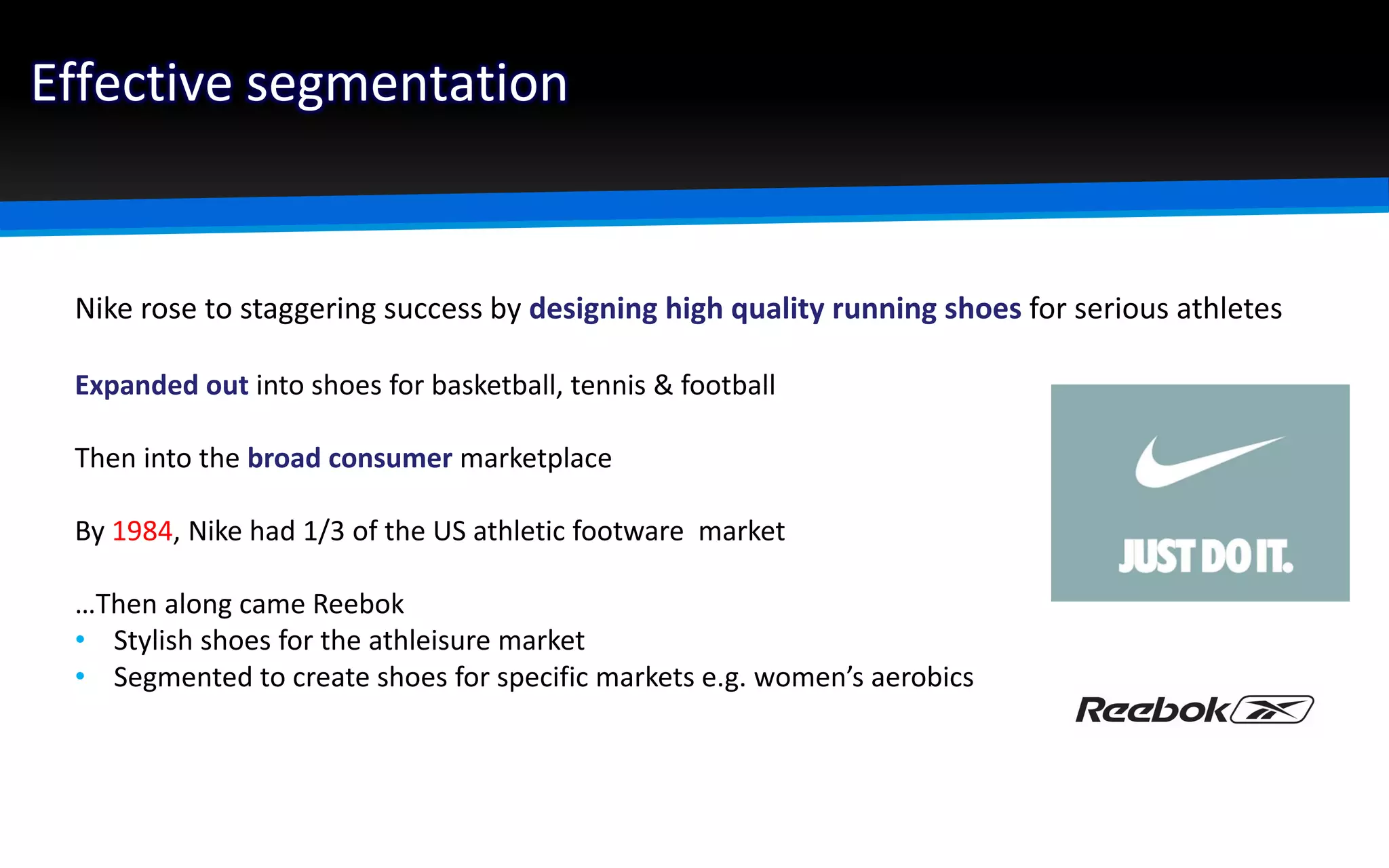
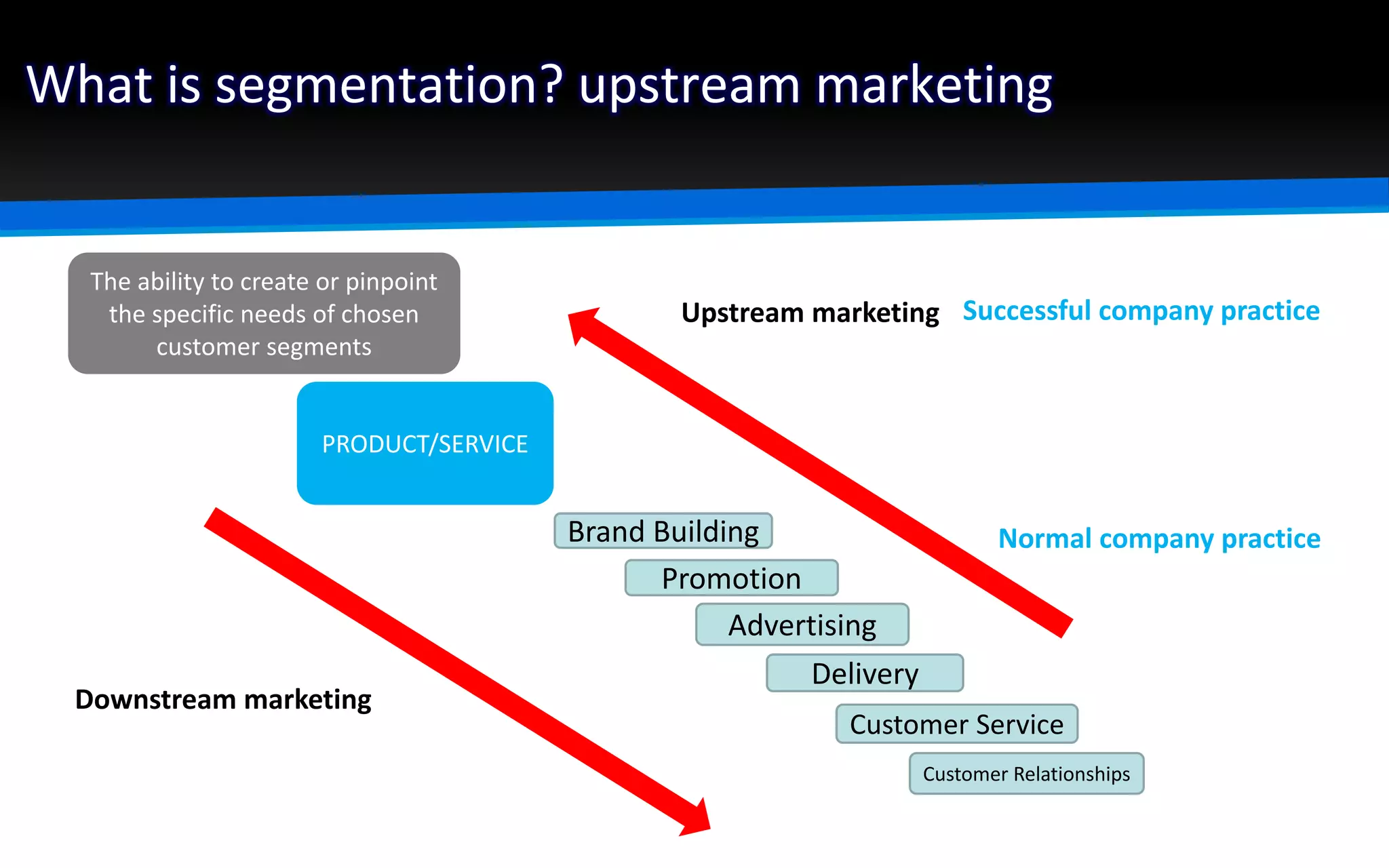
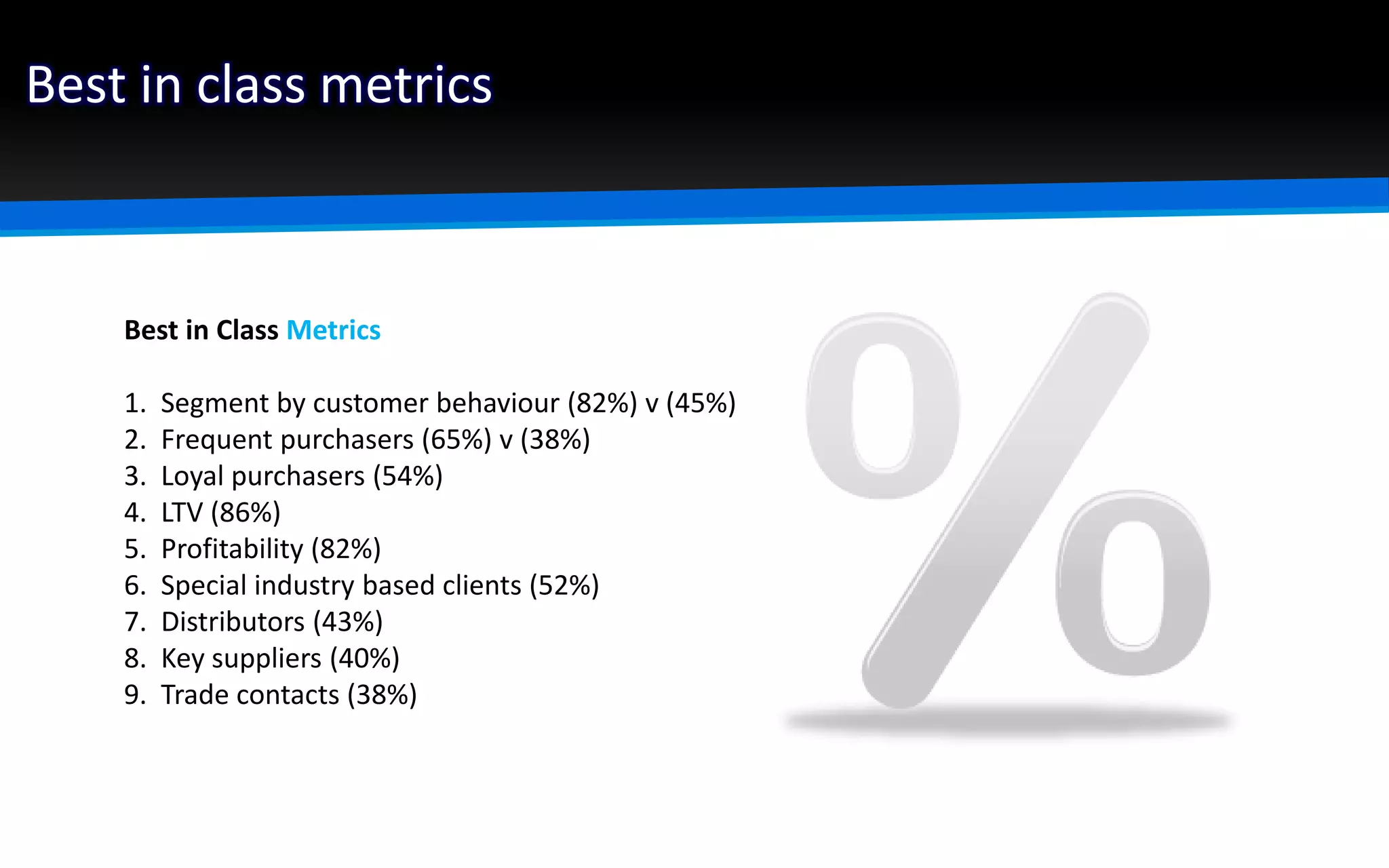
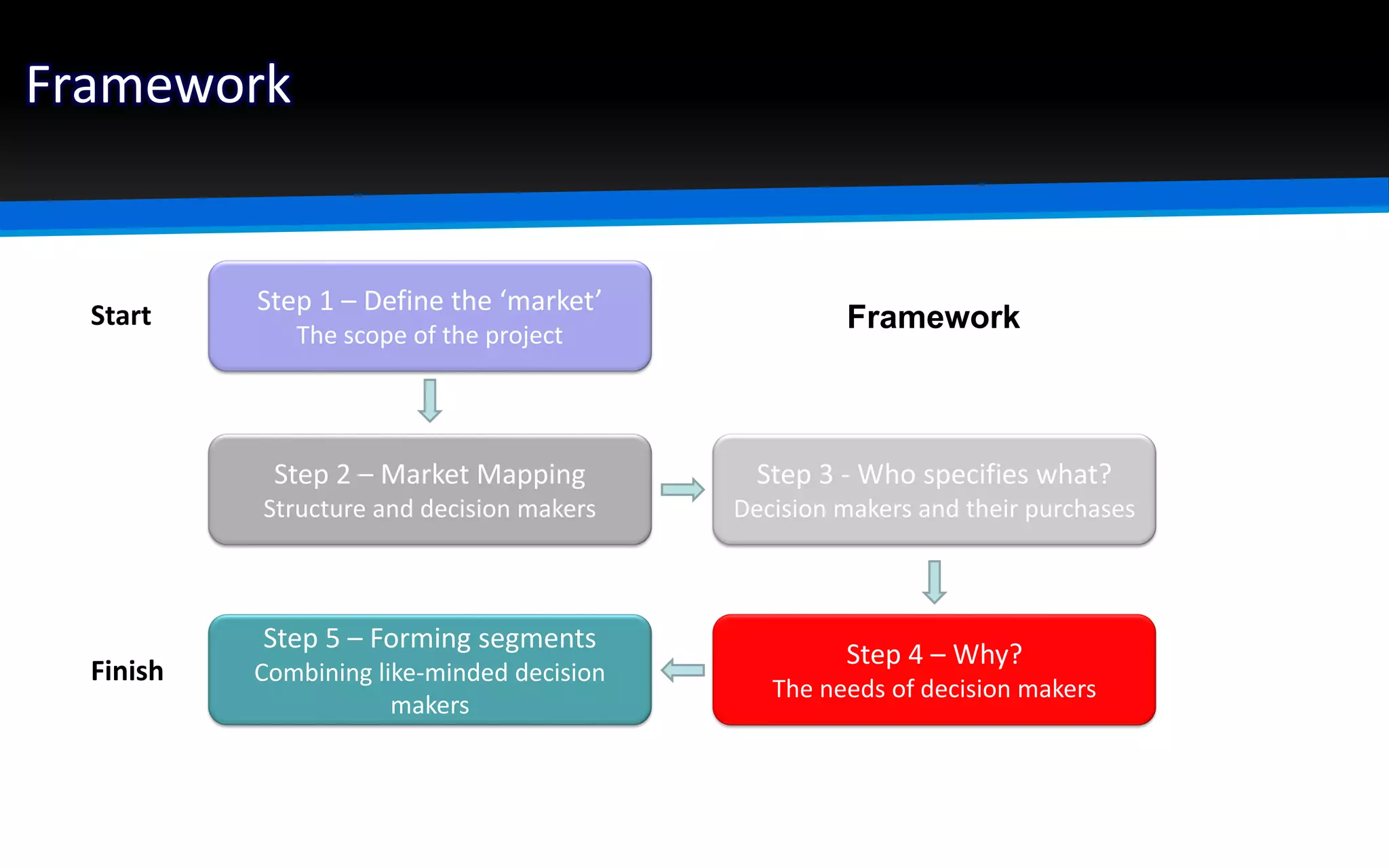
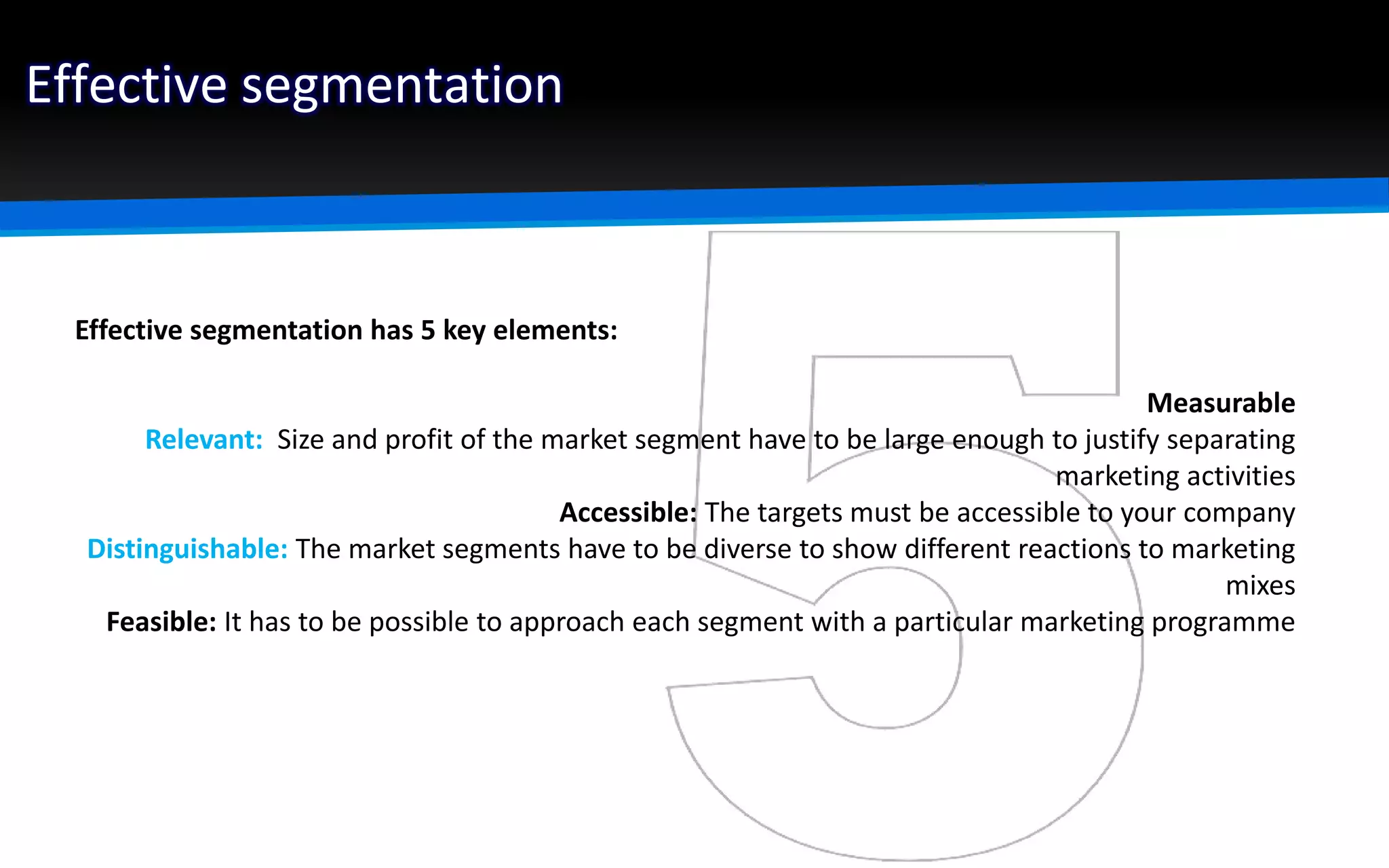
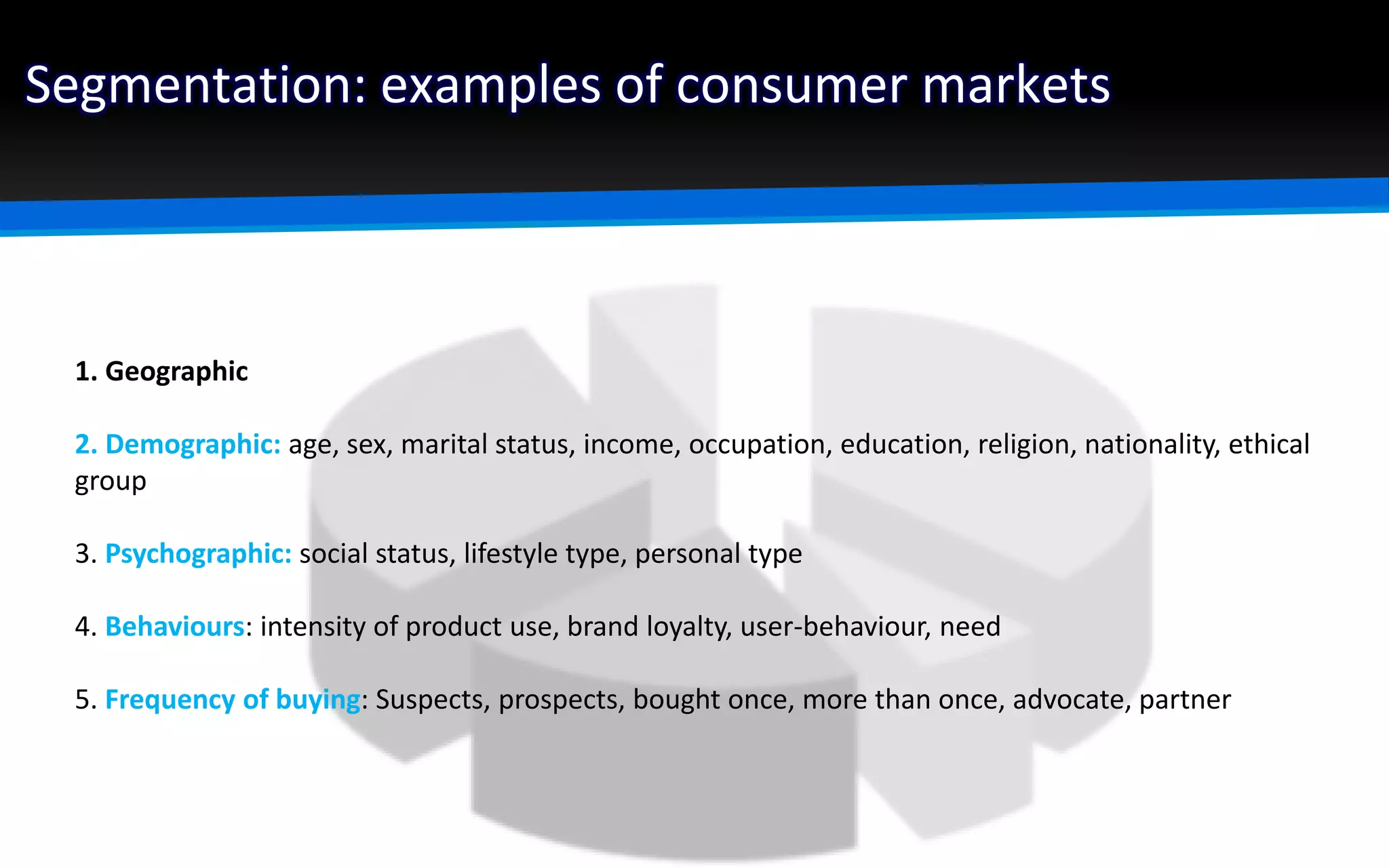
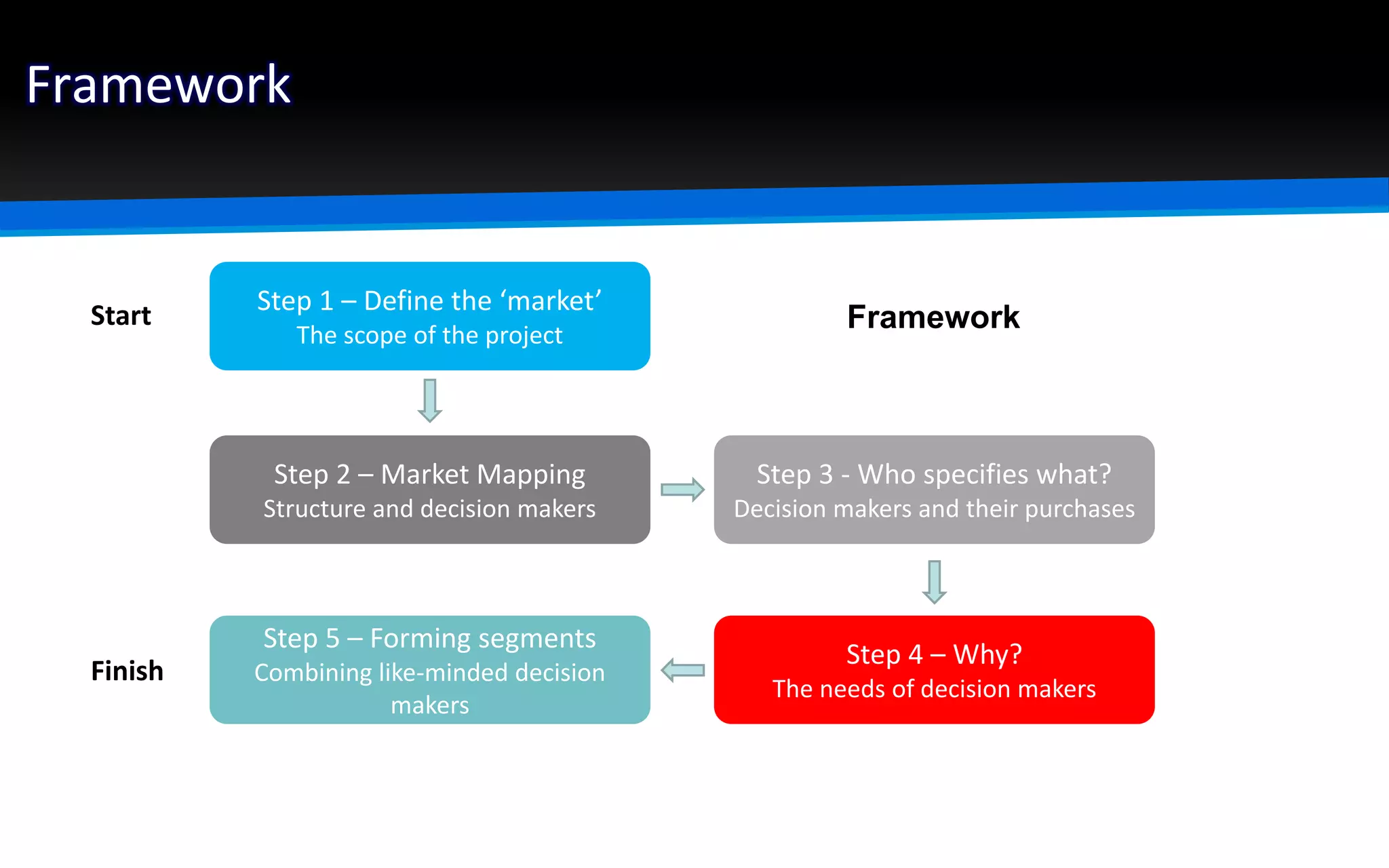
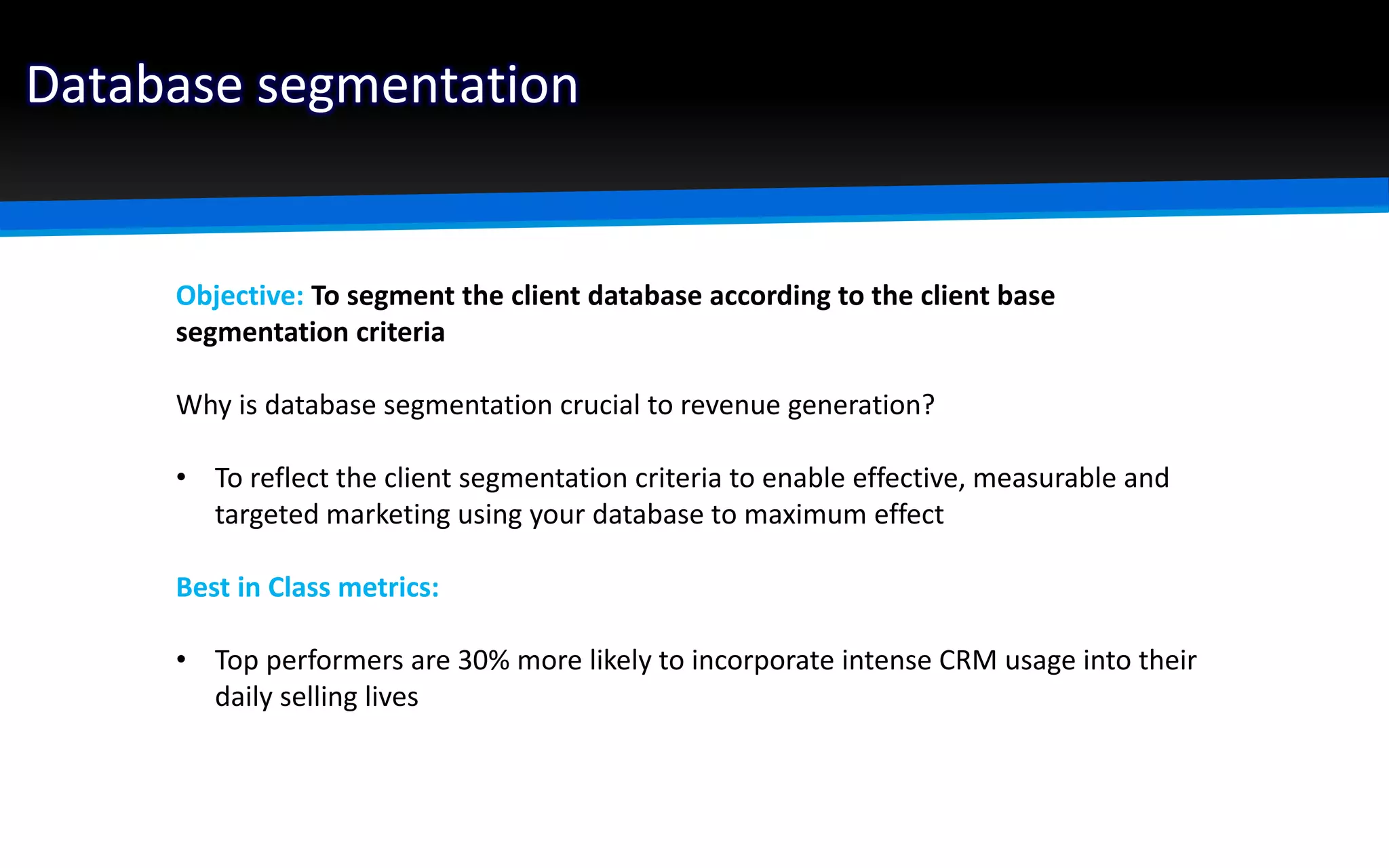
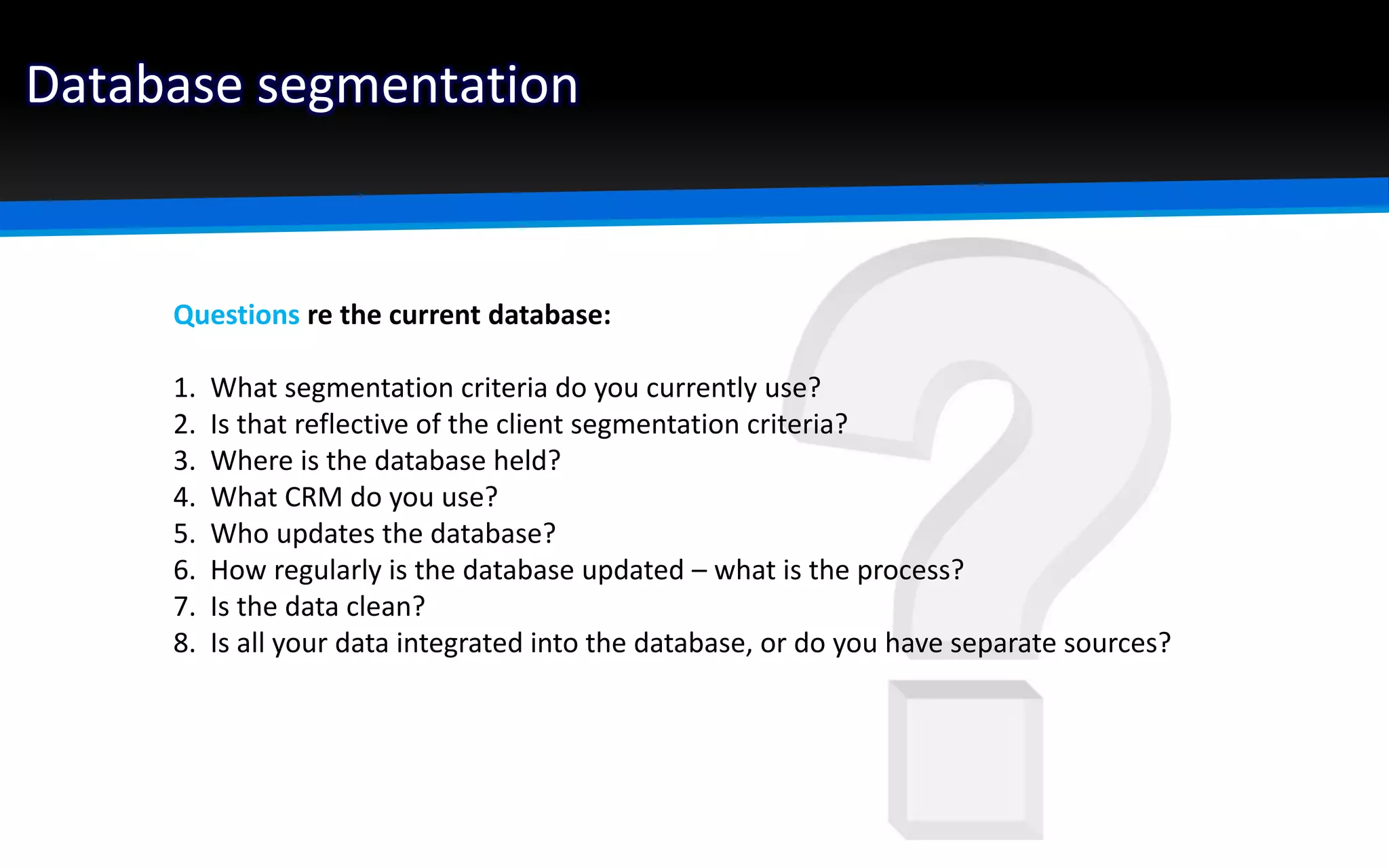
The document outlines the importance of market segmentation in increasing sales and client retention by tailoring marketing strategies to specific client needs. It details the segmentation process, emphasizing the necessity for distinct marketing approaches for different buyer segments. Key elements for effective segmentation include measurable market size, accessibility, distinguishable characteristics, and feasibility of targeted strategies.