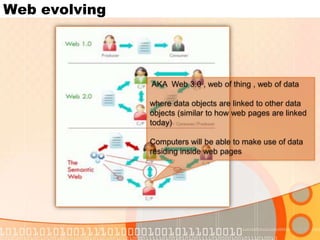
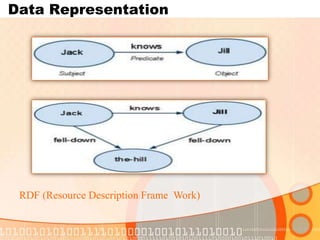
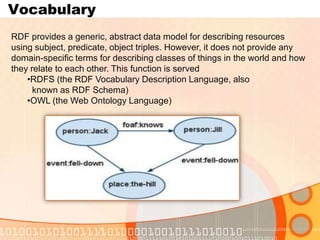
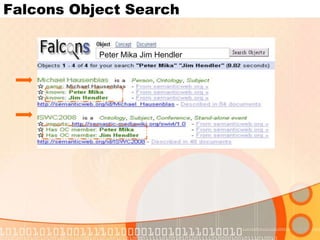
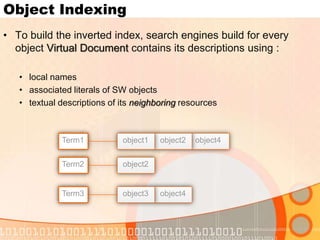
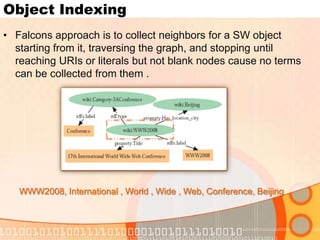
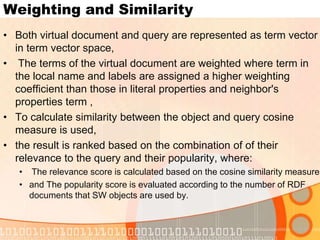
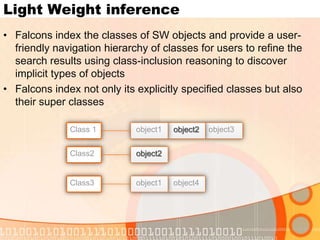
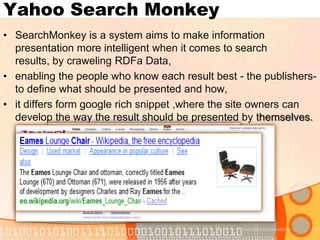
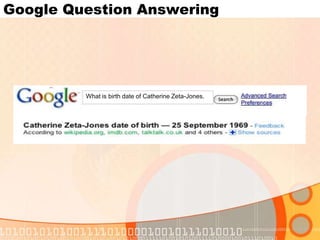
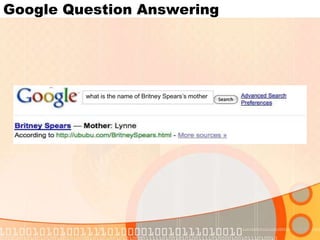
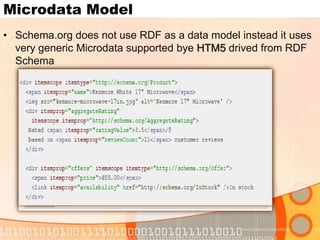
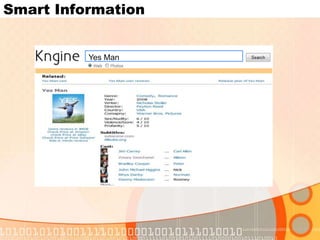
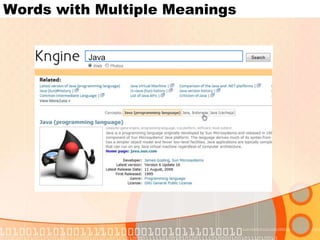
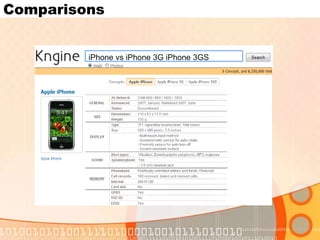
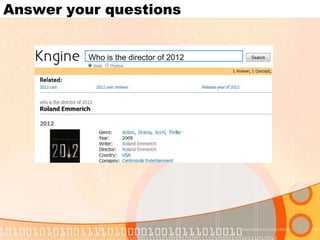
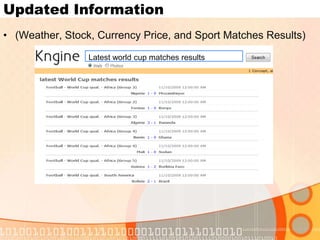
The document summarizes recent developments in semantic search engines. It discusses the principles of the semantic web and languages like RDF, RDFS, and OWL. It then summarizes the Falcons semantic search engine and how it indexes and searches semantic web objects. It also discusses efforts by Google, Yahoo, and Microsoft to incorporate semantic data through rich snippets, SearchMonkey, and Schema.org. Finally, it introduces the Kngine search engine as a new promising engine that aims to go beyond existing sources by indexing structured information on the web.