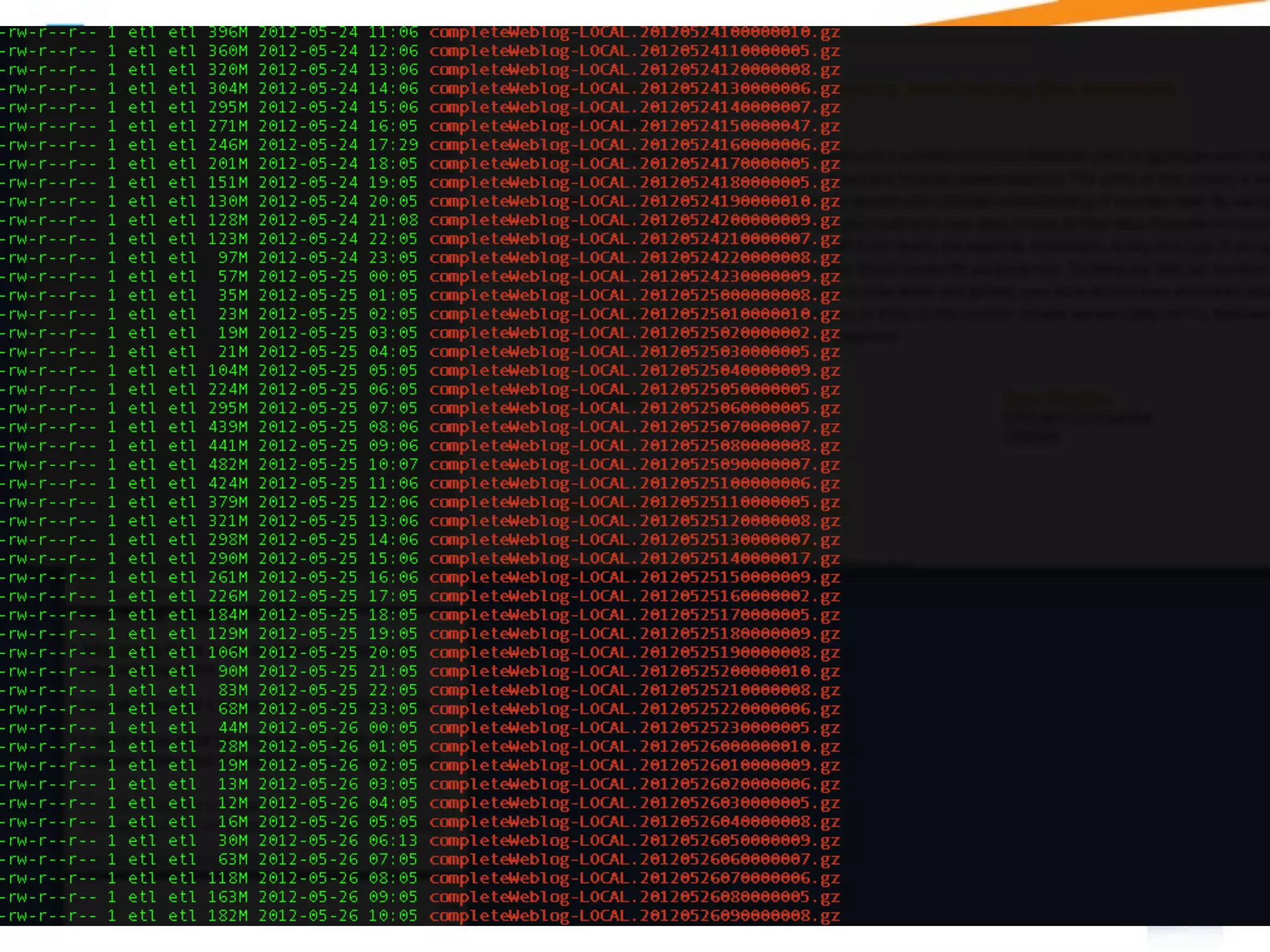
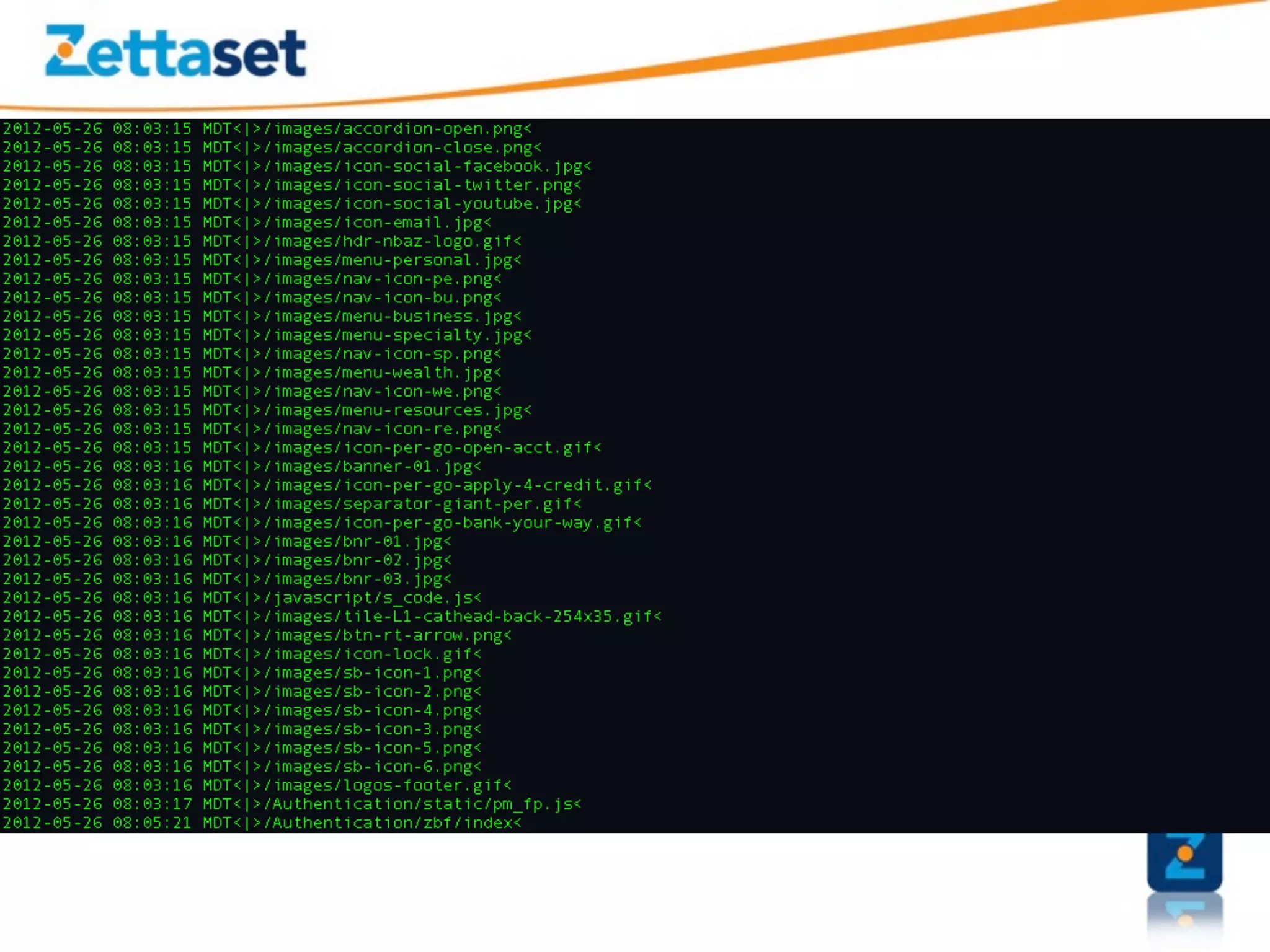
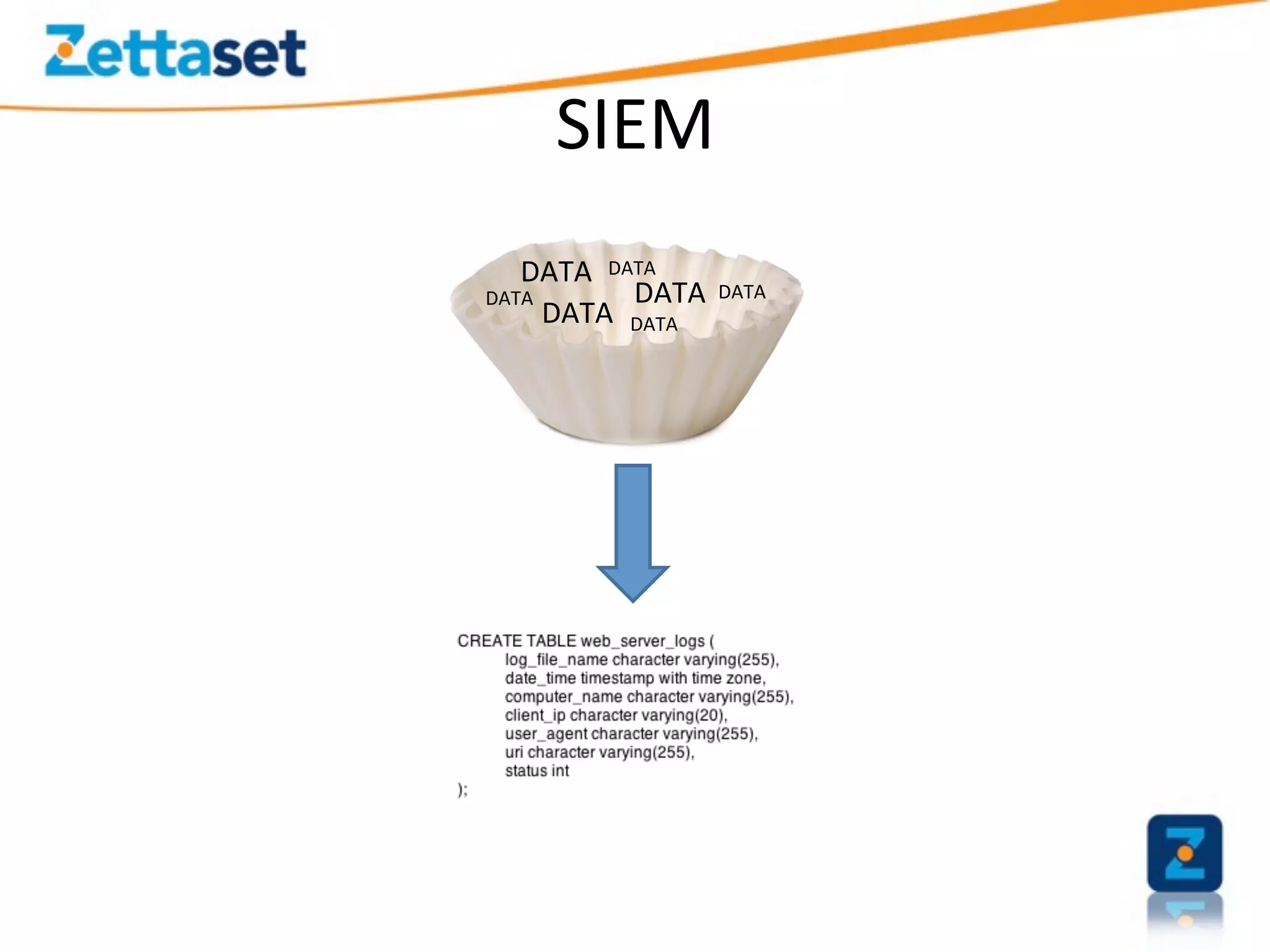
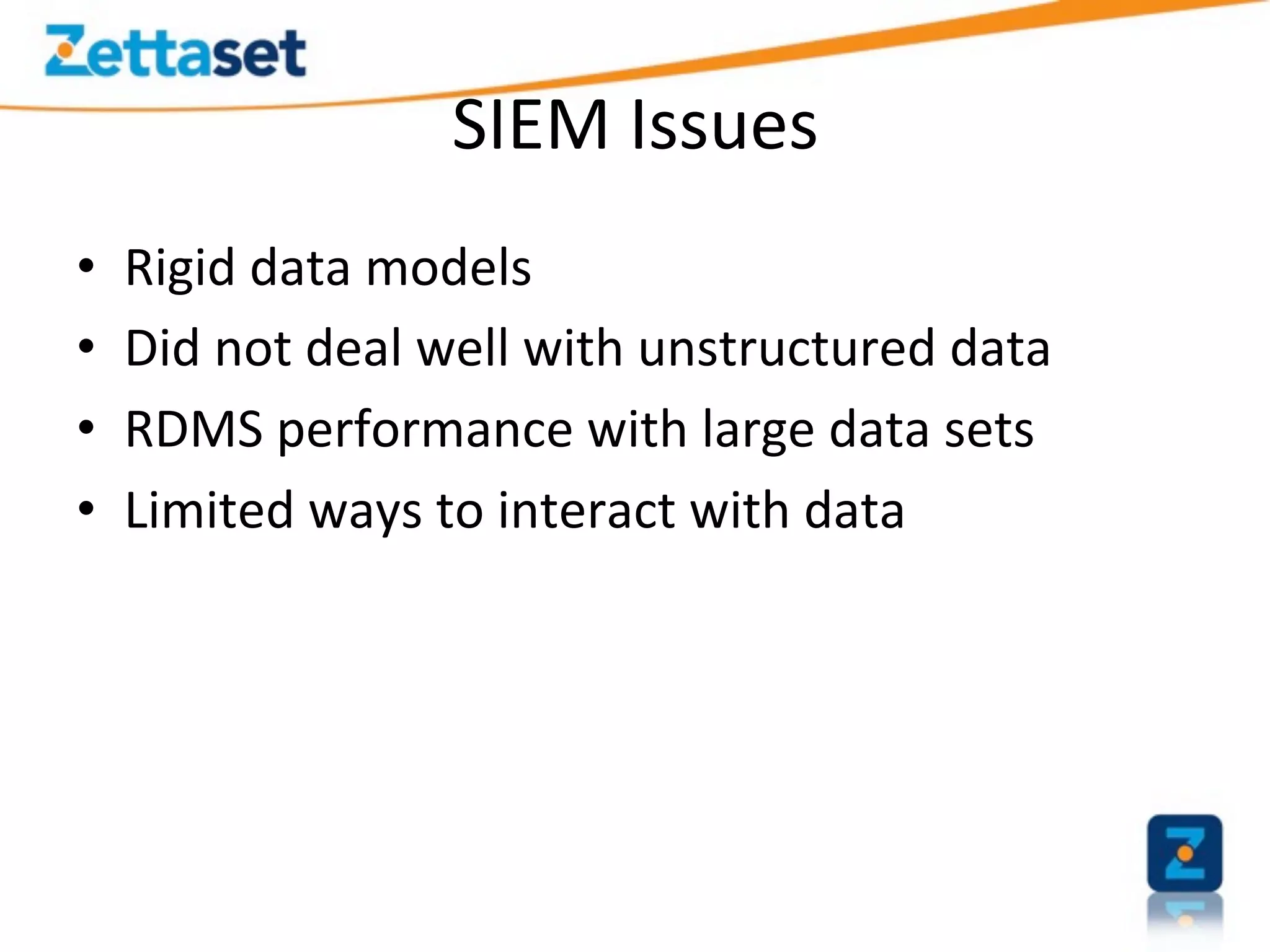
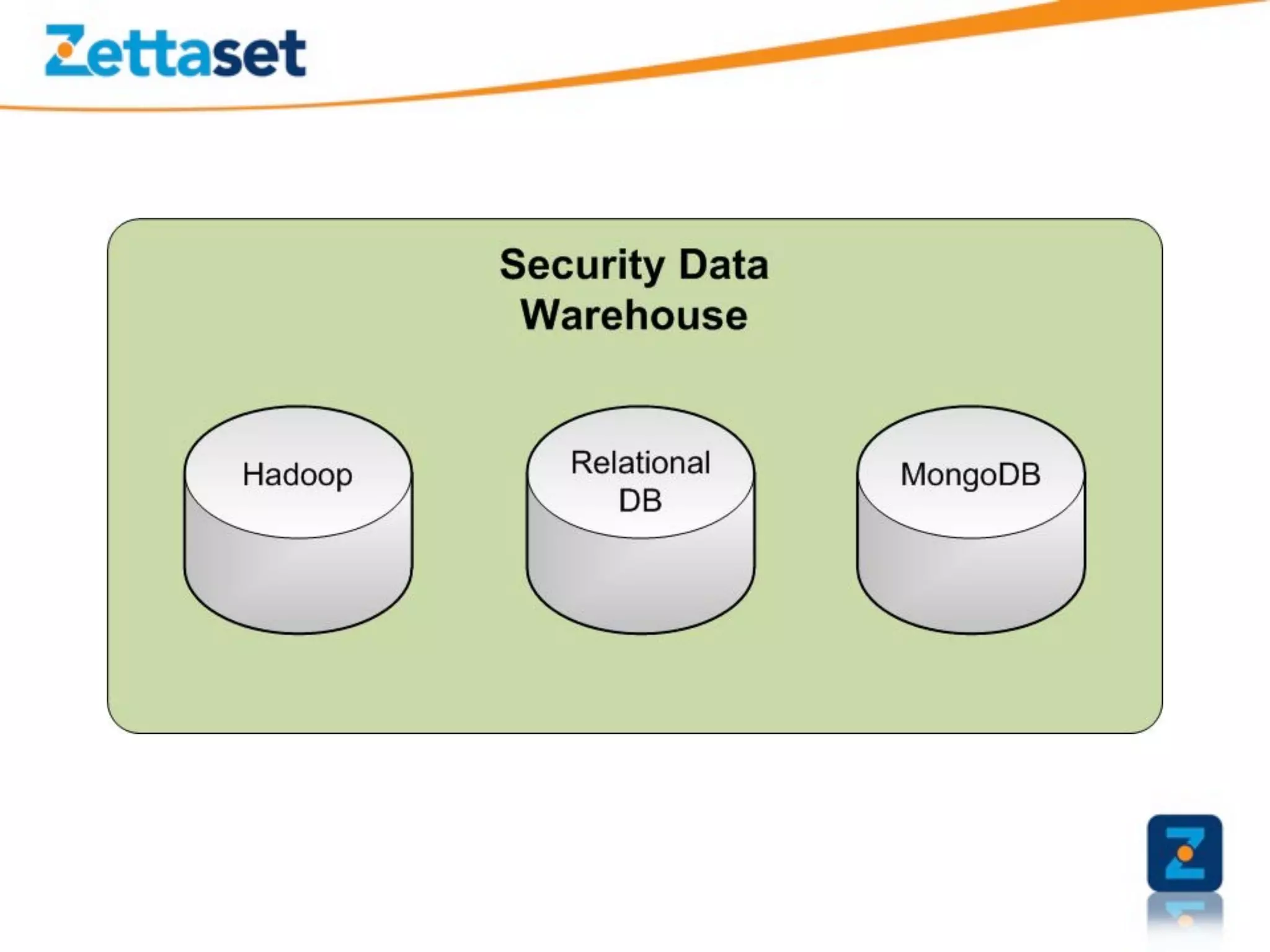
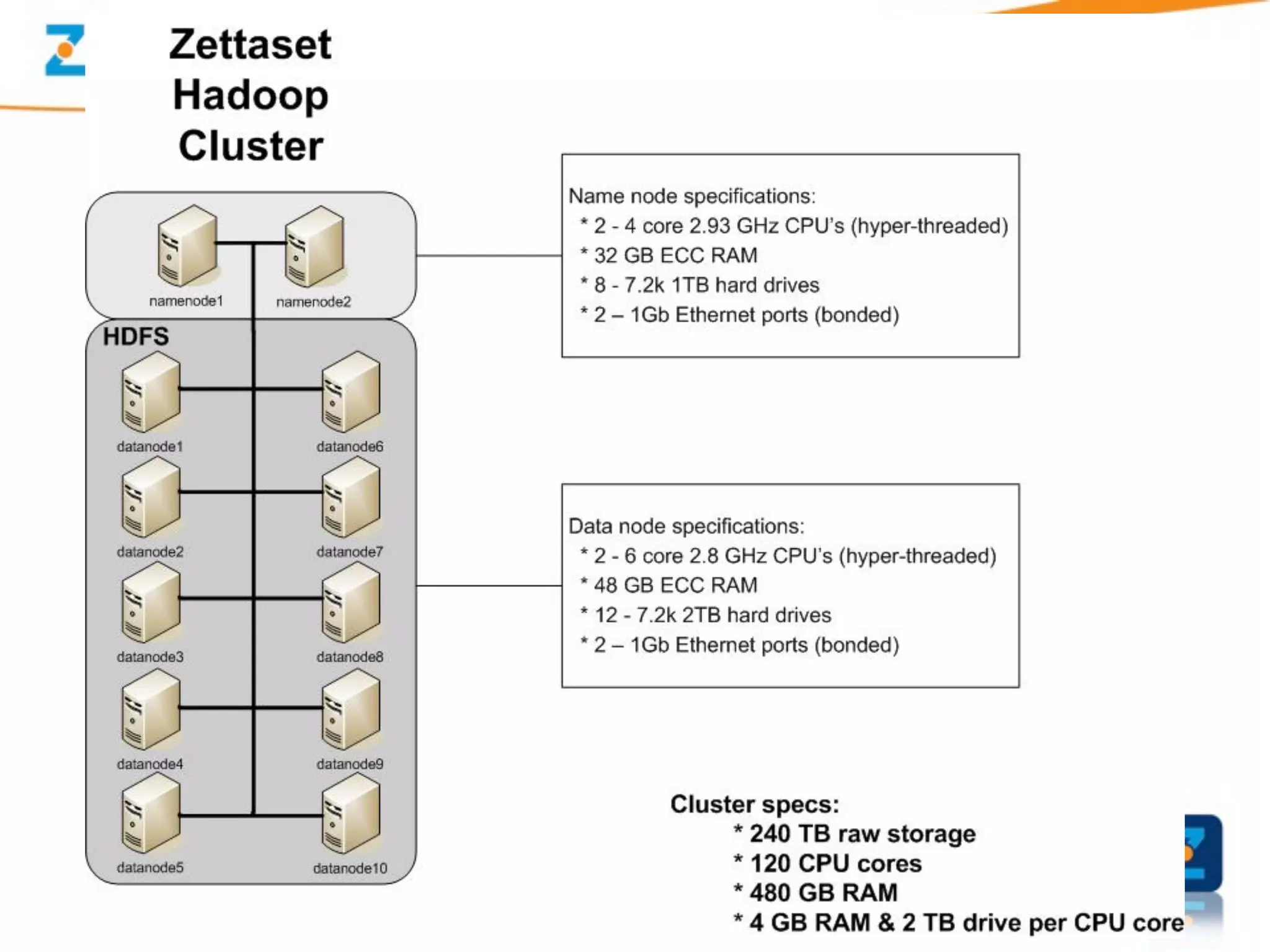
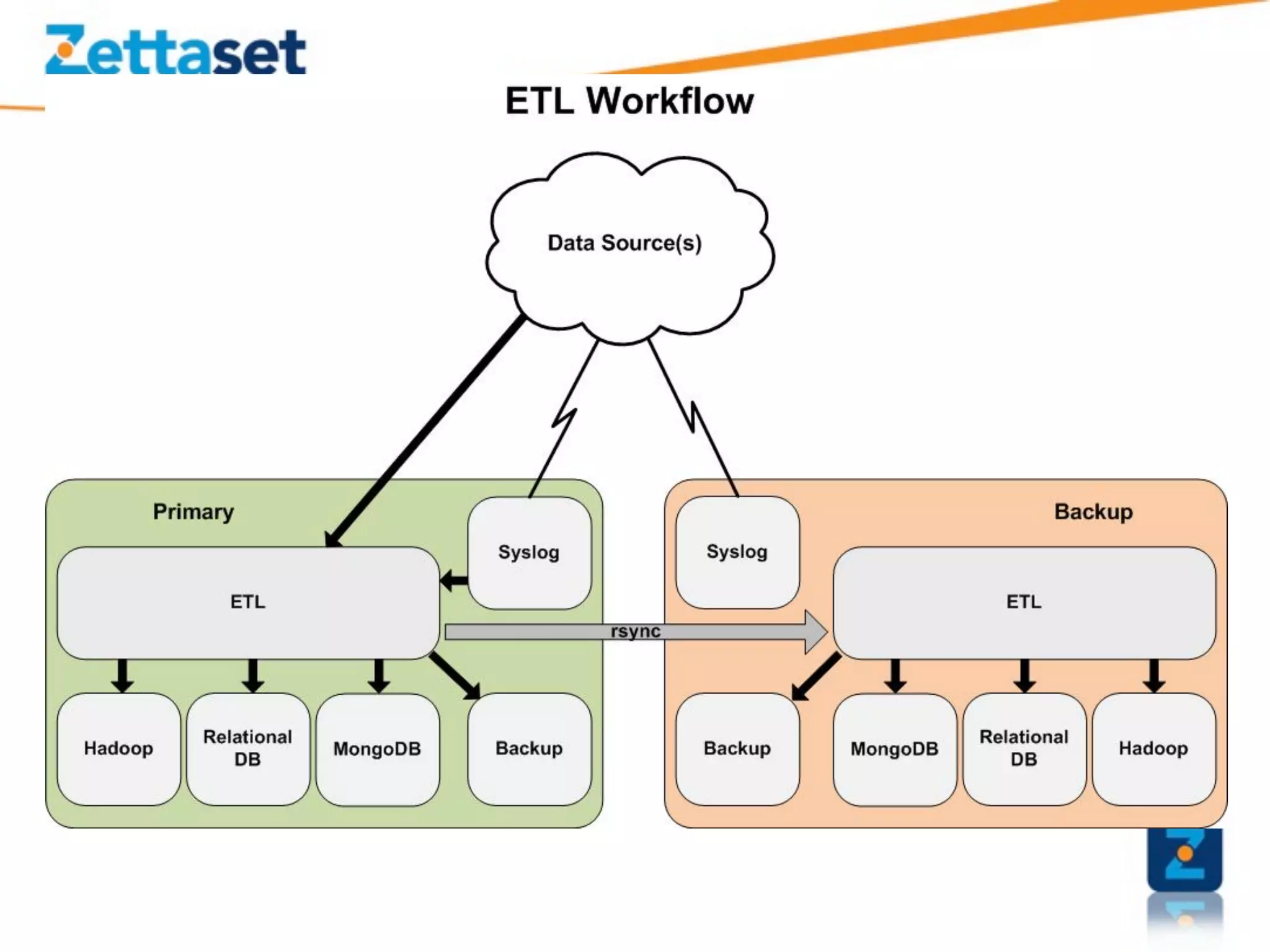
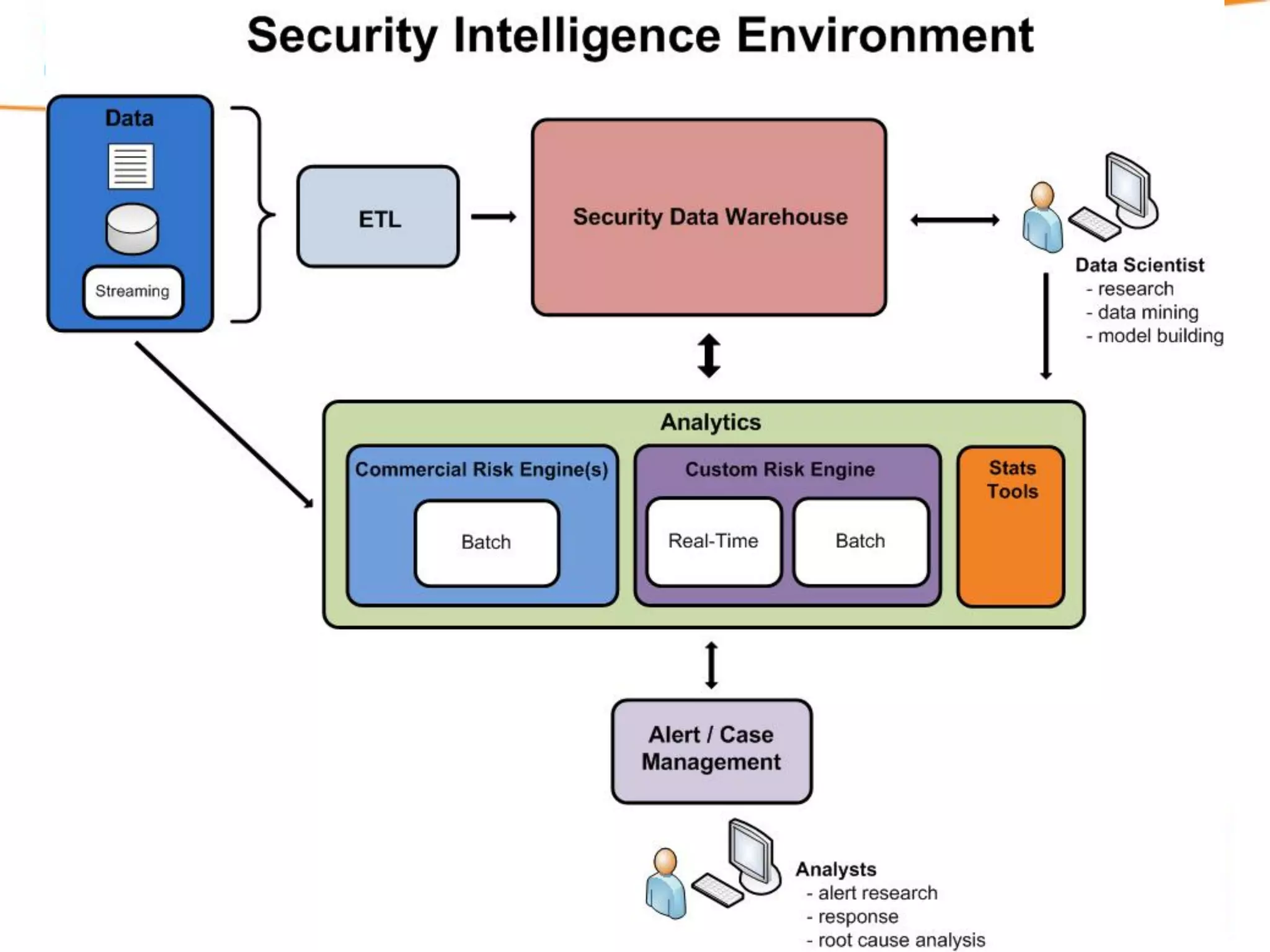
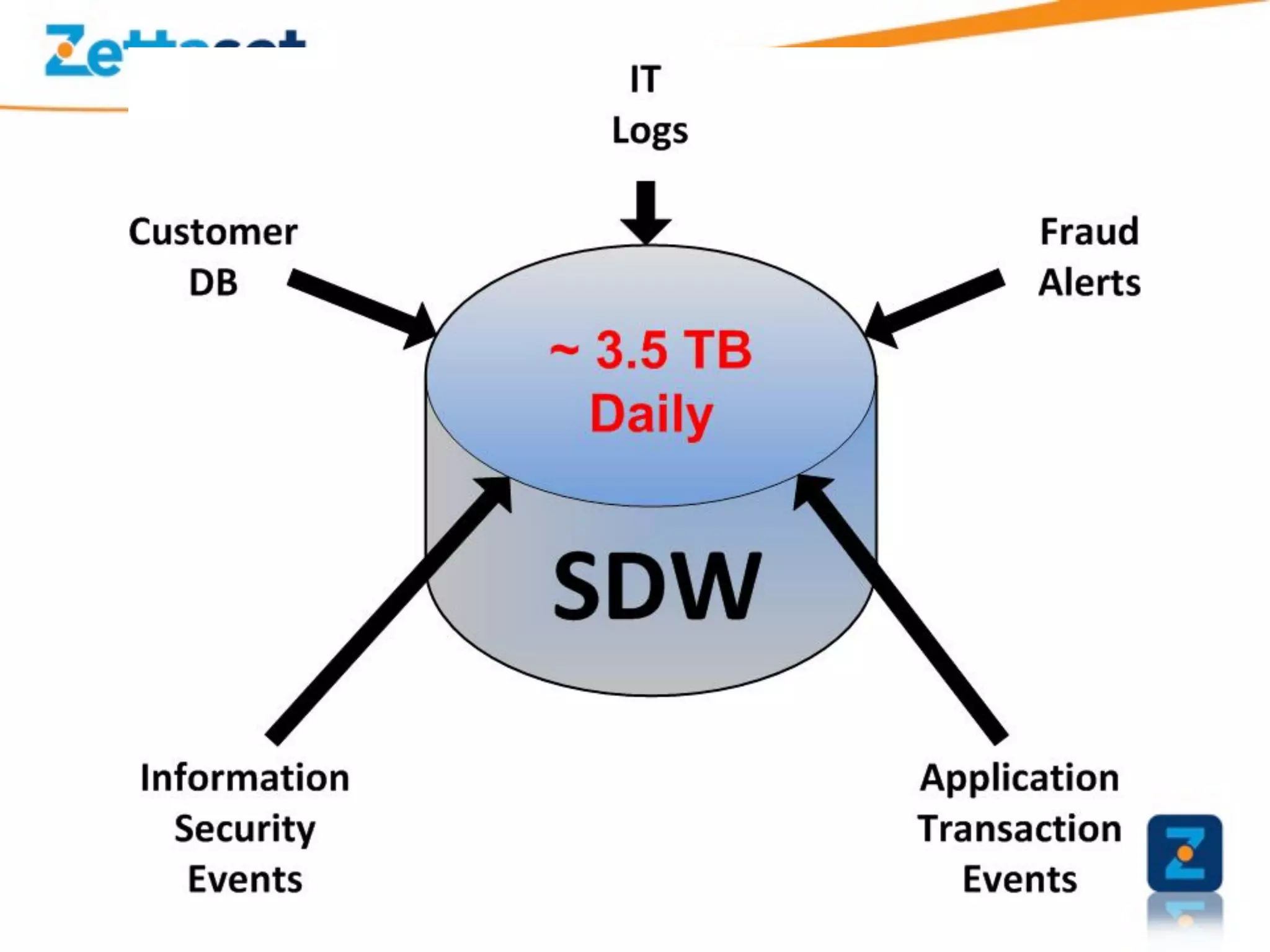
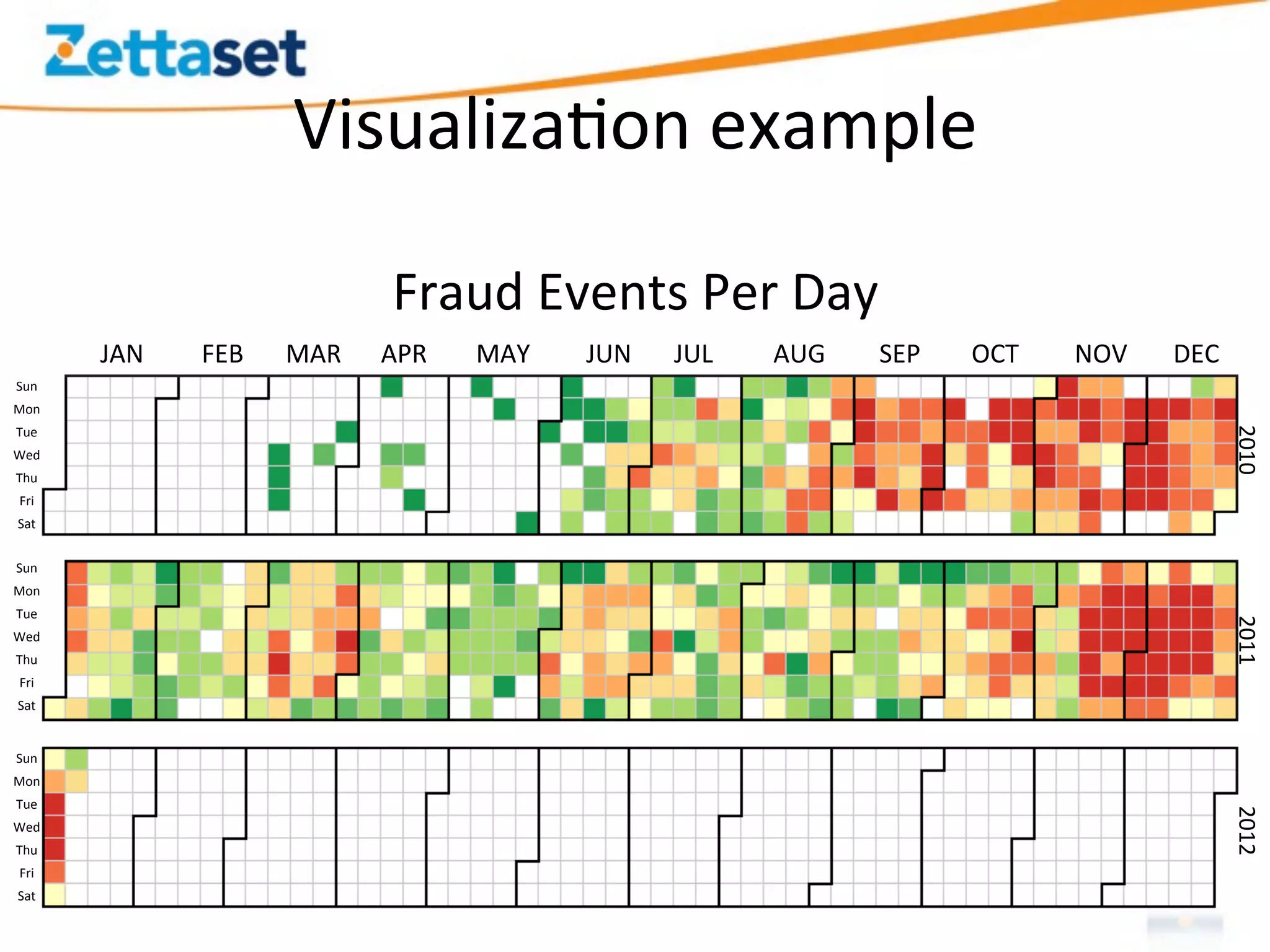
A Security Data Warehouse (SDW) is a massive database built using Hadoop and Hive that aggregates security and fraud-related event data from across an entire enterprise for long-term analytics. Zions Bank built an SDW to address limitations of their SIEM in dealing with large, unstructured datasets and to provide a common platform where security and fraud teams could collaborate by analyzing the complete historical data in one system. The SDW utilizes various Hadoop features for scalability, fault tolerance and handling different data types to support petabytes of stored data and thousands of daily analysis jobs.



![SDW
isn’t
a
product
• Security
is
never
a
product
it’s
a
process
• There
are
past
“processes”
that
help
build
the
system
– Key
example
is
SIEM:
SIEM
creates
a
“Big
Data”
problem
for
InfoSec.
Instead
of
dumping
that
data
a]er
60
days,
store
ALL
the
data
in
the
SDW
–
even
the
events
you’re
currently
not
logging
• When
fraud
teams
work
with
security,
the
common
pla`orm
will
accelerate
the
program](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securitydatadeluge-120620130015-phpapp02/75/Security-data-deluge-4-2048.jpg)