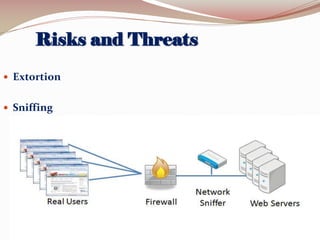
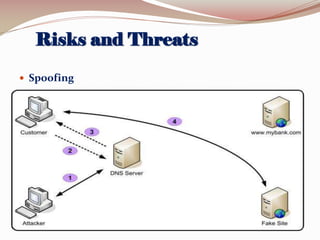
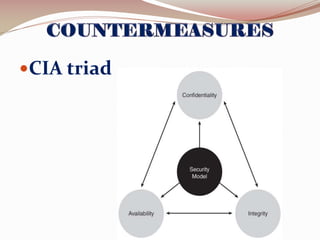
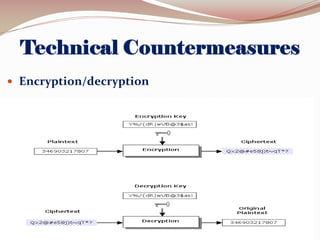
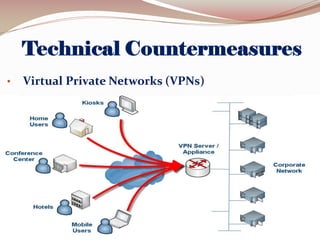
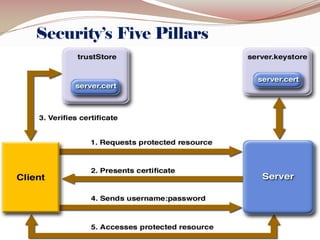
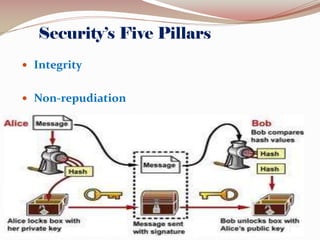
This document lists the group members for a project on security and then provides information on various topics related to security including: definitions of security, computer security, and information security; risks and threats such as fraud, denial of service attacks, malicious software, and computer criminals; and technical countermeasures like firewalls, encryption, and VPNs. It also discusses the CIA triad of security and the five pillars of security.