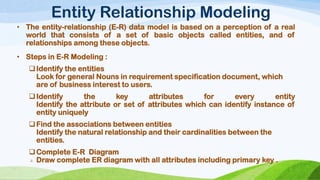
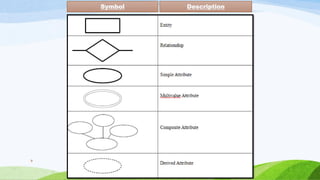
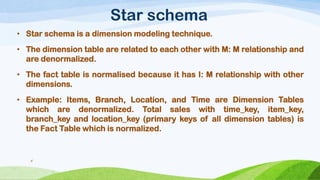
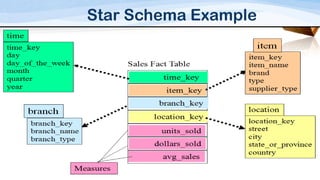
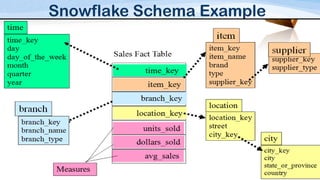
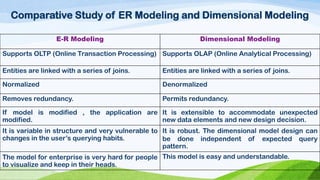
This document compares and contrasts dimensional modeling and E-R modeling. It provides examples of a star schema and snowflake schema dimensional model. It notes that dimensional modeling supports OLAP and online analytical processing while E-R modeling supports OLTP. Dimensional modeling uses a denormalized structure while E-R modeling is normalized. Dimensional modeling is more robust and understandable compared to E-R modeling.