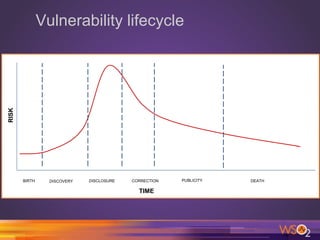
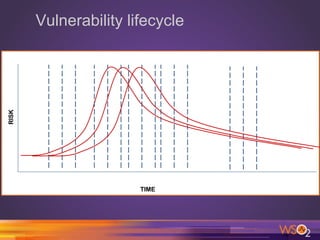
This document discusses ethics in information security and vulnerability disclosure. It outlines 10 commandments of computer ethics focusing on avoiding harming others, respecting privacy and property. It also describes the vulnerability lifecycle from birth to death. Different types of vulnerability disclosure are explained, including non-disclosure, limited disclosure, full disclosure, and responsible disclosure. Responsible disclosure involves notifying the vendor, allowing time for a patch to be developed, then publicly disclosing technical details without exploit code. The benefits of responsible disclosure for researchers are noted. Potential issues with disclosure are acknowledged. Cybersecurity laws and the Budapest Convention are briefly mentioned.