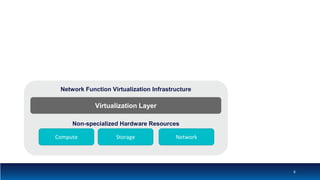
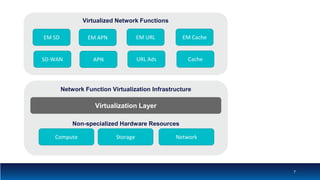
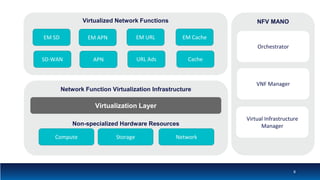
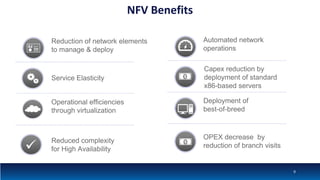
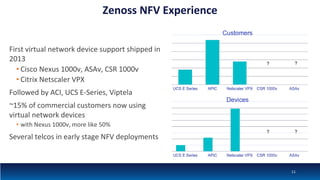
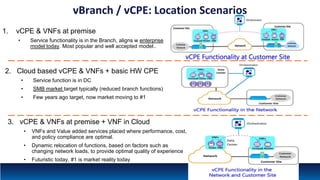
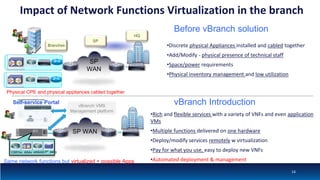
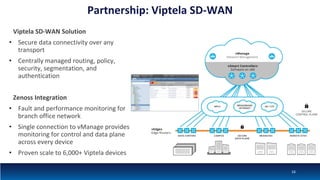
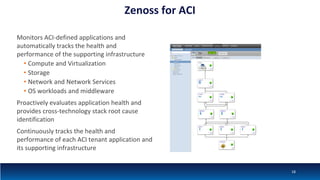
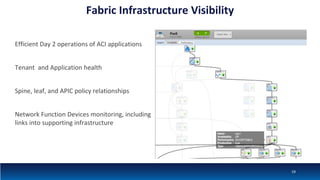
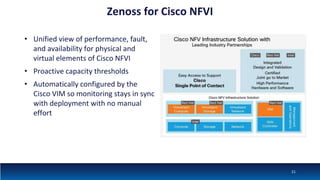
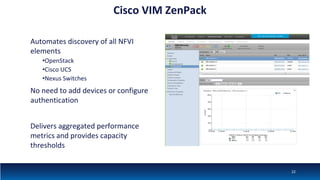
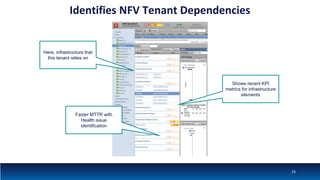
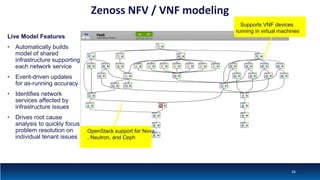
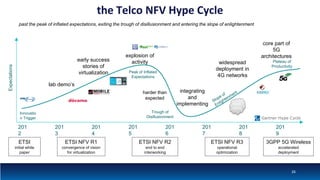
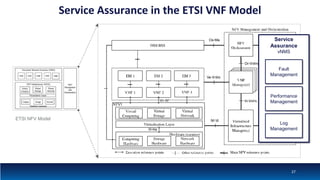
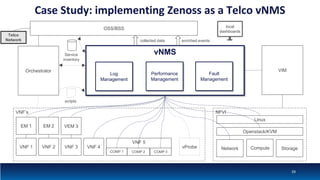
The document discusses Network Function Virtualization (NFV) service assurance, highlighting key aspects such as NFV technology overview, use cases, and a telco NFV case study. It emphasizes challenges in NFV adoption, particularly the cultural barriers and the need for integration between IT and network operations. The document also outlines the benefits of NFV, including operational efficiencies, service elasticity, and dynamic management of virtualized network functions.