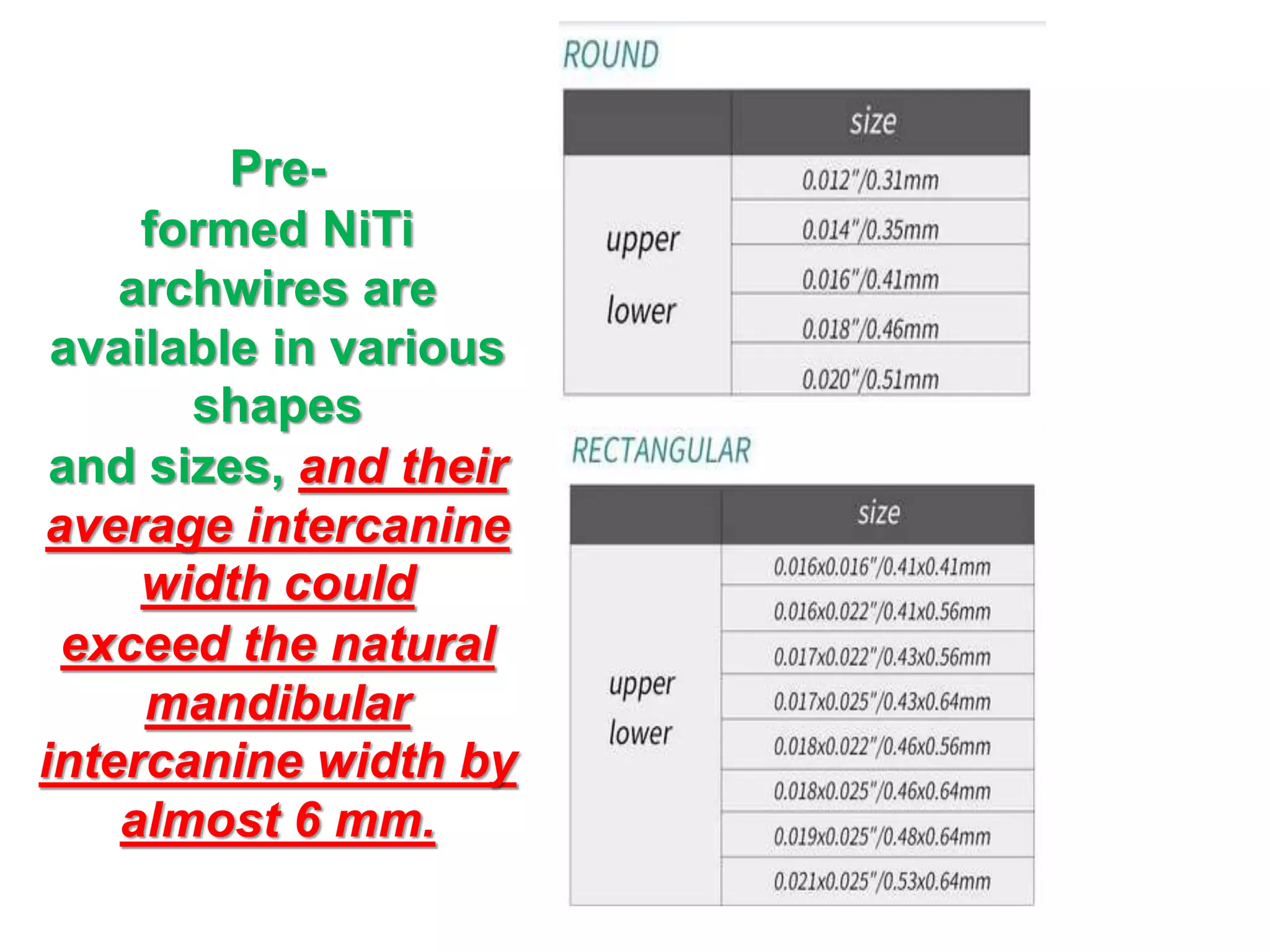
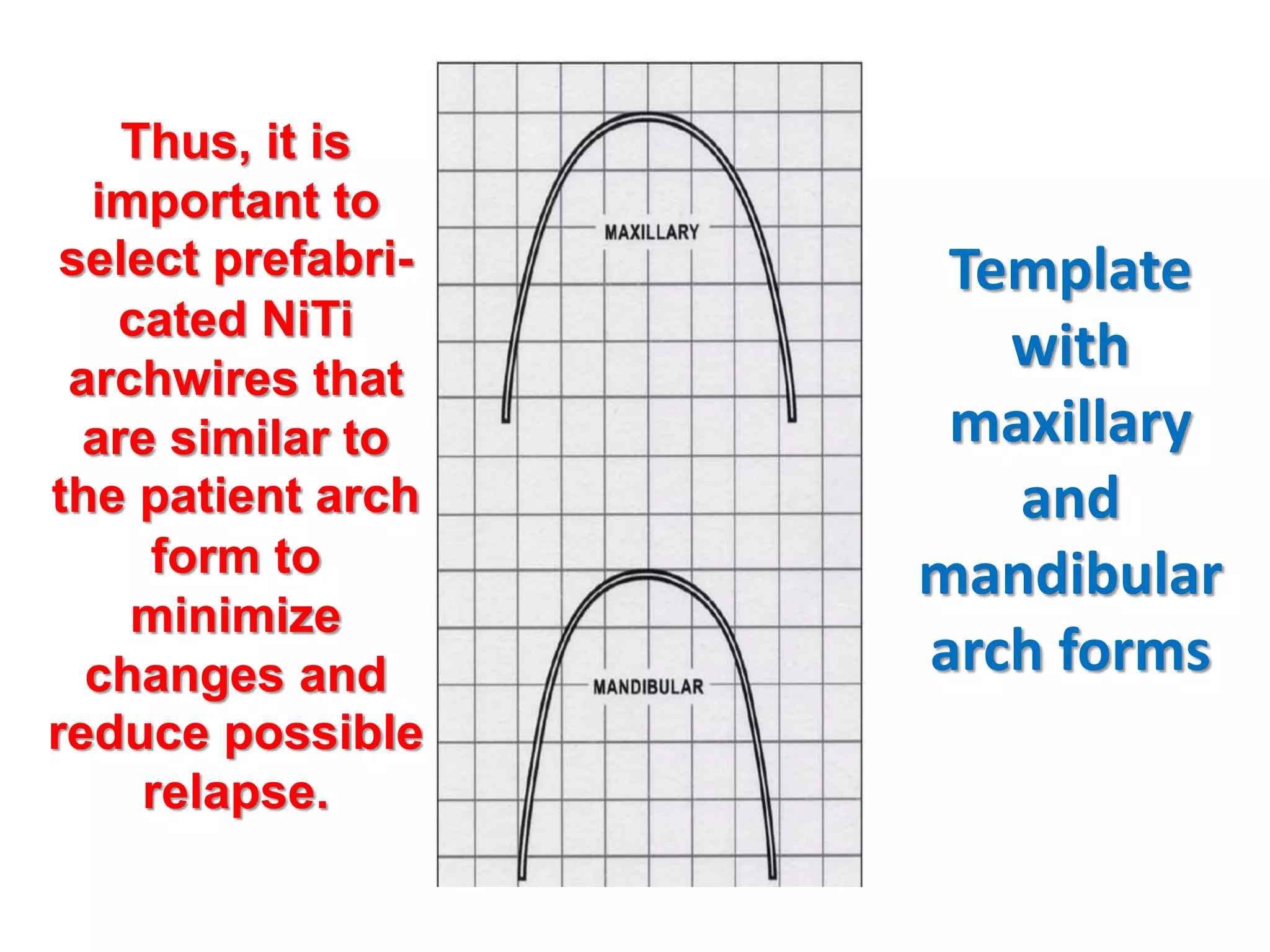
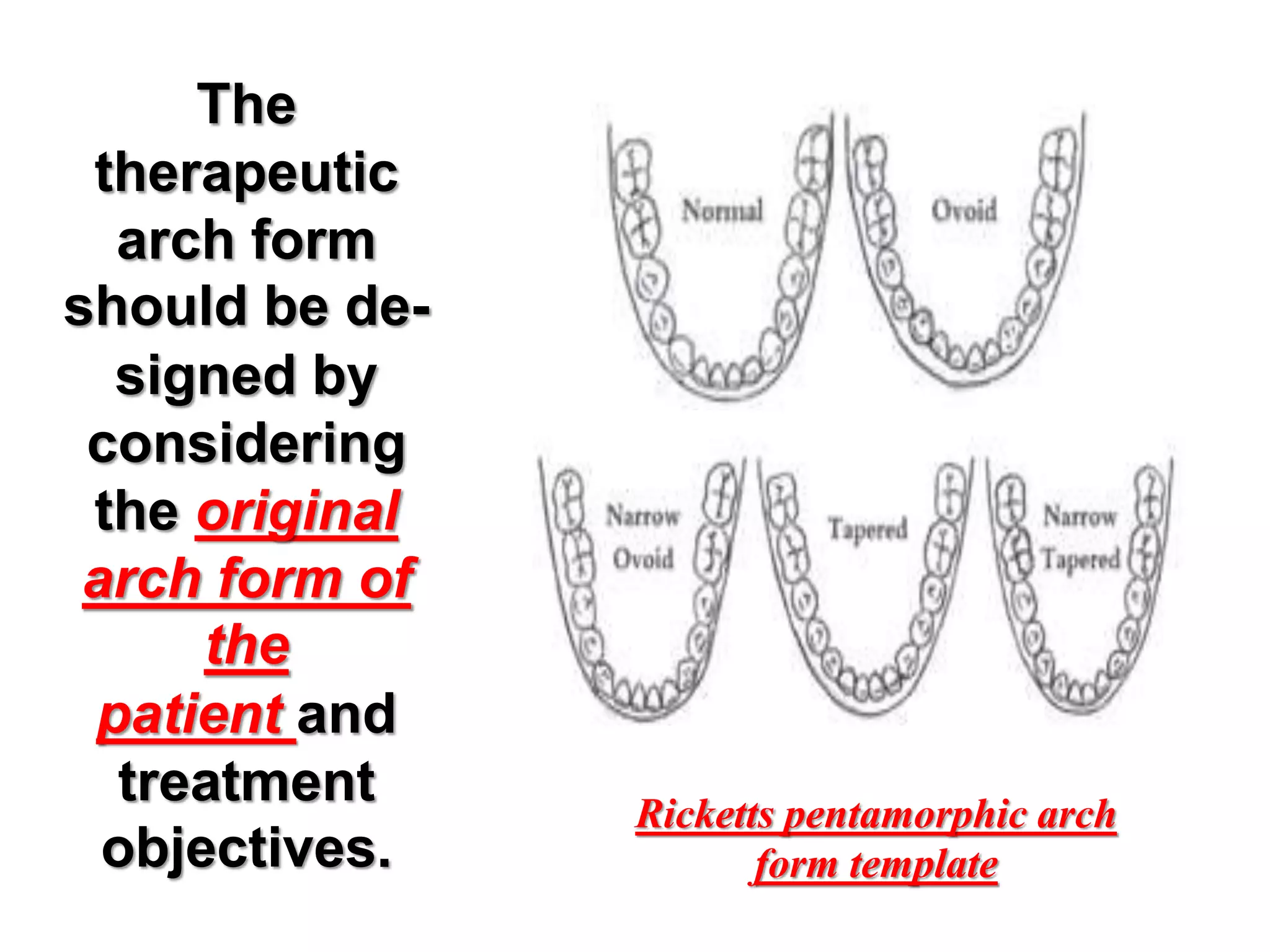
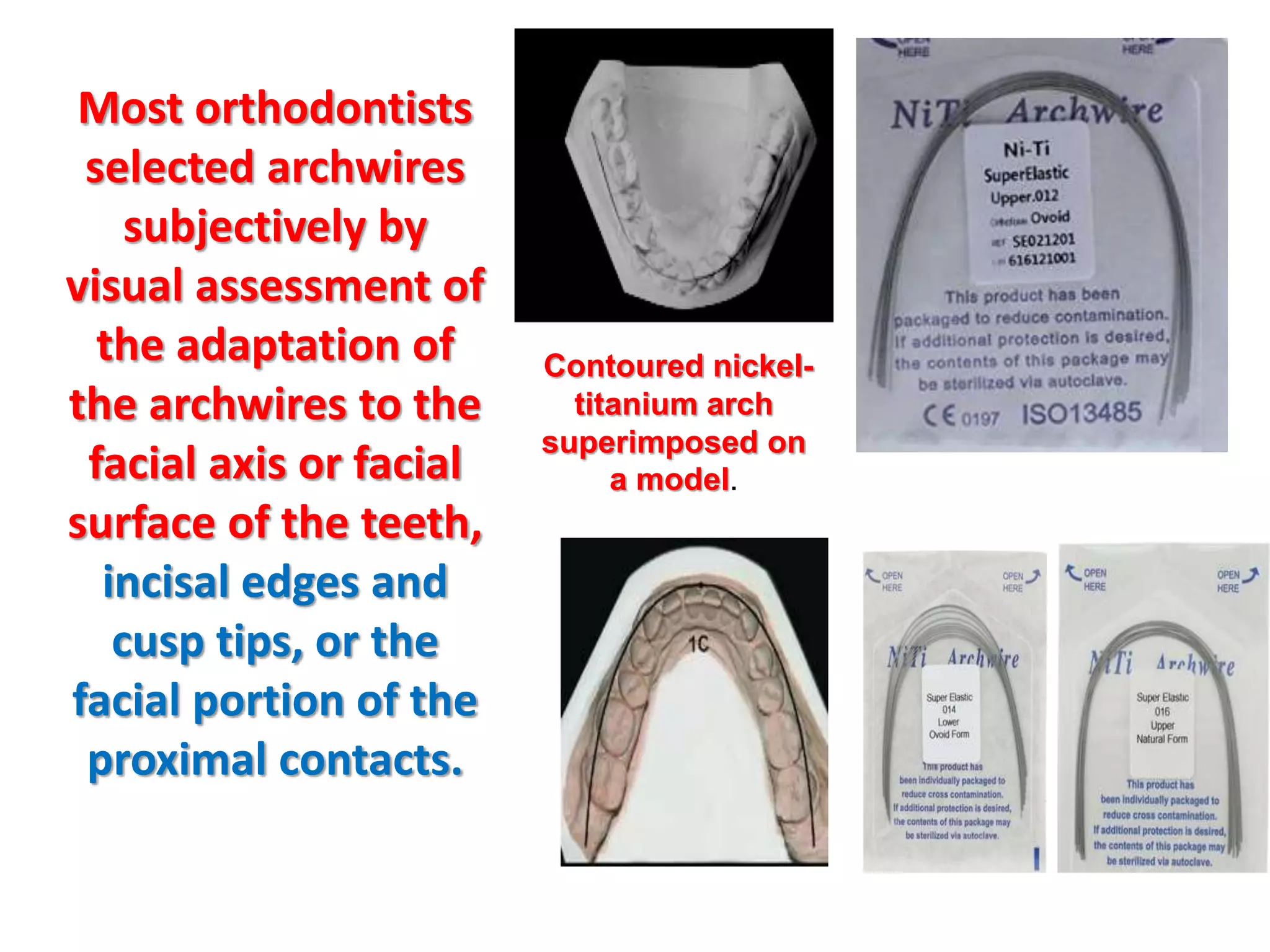
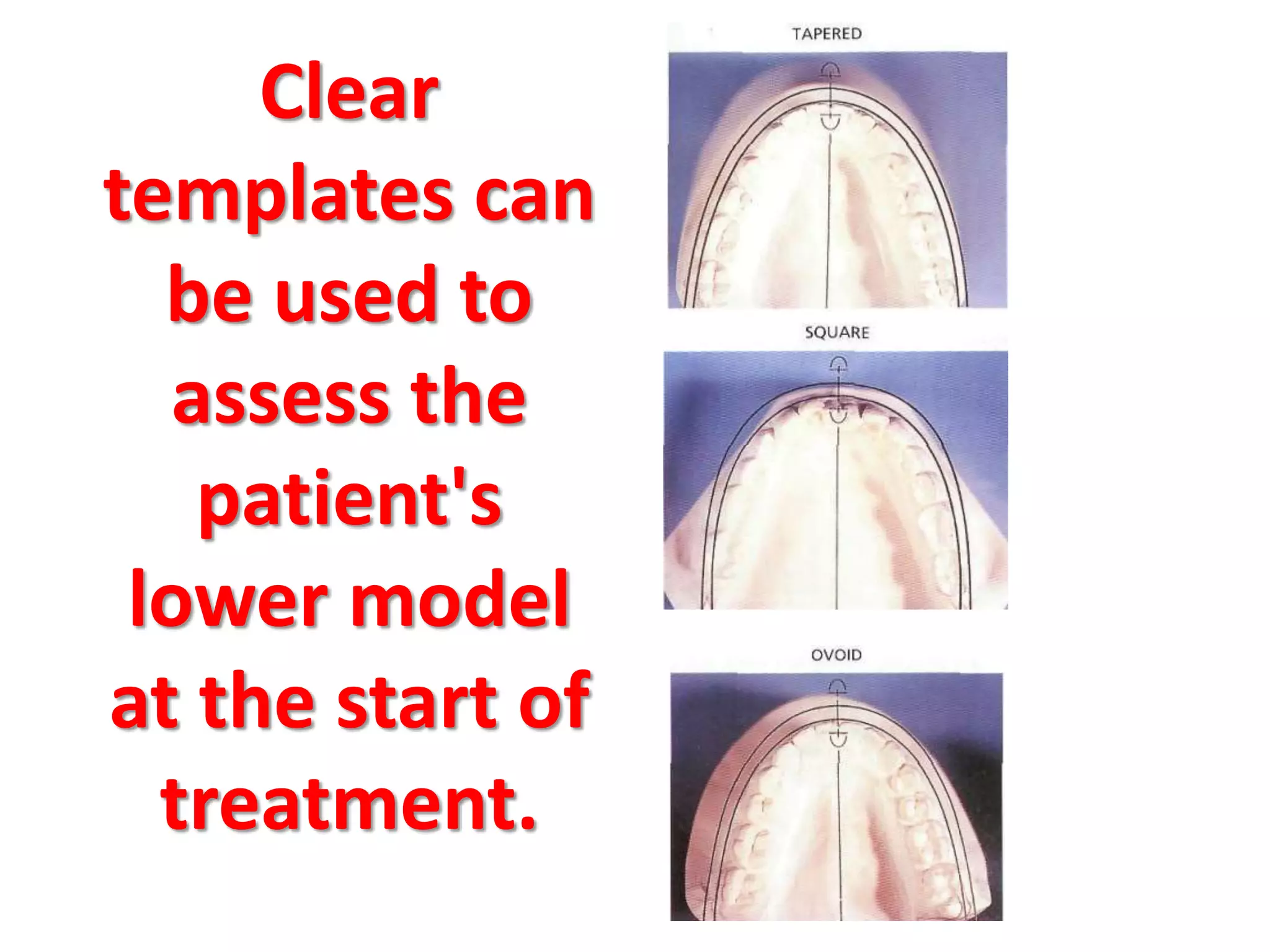
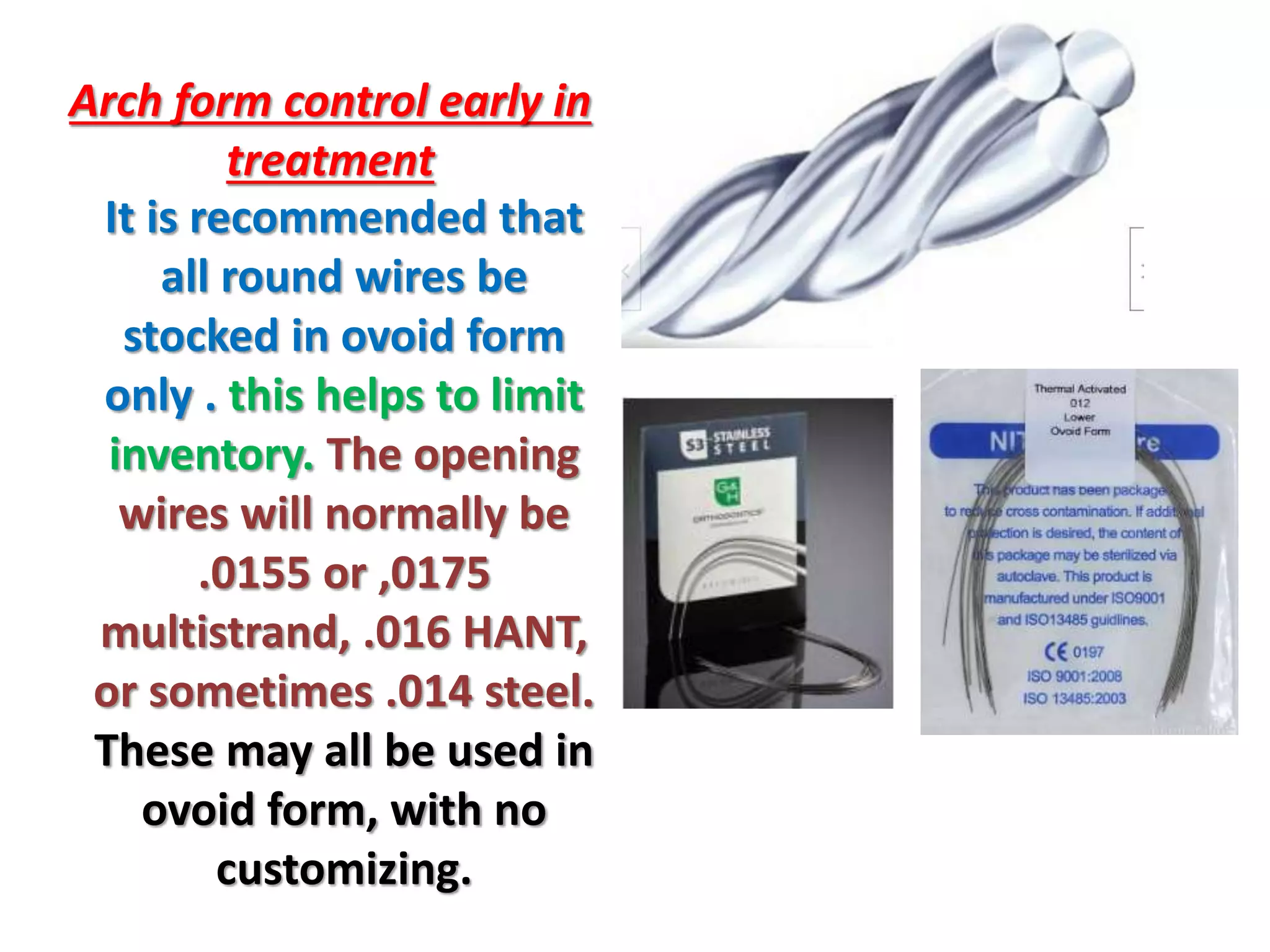
This document discusses orthodontic archwire selection during the alignment stage of treatment with preadjusted appliances. It provides details on different types of archwires used for alignment including multi-strand stainless steel, conventional and superelastic nickel-titanium (NiTi), and heat-activated NiTi wires. Superelastic NiTi wires are preferred for alignment due to their low stiffness, high springback, and ability to deliver nearly constant light forces during tooth movement. The document discusses various archwire sequences used during alignment and leveling, noting that there is no set sequence but heat-activated NiTi can replace multiple stainless steel wires to reduce visits and discomfort.