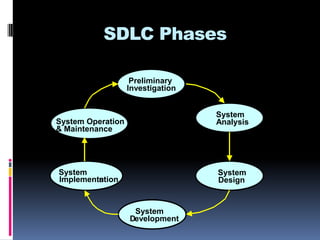
This document summarizes the six phases of the Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC): 1) Preliminary Investigation which determines if a new system is needed and identifies problems; 2) System Analysis which studies the existing system; 3) System Design which designs alternative systems; 4) System Development which builds the system; 5) System Implementation which converts to the new system and trains users; 6) Operations & Maintenance which maintains and evaluates the system long-term. Tools, documentation, and deliverables are discussed for each phase.