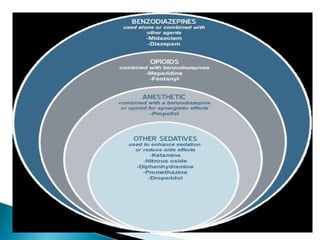
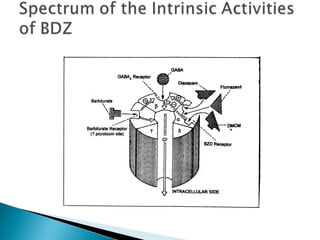
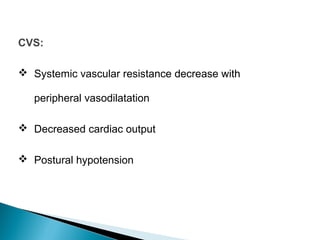
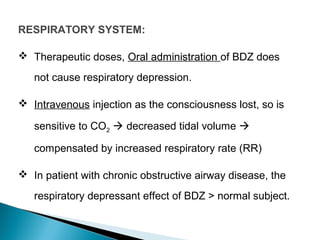
This document discusses benzodiazepines (BDZs), including their discovery, mechanism of action, effects, and examples like diazepam and midazolam. It notes that BDZs bind to GABA receptors in the brain to have sedative, anxiolytic, hypnotic, amnestic, and anticonvulsant effects. Their onset and duration of action depends on lipid solubility. While generally safe, they can cause respiratory depression, especially in high doses or with pre-existing lung conditions. Their effects are reversed by the antagonist flumazenil. Midazolam is water-soluble and shorter-acting than diazepam. It is metabolized in the liver