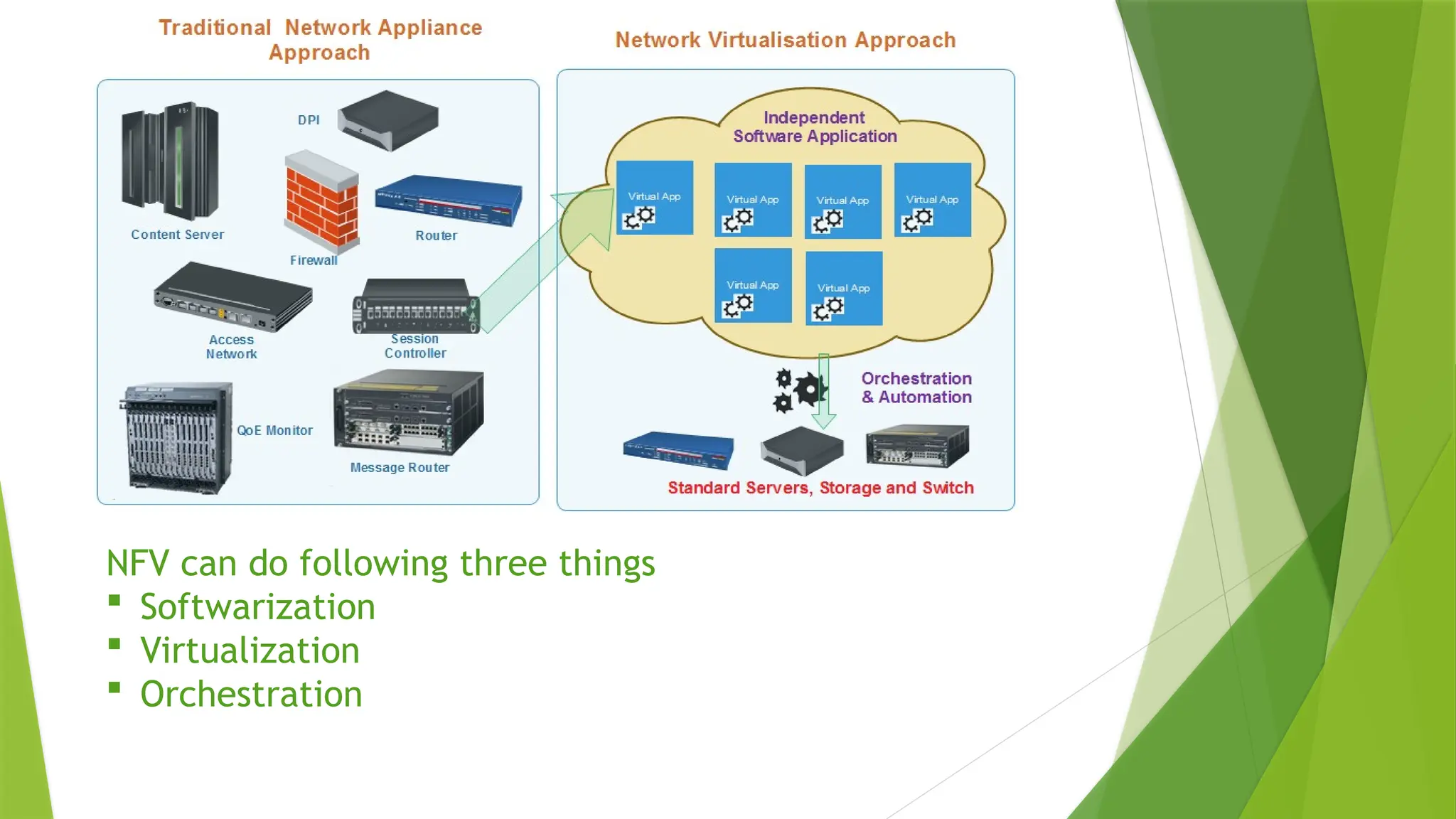
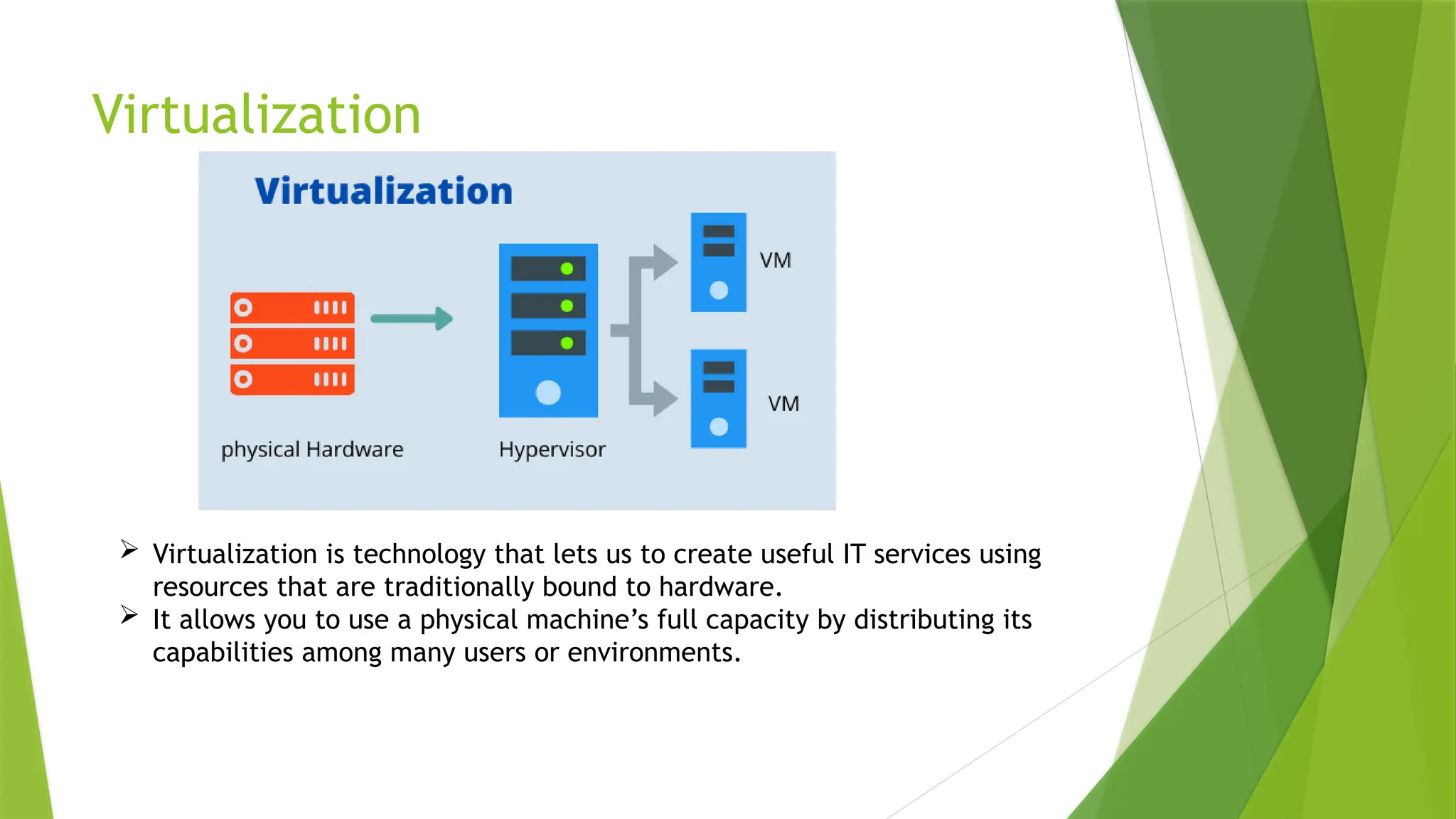
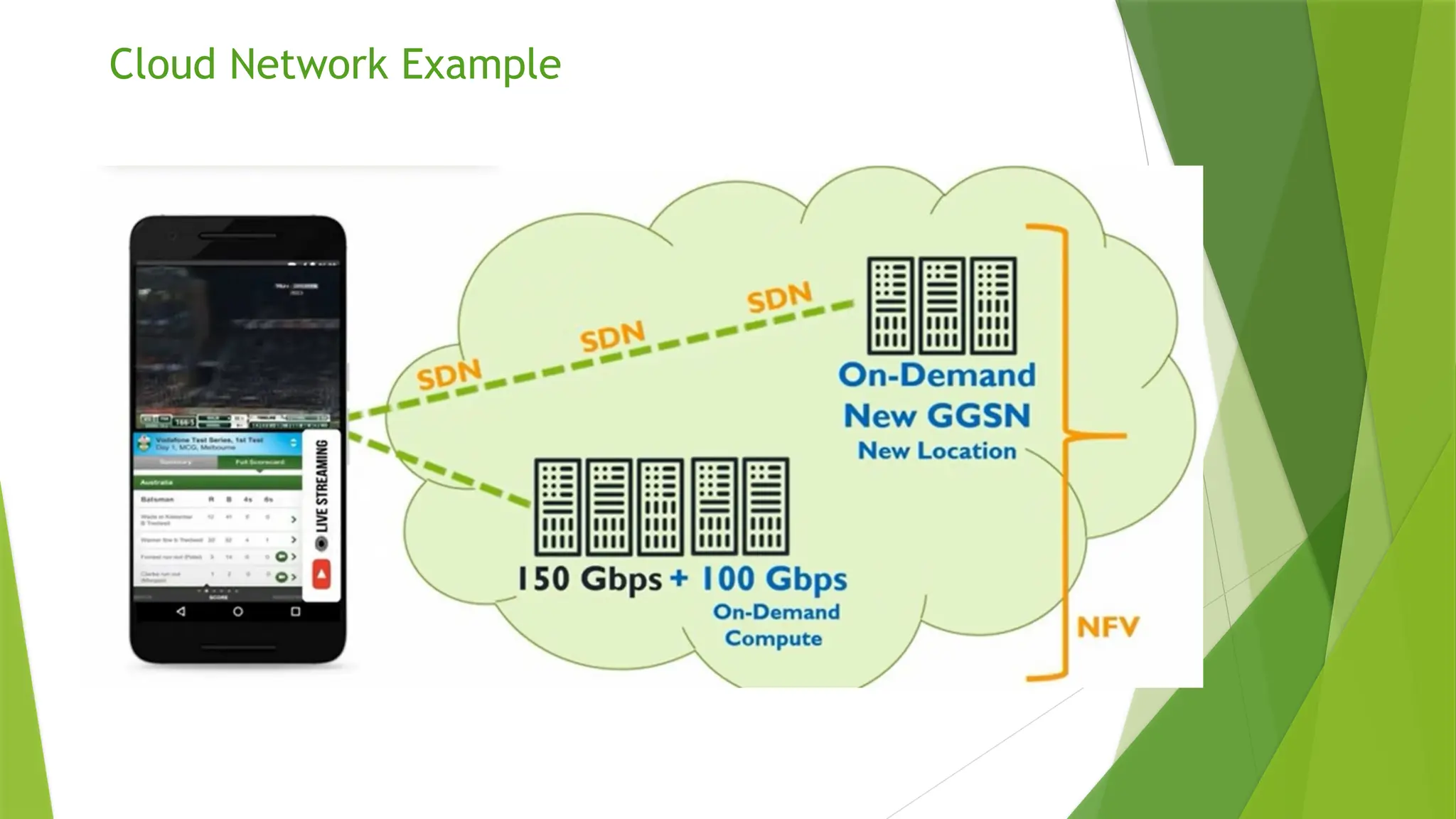
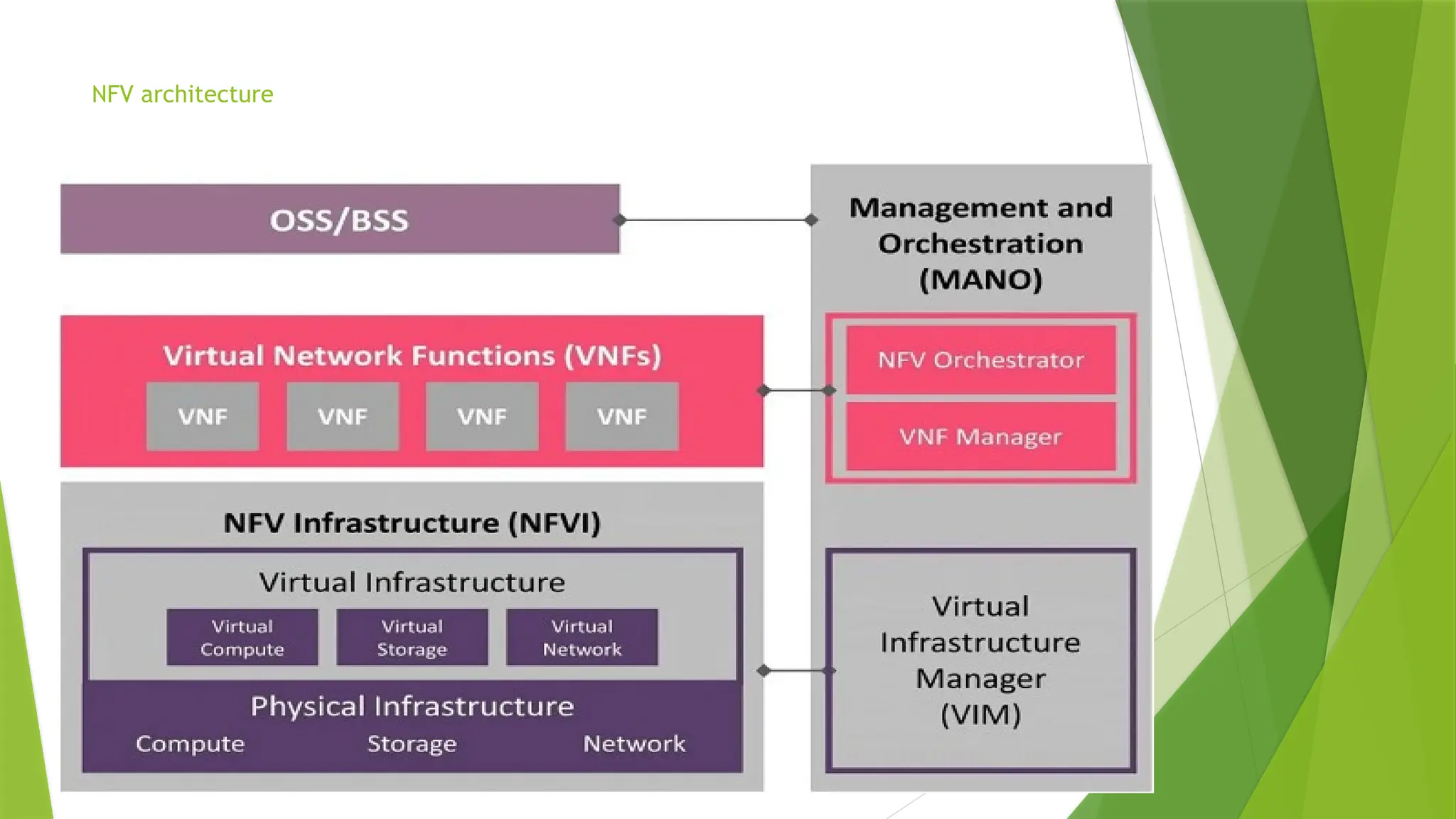
Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) refers to the replacement of traditional network hardware, like routers and firewalls, with virtual machines that run on a hypervisor, enabling service providers to utilize standard hardware. The NFV architecture consists of four layers: Virtualization Network Function (VNF) layer, NFV Infrastructure (NFVI) layer, Operation Support Subsystem (OSS) layer, and Management and Orchestration (MANO) layer, each playing a crucial role in managing and deploying virtualized network services. While NFV offers benefits such as reduced hardware needs and improved scalability, it also presents risks related to security, malware containment, and the complexity of managing multiple layers.